
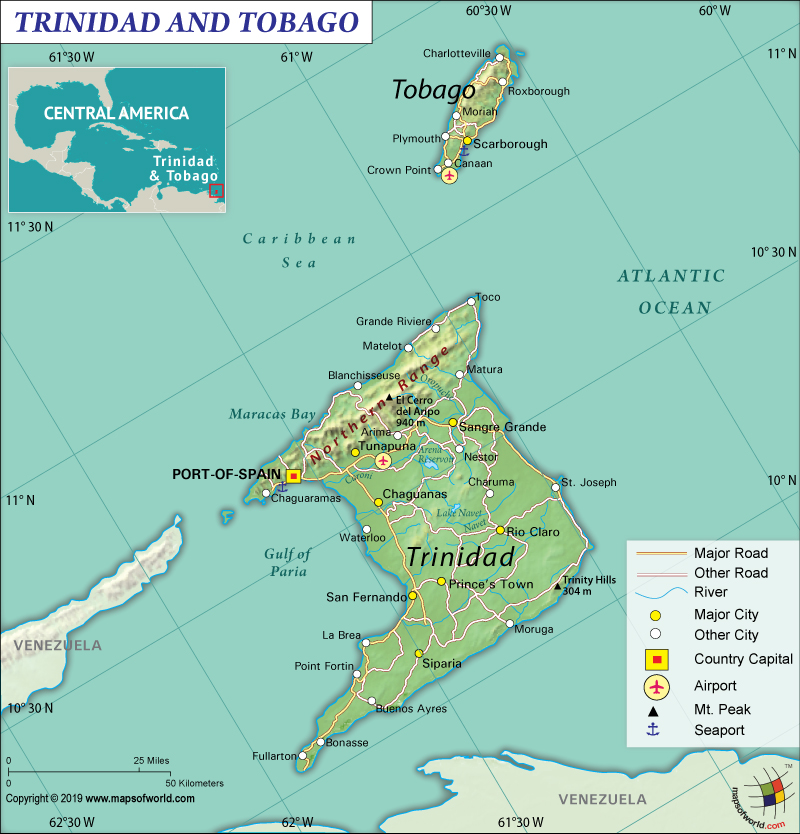
Map of Trinidad and Tobago which lies in North America (Caribbean)
| Official Name | Republic of Trinidad and Tobago |
| Continent | North America (Caribbean) |
| Capital | Port of Spain |
| Largest City | Chaguanas |
| Coordinates | 10.440128, -61.229318 |
| Area | 1,981 sq. mi ( 5,131 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 0 mi ( 0 km) |
| Coastline | 225 mi ( 362 km) |
| Currency | Trinidad and Tobago dollar (TTD) |
| Neighboring Countries | Barbados, Guyana, Venezuela, Grenada |
| Population | 1,359,193 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | English |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 31 August (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Forged From the Love of Liberty” |
| Form of Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
| President | Paula-Mae Weekes |
| Prime Minister | Keith Rowley |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 32,227.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 16,843.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.784 (2017), Rank: 69 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 115 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 19 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | left |
| Calling Code | +1 (868) |
| Time Zone | UTC-4 (AST) |
| Internet TLD | .tt |
Trinidad and Tobago is an island nation that is part of the southernmost set of islands in the Caribbean. It consists of two main islands: Trinidad and Tobago. This island nation is situated between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean. Many smaller islands are located just 11 km (7 mi) off the coast of Venezuela’s northeastern parts and 130 km (81 mi) south of Grenada.
Trinidad and Tobago is spread across a total area of 5,131 sq. km (1,981 sq. mi), out of which the entire 5,128 sq. km (1,980 sq. mi) is land area. It is mainly a hilly island that also has a few small mountains and plains. The island country has a 362 km (225 mi) long coastline.
As a matter of fact, mountain ranges crisscross the Trinidad Island and the most dominant one in this island is the Northern Range. The terrain is characterized by rugged hills and peaks of small mountains. The highest peak in Trinidad is El Cerro del Aripo, whose elevation is 940 m (3,084 ft). Sea level at the Caribbean Sea is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Trinidad and Tobago is 83 m (272 ft).
Similarly, the central parts of Trinidad are mainly occupied by the lower Central Range. The southern coastline is bordered by a group of scattered hills. Many rivers and streams are present in Trinidad and the most significant ones are Ortoire and Caroni rivers.
Likewise, down the spine of Tobago Island is a central ridge and, in some places, the elevation exceeds 600 m (1,968 ft). Along the coastline, there are a narrow coastal plain, beaches, and bays. The narrow coastal plain rises to the hills. Tobago Island also has many small rivers and streams.
Further, a warm and tropical climate is found in Trinidad and Tobago. There are two distinct seasons found in this island nation and they are a dry season (January-to-May) and a wet season (June-to-December). These islands experience warm days and cool nights along with moderate-to-small low-level winds.
Daytime convection leads to rainfall. During the wet season, Trinidad and Tobago experiences hot and humid days/nights, low wind speeds, and high rainfall level. The extent of rainfall increases because of the migration and latitudinal shift of equatorial weather systems.
Furthermore, northeast trade winds dominate the island and they mainly blow from the northeast direction. This country doesn’t come within the main hurricane alleys. The climate mostly remains cooler in the Northern Range of Trinidad. However, the plains experience sweltering heat. The comparatively cooler climate on the Northern Range is due to the heavy rains, mist, and constant cloud cover in the mountain areas. In Port of Spain, the recorded high temperature is 39 °C (102 °F) and the low temperature is 12 °C (54 °F).
To begin with, Trinidad and Tobago is one of the wealthiest Caribbean nations whose nominal GDP was US$23.41 billion and its growth rate was 0.7% in 2018. This island nation has emerged as an ideal venue for foreign investment in LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) and petrochemicals.
However, while petroleum and gas contribute around 40% to the GDP and 80% to the export, the sector contributes only 5% to employment. The United States is the largest trading partner of Trinidad and Tobago, accounting for 48% of the total exports and 28% of the total imports. The country has a stable and well-regulated financial system with regional financial centers.
In addition, over 60% of the labor force is involved in the services sector, followed by 20% in the construction and utility sectors. The economy currently lacks adequate diversification. That’s why, besides oil and gas, the country has started emphasizing industries related to aluminum, petrochemicals, plastics projects, tourism, shipping, information and communications technology, and agriculture.
While the unemployment rate is just below 5%, the poverty rate is hovering around 4%.
Both the major islands of Trinidad and Tobago have a dense network of roads and highways. Scarborough and San Fernando are connected to the Port of Spain with a fleet of ferries. The Trinidad island is linked together with the help of Sir Solomon Hochoy Highway, Churchill Roosevelt Highway, and the Uriah Butler Highway. In Tobago Island, there is only one major highway and that is the Claude Noel Highway.
Moreover, public buses, minibuses, and private taxis are the main road transport facilities available in the country. There are 4 airports (2 paved and 2 unpaved) available on Trinidad and Tobago. Both the main islands have international airports.
Additionally, the major seaports of the country are Point Fortin, Scarborough, Port of Spain, and Point Lisas. There are 102 merchant marine ships.
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, UNESCO, CELAC, UNIDO, FAO, UNCTAD, G-24, G-77, NAM, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (compliant country), Paris Club (associate), Pacific Alliance (observer), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…