What are the Key Facts of Tonga?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Tonga |
|
Continent |
Oceania |
|
Capital |
Nukuʻalofa |
|
Largest City |
Nukuʻalofa |
|
Coordinates |
-21.138270, -175.208970 |
|
Area |
289 sq. mi ( 748 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Coastline |
260 mi ( 419 km) |
|
Currency |
Paʻanga (TOP) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Fiji, Wallis and Futuna (FR), Samoa, Niue, New Zealand, New Caledonia (FR), Vanuatu |
|
Population |
100,651 (2016 Census ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, Tongan |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
4 November (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Ko e fasi `o e tu”i `o e `Otu Tonga” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Tupou VI |
|
Prime Minister |
Pohiva Tuʻiʻonetoa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 6,408.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 4,364.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.726 (2017), Rank: 98 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
99.41 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
1 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+676 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+13 |
|
Internet TLD |
.to |
Where is Tonga?
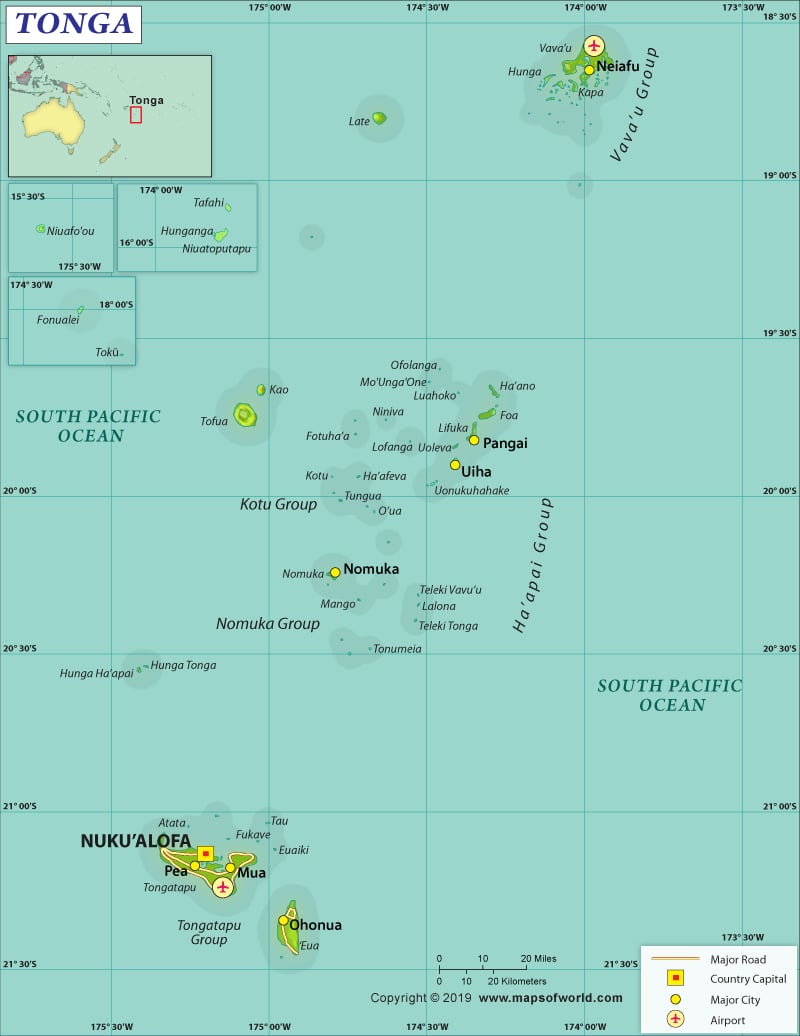
Tonga is an archipelago located in Oceania. It is situated around 2/3rd of the way from Hawaii to New Zealand in the Pacific Ocean.
What is the Geography of Tonga?
Tonga is spread across a total area of 748 sq. km (289 sq. mi), out of which 717 sq. km (277 sq. mi) is land area and 30 sq. km (12 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 0 km (0 mi) long land boundary and a 419 km (260 mi) long coastline.
This archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean consists of 176 islands, out of which 36 are inhabited. While Tongatapu, Vava’u, and Ha’apai are the most populated islands in this archipelago, the most populated one is Tongatapu.
The relatively frequent volcanic activity takes place in Tonga of its location within the Pacific Ring of Fire. The western islands of this archipelago are volcanic in origin and make up the Volcanic Arch. Above the Tonga Ridge, the eastern islands of this country are situated. Elevated limestones, as well as uplifted coral formations, have created these eastern islands, which run parallel to the Volcanic Arch.
One of the deepest parts of the Kingdom of Tonga is known as the Tonga Trench. It is situated in the eastern parts of this island country. The Horizon Deep, the deepest point is around 10,882 m (35,702 ft) below the water surface.
The highest elevation point of Tonga is the Kao Volcano at 1,046 m (3,432 ft) on Kao Island, which is situated in the central Ha’apai group of islands. The Pacific Ocean at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point. A volcanic Ridge of 329 m (1,078 ft) height is situated on the 2nd largest island of Tonga named Tongatapu group.
There are no major rivers located on any of the islands in this archipelago. The only stream is present on Niuatoputapu.
A tropical climate prevails in this Oceania archipelago. Trade winds influence Tonga. While June-to-October is the dry season (remains cool), December-to-April is the rainy season (which is usually hot and humid).
The climate remains hot and rainy even during May-November on the northernmost islands. However, the relatively drier season can be found on the southern island from May to November. In these southern islands, the climate remains pretty cool during June-September. Brief showers and thunderstorms take place across the country even in relatively drier season. March is the rainiest month.
An equatorial climate (which remains hot as well as humid round the year) persists on the northernmost islands including Tafahi, Niuatoputapu, and Niuafo’ou. While February-March is the hottest months with an average temperature of 31 °C (88 °F), July-August is the least hot months with an average temperature of 29 °C (84 °F).
Tonga receives lots of rainfall, which usually exceeds 2,300 mm (90 in). November-April gets maximum rainfall with a per month precipitation higher than 200 mm (8 in). May and October are two transitional months when this island nation gets 170-180 mm (6.7-7.1 in) of rainfall per month. June-September is the less rainy period with a per month rainfall of 100-140 mm (4-5.5 in).
June-September is the best time to visit Tonga when it gets the least rainfall and the temperature remain slightly less.
What is the Economy of Tonga?
The economy of Tonga is mainly dependent upon agriculture and tourism. Agricultural products such as yams, vanilla beans, coconuts, bananas, watermelons, cassava, taro, squash, tomatoes, limes, breadfruit, and maize corn are the main agricultural produce and export items of the country.
The economy is highly dependent upon remittances sent by the Tongans living abroad as well as external aid. The country has to import a significant proportion of its required food items from other countries, mainly New Zealand. Both the basic infrastructure and the social services of the country are significantly developed. 97% of the population has access to electricity (2016).
In 2018, the nominal GDP of Tonga grew at a rate of 1.5% (less than 2.7% in 2017) to reach an annual GDP of 488 million. The per capita GDP in 2018 was US$4,858 (a growth rate of 4%). Lots of construction activities are going on in Tonga, thanks to the donor-funded projects including the World Bank development projects and the preparations for the 2019 Pacific Games.
Tongan economy has a significantly high negative balance of trade, which was $88.5 million in 2017. While the country imported $103 million of goods, it exported just $15 million value of goods. The main exports were cashews, Brazil nuts, coconuts, cassava, other processed fruits/nuts, non-fillet fresh fish, and other vegetables. The major imports were processed fish, cars, sheep/goat meat, frozen bovine meat, and poultry meat.
In 2018, the rate of unemployment was 1.03%, the least since 1998. However, the economy is plagued with poverty, which was 22.1% in 2015. 16-out-of-1,000 babies born die before reaching 5-years.
A 2015-2025 national vision of a “more progressive Tonga supporting a higher quality of life for all” was launched a few years back under the Tonga Strategic Development Framework.
What is the Transportation System of Tonga?
Just 680 km (423 mi) of roadways are available in the country, out of which 184 km (114 mi) is paved and 496 km (308 mi) is unpaved. Tonga has 6 airports, out of which only one has paved runway and the other 5 don’t. The major seaports of the country are Pangai, Neiafu, and Nuku’alofa. Tonga has 33 merchant marine vessels.
What International Organizations is Tonga part of?
WTO, IMF, UNESCO, WHO, ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITU, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs)


