
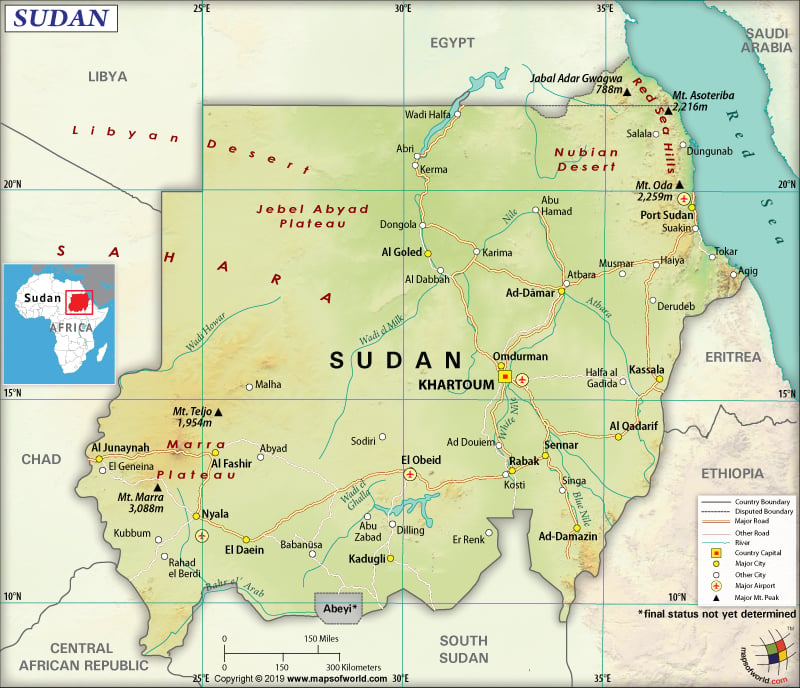
Map of Sudan which lies in the continent of Africa
| Official Name | Republic of the Sudan |
| Continent | Africa |
| Capital | Khartoum |
| Largest City | Khartoum |
| Coordinates | 15.000000, 30.000000 |
| Area | 728,215 sq. mi (1,886,068 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 4,237 mi (6,819 km) |
| Coastline | 530 mi (853 km) |
| Currency | Sudanese pound (SDG) |
| Neighboring Countries | Egypt, Libya, Chad, Central African Republic, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea Maritime neighbor: Saudi Arabia |
| Population | 41,592,539 (2019 est.) |
| Official Languages | English and Arabic |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | 1 January (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Nahnu Djundulla Djundulwatan” |
| Form of Government | Presidential republic |
| President | Vacant (as of 2019) |
| Sovereignty Council Chairman | Abdel Fattah al-Burhan |
| Prime Minister | Abdalla Hamdok |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 4,759.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 977.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.508 (2018), Rank: 168 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 60.7 (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 71 (SIPRI, 2018) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 1 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +249 |
| Time Zone | UTC+2 (CAT) |
| Internet TLD | .sd |
Sudan is a north-east African country located between Eritrea and Egypt. It borders the Red Sea (to the northeast).
Sudan has a total area of 1,886,068 sq. km (728,215 sq. mi) out of which 1,731,671 sq. km (668,602 sq. mi) is land area and 129,813 sq. km (50,121 sq. mi) is the water area.
It has a 6,819 km (4,237 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with seven neighbouring countries:
The country has an 853 km (530 mi) long coastline.
Sudan has a generally flat, featureless plain. However, the northern part is dominated by desert. The mean elevation of this North African country is 568 m. While Jabal Marrah at 3,042 m (9,980 ft) is the highest elevation point, the Red Sea at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point.
Several mountain ranges punctuate the flat plains. The Marrah Mountains containing the highest elevation point Jabal Marrah are located on the western edge of Sudan. Along the northeastern edge, the Red Sea Hills are situated. The Deriba Crater, measuring around 3-4 miles (5-8 km) in diameter from the outer edges, is located in Darfur. This crater is filled with water.
Some of the significant mountains in Sudan are Deriba Caldera, Idwa, Mogulduma and Jabal Ubbor. The longest rivers that flow through this country are Nile, White Nile, Blue Nile, Atbarah, Bahr al-Arab, etc.
The climatic condition ranges between the hyper-arid climate in the northern parts of Sudan and tropical wet-and-dry climate in the far southwest. A considerable variation in temperature is not witnessed as per the change in seasons. Arabian Peninsula’s dry northeasterly winds and the Congo River basin’s moist southwesterly winds determine the longevity of wet and dry seasons in the country.
Dry northeasterly, continental trade winds remain a dominant climatic factor during January-March. Except for a small region in northwestern Sudan, practically no rainfall takes place during this period. At the end of the dry season, the temperature remains highest. The sky remains cloudless, and the air remains dry.
May-June is the warmest period with average temperature revolving around 41.9 °C (107.4 °F) in Khartoum. Sometimes, the highest temperature also reaches 48 °C (118.4 °F). January experiences the lowest temperature with average lows of 15 °C (59 °F) in January. Sometimes, the temperature also dips to 6 °C (42.8 °F) during winter in Khartoum.
The nominal GDP of Sudan was US$40.852 billion in 2018, and the annual GDP growth rate was -2.321%. In 2017, the country had a negative balance of trade amounting to US$5.2 billion. While the value of export was US$4.67 billion and the value of imports was US$9.9 billion.
The main export items of the country are gold, oil or petroleum products, Arabic gum, peanuts, livestock, sesame, cotton, sugar, etc. The main import items are food items, refinery, textiles, transport equipment, manufactured goods, wheat, chemicals, and medicines.
The rate of unemployment was 12.9% in 2018, higher than 12.7% in 2017. Around 47% of the population lives under the poverty line. Human Development Report 2019 shows that the HDI value of the country was 0.507 in 2018, which is one of the lowest in the world. Sudan has a rank of 168 out of 189 countries.
There is around 11,900 km (7,394 mi) roadway available in Sudan, out of which 4,320 km (2,684 mi) are paved, and 7,580 km (4,710 mi) are unpaved. Taxis and bakassis (minibus shared taxi) are the primary public transport on roads. Car rental facilities are also available from major city centres as well as airports.
There is a 7,251 km (4,506 mi) long railway available in this country. While 5,851 km (3,636 mi) is narrow-gauge, 1,400 km (870 mi) is 0.600-m gauge railway track meant for cotton plantations. The country has 4,068 km (2,528 mi) long waterway, out of which navigation remains open all year round on the White Nile River and Blue Nile River. There are 18 merchant marine vessels, and the major seaport is Port Sudan (a port city in eastern Sudan).
Sudan has 74 airports, out of which 16 have paved runways, and 58 have unpaved runways. Six heliports are also there in the country. Khartoum International Airport (in Khartoum) and Port Sudan New International Airport (in Port Sudan) are the leading international airports in Sudan. Other important airports are Wadi Halfa Airport (in Wadi Halfa), Nyala Airport (in Nyala), Kassala Airport (in Kassala), El Obeid Airport (in Al-Ubayyid), El Fasher Airport (in Al-Fashir), Dongola Airport (in Dunqulah), and Atbara Airport (in Atbarah).
UN, UNESCO, WHO, IMF, ILO, ABEDA, ACP, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AU, CAEU, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), ICC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link:
Related Maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…