What is the Anti-Bribery Convention?
The ‘Convention on Combating Bribery of Foreign Public Officials in International Business Transactions,’ is a convention of the ‘Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development,’ which aims at eradicating bribery of foreign public officials in international business transactions. It establishes legally binding standards to criminalize bribery and provides with related measures to bring this into effect.
Dealing with the supply side of the act of bribery, it is the first and the only international anti-corruption instrument. The goal is to make a level playing field in the contemporary international business environment, while also expecting the adherents to commit to enforcing their foreign bribery laws and co-operate in combating foreign bribery.
The principles for the foundations were created in 1989, with the establishment of an ad hoc committee for the comparative review of national legislations associated with the bribery cases of foreign public officials. This was followed by the adoption of the recommendations put forth by the ‘Council on Bribery in International Business transactions,’ in 1994. The convention was signed on 1997 and came into force in 1999. Inclusive of 44 countries today, it started with the 36-member states of the OECD and added 8 non-OECD countries as signatories. All countries party to the convention ensure that their national parliaments approve and abide by the convention laws and legislate in accordance with its ratification and implementation. A revised edition was also adopted in 2009.
The act of bribery is defined as the offering, giving, soliciting or receiving of any item of value as means of influencing the actions of an individual holding a public office or legal duty. A total of 443 individuals and 158 entities have been sanctioned in criminal proceedings for foreign bribery between the conception of the convention to 2016. Whereas a total of 121 individuals have been sanctioned in the administration and civil proceedings for foreign bribery. These include cases of money laundering as well as false accounting.
Marking the 10th anniversary of the convention, recommendations for further combating bribery of foreign pubic officials was released, in 2009. It strengthens the framework for adopting the best practices to make companies liable to foreign bribery, to avoid their misuse and escapism from detection, investigation and prosecution by using agents, intermediaries and foreign subsidiaries to bribe on their behalf. It also focuses on improving co-operation between the nations to share information on the evidence in the bribery cases and prosecutions. It aims at fostering protection to the whistleblowers and create effective channels to report the internal and external cases of foreign bribery.
Roundtable Conference on 20 years of the ‘Anti-Bribery Convention’ (2017):
The OECD ‘Working Group on Bribery‘ (WGB), hosted the roundtable conference in Paris on 12th December 2017. This paved an opportunity for the governments, private sector, civil society, and the media to reflect on the 20 years of the OECD Anti-Bribery Convention. This was also followed up by the launch of the publication ‘The Detection of Foreign Bribery’, on the occasion.
Current Advances:
- Two countries- Austria and Israel, were added to the list of WGB members, that have imposed sanctions for foreign bribes.
- Three countries– France, Netherlands, and the Slovak Republic, adopted key reforms to support effective anti-bribery law enforcement measures. These include introduction of negotiated settlements, broadened jurisdiction, enhanced whistleblowers protection and amended laws on the liability of legal persons.
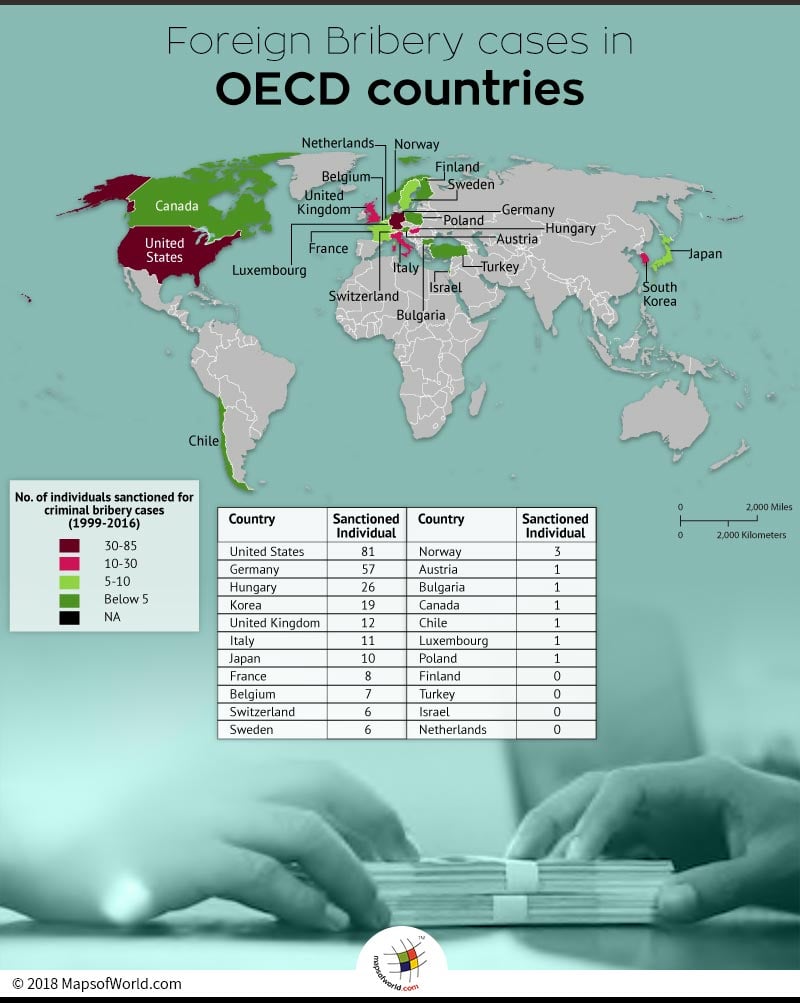
Below lying table depicts country-wise sanctioned and acquitted (Individual) foreign bribery cases:
|
Country |
Sanctioned Individual |
Acquitted Individual |
|
Finland |
0 |
18 |
|
United Kingdom |
12 |
7 |
|
Belgium |
7 |
6 |
|
Italy |
11 |
5 |
|
Norway |
3 |
5 |
|
France |
8 |
4 |
|
Switzerland |
6 |
4 |
|
United States |
81 |
4 |
|
Germany |
57 |
3 |
|
Austria |
1 |
2 |
|
Hungary |
26 |
2 |
|
Turkey |
0 |
1 |
|
Bulgaria |
1 |
0 |
|
Canada |
1 |
0 |
|
Chile |
1 |
0 |
|
Israel |
0 |
0 |
|
Japan |
10 |
0 |
|
Korea |
19 |
0 |
|
Luxembourg |
1 |
0 |
|
Netherlands |
0 |
0 |
|
Poland |
1 |
0 |
|
Sweden |
6 |
0 |
Know more:
Related maps: