
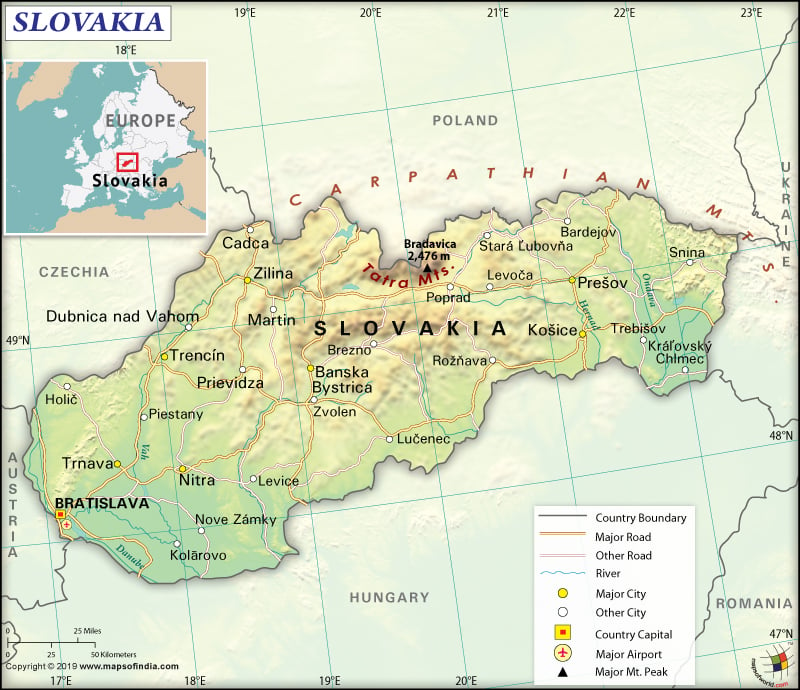
Map of Slovakia which lies in the Continent of Europe
| Official Name | Slovak Republic |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Bratislava |
| Largest City | Bratislava |
| Coordinates | 48.666667, 19.500000 |
| Area | 18,933 sq. mi ( 49,035 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,001 mi ( 1,611 km) |
| Coastline | 0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Neighboring Countries | Ukraine, Hungary, Austria, Czechia, Poland |
| Population | 5,450,421 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | Slovak |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 1 January (Independence from Czechoslovakia) |
| National Anthem | “Nad Tatrou sa blyska” |
| Form of Government | Unitary parliamentary republic |
| President | Zuzana Čaputová |
| Prime Minister | Igor Matovic |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 34,329.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 19,546.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.855 (2017), Rank: 38 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 67 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 36 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +421 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Internet TLD | .sk |
Slovakia is a Central European country. It shares its 1,611 km (1,001 mi) long border with Hungary (627 km or 390 mi) to the south, Poland (541 km or 336 mi) to the north, Czech Republic (241 km or 150 mi) to the northwest, Austria (105 km or 65 mi) to the west, and Ukraine (97 km or 60 mi) to the east.
To start with, Slovakia is spread across a total area of 49,035 sq. km (18,933 sq. mi), out of which 48,105 sq. km (18,573 sq. mi) is land area and 930 sq. km (359 sq. mi) is water area. This landlocked country doesn’t have any coastline.
Further, the mean elevation of Slovakia is 458 m (1,503 ft). While Gerlachovsky Stit is the highest elevation point at 2,655 m (8,711 ft), the lowest elevation point is Bodrok River at 94 m (308 ft). The major mountains of the country are Gerlachovský štít, Lomnický štít, Ľadový štít, Pyšný štít, Zadný Gerlach, etc.
Additionally, the major rivers of Slovakia are Váh, Hron, Ipeľ, Nitra, Hornád, Danube, and many more. Sunny Lakes, Golden Sands, and Duchonka are the major lakes of the country. Other major water reservoirs are Orava, Domaša, Zemplínska Šírava, Liptovská Mara, and Sĺňava. The only European geyser that is located outside the Scandinavias is Geyser Herľany and it is situated near Kosice.
Besides, the central Slovakian landform consists of rugged and heavily forested Ore Mountains. Along the northern border of the country, the Carpathian Mountains cover can be found. All the tallest mountain peaks belong to the Tatra Mountains. Fertile lowlands can be found along the southeastern border as well as the Danube River plain. Hron river basin covers around 11% of Slovakia’s territory.
The Slovakian climate lies within temperate-to-continental-climate zones. While summers remain relatively warm, the winters remain cold, cloudy and humid. However, weather in the mountainous north differs from that of the plains in the south. In a year, the temperature can vary from as high as 40.3 °C (104.5 °F) to as low as −41 °C (104.5 °F). However, temperatures below −30 °C (−22 °F) are rare.
At the same time, southern Slovakia and Bratislava are the warmest regions of the country. In summer, the temperature can reach as high as 30 °C (86 °F) during the daytime. However, at night the temperature comes down to 20 °C (68 °F). The average winter temperature during daytime ranges within −5 °C (23 °F) and 10 °C (50 °F). At nighttime, the temperature remains freezing but hardly ever goes below −10 °C (14 °F).
Slovakia has a high income and developed economy whose nominal GDP was US$106.472 billion in 2018 and the economy was growing at a rate of 4.11%. The OECD Economic Outlook (February 2019) has said that the Slovakian economy is all set to become the fastest-growing developed country in the world in 2019-20. OECD expects the economy to grow by 4.3% in 2019, followed by 3.6% in 2020.
Moreover, over 70% of the labor force is employed in the services sector, followed by industry (over 20%) and agriculture (below 5%). The service sector contributes over 60% to the GDP, followed by industry (35%) and agriculture (below 4%).
Furthermore, the economy of Slovakia has a marginal trade surplus. The major export items are vehicles and related parts, nuclear reactors and furnaces, machinery and electrical equipment, iron/steel, and others. Vehicle parts and crude petroleum are the main import items of Slovakia.
In 2018, the unemployment rate had come down to 6.7%. It is further expected to come down to 6.1% and 5.5% in 2019 and 2020 respectively. New automotive production capacity is expected to boost the export sector. The overall economy will become stronger with enhanced investment, thanks to the new public infrastructure projects and supportive financial conditions.
Slovakia has a well-developed railway network as well as a highway system. The public transport system consists of buses, tramways, trolleybuses, trains, and taxis. The outskirts of the country can be traveled on trains and buses. Municipal Public Transport (also called MHD) helps passengers travel at affordable price.
There are 56,926 km (35,372 mi) of roadways present in Slovakia. It includes 464 km of highways and other national roads and local roads. 3,580 km (2,225 mi) of railway network is present in the country. Most of them (3,435 km or 2,134 mi) is standard gauge.
Airways are also pretty developed in Slovakia. 35 airports are there in the country, out of which 21 have paved runways and 14 have unpaved runways. MR Štefánik Airport is the main airport of Bratislava (capital of Slovakia). 172 km of waterways (107 mi), mostly on Danube River in the country help in transporting passengers, freight ships, and cargo.
WTO, IMF, Australia Group, NATO, BIS, UN, CD, Schengen Convention, CE, ILO, CEI, UNCTAD, CERN, UNESCO, EAPC, UNFICYP, EBRD, UNIDO, ECB, UNTSO, EIB, EMU, NSG, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NEA, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, ICC (national committees), BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OIF (observer), SELEC (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…