
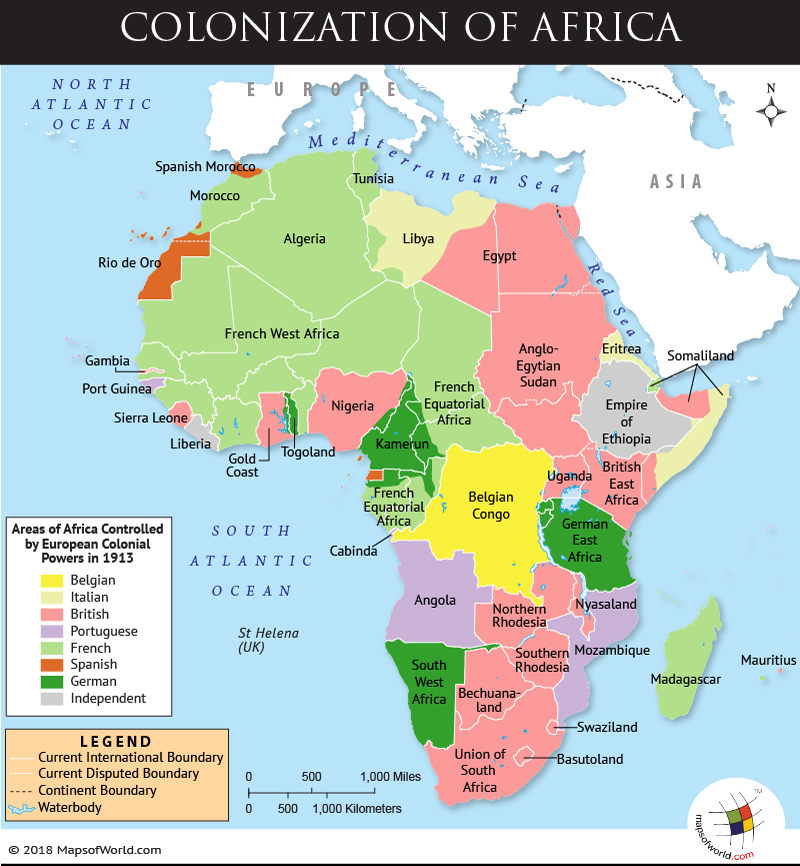
Scramble for Africa was the division and colonization of African territories by European powers
The Scramble for Africa is referred to as the period between 1881 and 1914 when European powers were dividing and colonizing African territories. It was during the era of ‘New Imperialism’ when European governments focused on enhancing their empires and acquiring territories around the world. They exploited the resources prevailing in underdeveloped countries, by asserting their governance over the regions.
In 1870, Africa had only 10% of its area under the control of Europe, but by 1914 over 90% of the continent was in the hands of different powers, leaving only Ethiopia, the Dervish state (part of present-day Somalia), and Liberia outside of European hands.
Africa was a land rich in mineral resources and ripe territories. Outsiders felt there was also a lack of civilization. This attracted colonial powers, to gain immense commercial profits. Colonial powers looked to assert their governance and utilize the vast potential prevailing in Africa for their own good. With a façade to develop culture, and rule over Africa only until the people are able to govern themselves, European rulers decided to invade and exploit the region.
One of the biggest draws was the presence of gold and diamond in the African countries, which were unavailable in Europe. European industry wanted to gain consumers in Europe for raw materials like copper, cotton, cocoa, rubber, palm oil, and even tea. Moreover, Egypt and South Africa had access to the sea which could help the powers access the world. The plentiful raw materials could be easily exported to other countries. The race for Africa had thus begun, and each power wanted to be the strongest and attain the largest profits. What came next was rapid industrialization in the African continent and numerous technological advancements. Transportation facilities of the territories had improved. Gradually, European industry grew dependent on the sea routes, with Britain building the southern and eastern coasts of Africa for its routes linked to Asia, especially the British Raj which ruled India.
Troubles between colonial powers like the UK, France, and Germany became evident. The Berlin Conference (1884-1885) was held to discuss the issues that were arising between nations. Convened by Otto von Bismarck, records suggest that the mediation was focused to resist European aggression which was leading to the exploitation of resources and African citizens. The Isthmus of the Suez Canal was the reason behind major clashes between the nations, as all wanted access to it. Diplomats then worked on strategic plans for the African scramble. Eventually, everyone decided that the neutrality of the Congo River had to be sustained for everyone to benefit from it. King Leopold II of Belgium was elected as the ruler of the region, on the condition that each power would be allowed free trade from the canal. Hence, the region near the sea was named “the Congo Free State”. Africa was divided and each region was designated to a particular power, so no conflicts arose. Numerous other strategies were laid in the Berlin Conference, to prevent any form of war within the European countries.
Despite the efforts, the resolutions were only partially upheld. Africa lost an abundance of its natural resources under European rule and the local economy was failing. Everyone observed the profits Europe had been attaining with the exploitation of African land and its citizens. Eventually, the African countries started to demand independence in the years following WW II, and by the end of the 1960s, the majority of the African nations had gained freedom and built their own governance.
Know more:
Related maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…