What are the Key Facts of Slovenia?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Slovenia |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Ljubljana |
|
Largest City |
Ljubljana |
|
Coordinates |
46.116667, 14.816667 |
|
Area |
7,827 sq mi ( 20,273 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
752 mi ( 1,211 km) |
|
Coastline |
29 mi ( 47 km) |
|
Currency |
Euro (EUR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Austria, Hungary, Croatia and Italy |
|
Population |
2,080,908 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Slovene |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
25 June, Independence from Yugoslavia |
|
National Anthem |
“Zdravljica” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
|
President |
Borut Pahor |
|
Vice President |
Marjan Šarec |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$36,387.5 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$23,601.4 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
HDI |
0.896 (2017), Rank: 25 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
87 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
40 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
Right |
|
Calling Code |
+386 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.si |
Where is Slovenia?
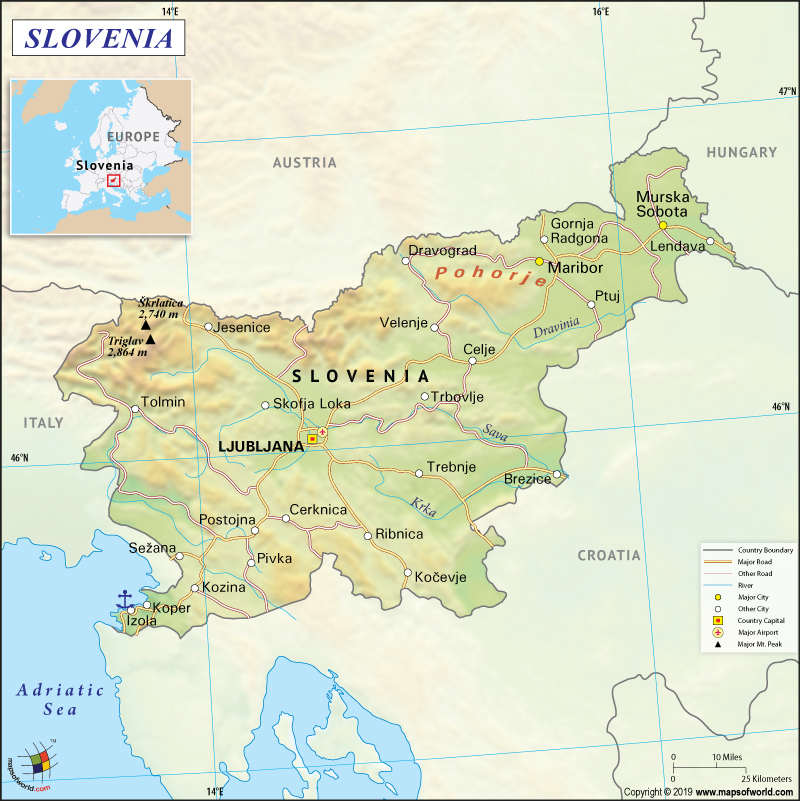
Slovenia is located in southern Central Europe. It is bordered by Austria to the north, Italy to the west, Croatia to the southeast, Hungary to the northeast, and the Adriatic Sea to the southwest.
What is the Geography of Slovenia?
Slovenia, a successor of Yugoslavia, is a Central European country that is spread over an area of 20,273 square kilometers (7,827 square miles). This almost landlocked country has a 46.6 km (29 miles) long coastline between Italy and Croatia at the Adriatic Sea. The country has vast biological diversity. Rivers and streams are spread over 26,000 kilometers (16,156 miles). There are around 7,500 water springs, including therapeutic mineral springs, present in the country.
Most of the landforms in Slovenia are mountainous terrains. Almost half of Slovenia is covered by forests, making it the 3rd most forested European country (after Finland and Sweden). The largest remnants of primeval forest can be found in the Kočevje area.
Four major European geographic regions are found here:
- Alps: 42.1% of the country
- Dinaric Alps: 28.1% of the country
- Pannonian Plain: 21.2% of the country
- Mediterranean: 8.6% of the country
While 5,593 square kilometers area of Slovenia is covered by grassland, gardens cover an area of around 2,471 square kilometers. This includes orchards and vineyards over 363 square kilometers and 216 square kilometers respectively. While Triglav National Park is the largest protected natural area (spread over 83,807 ha), Postojna Cave is the largest karst cave (spread over 19.5 km).
Slovenia’s climate is characterized by cold winters and warm summers. However, the pleasant sub-Mediterranean climate can be found in the coastal areas. Slovenia gets lots of snow throughout the year. The sun shines for around 2,000 hours every year.
In January, the average temperature remains -2°C, while, in July, the average temperature remains 21°C.
Average rainfall varies from one region to another in Slovenia. Alps region gets maximum rain, ranging up to 3500 mm. Central Slovenia gets 1400 mm rain, while South east region gets only around 800 mm rain.
The mean elevation of Slovenia is 492 meters. While the lowest elevation is at the Adriatic Sea, the highest elevation point is 2,864 meters. The ranges of the Dinaric Alps vary from 700 meters (2,300 feet) to 2,200 meters (7,200 feet). The Julian Alps is the highest alpine range located in Slovenia. The highest peaks in the country are Mount Triglav (2,864 meters or 9,396 feet) and Mount Stol (2,236 meters or 7,336 feet).
Sava River is the longest river (221 kilometers or 137 miles) of the country, followed by Drava and Mura. Lake Cerknišco is the largest lake in Slovenia that covers an area of 24 square kilometers (9.3 square miles). Most of the mineral and thermal springs (78 of them) are located in the Pannonian Plain. Slovenia’s coastline is known as Slovene Riviera (46.6 km or 29 miles long), which is located on the Gulf of Trieste.
What is the Economy of Slovenia?
Slovenia, a part of the European Union, is one of the leading Central European economies having the highest per capita GDPs. While Slovenia’s estimated nominal GDP is $54.242 billion, the estimated PPP GDP is $75.976 billion for the year 2018. This country is categorized as a developed country, thanks to the advanced infrastructure, highly educated population, and its strategic geographic location.
After joining the OECD in 2012, the country experienced an export-led growth from 2014 to 2016 (propelled by the strong demands of the European market). In 2017, the economic growth rate reached 5%. Strong exports coupled with increasing consumption boosted labor demand. This brought down the high unemployment rate to below 5.5%. All these factors along with increased tax collection and social security contributions helped Slovenia to consolidate its fiscal position.
While 2/3rd of the population is employed in the services sector (including tourism), 1/3rd is employed in manufacturing and construction.
What is the Transportation System of Slovenia?
The road network forms the largest transport system in Slovenia, accounting for around 80% of the total transport system in the country. Private cars are more popular than public transport. In the Slovenian towns, buses are the main public passenger transport. The 4 major bus stations are located in the capital city Ljubljana, Kranj, Celje, and Maribor. The highest category roads are the state roads – motorways and expressways (around 400 km are complete till now).
Slovenia has 3 main ports; they are Port of Koper, Port of Piran, and Port of Izola. While Koper handles maritime passenger traffic, the two smaller ports transport both passenger and cargo.
There are 12 public airports in the country out of which three are international airports – Ljubljana Jože Pučnik Airport, Maribor Edvard Rusjan Airport, and Portorož Airport.
The state-owned Slovenian Railways operates 1,229 km (or 764 miles) of standard gauge tracks as well as 331 km (206 mi) of double track. The Pan-European railway corridors V and X pass through this European country. All international passenger trains halt at Ljubljana Railway Hub.
What International Organizations is Slovenia Part Of?
EU, WTO, IMF, NATO, WHO, UNESCO, Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA (cooperating state), FAO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF (observer), OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SELEC, UN, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ZC