What are the Key Facts of Senegal?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Senegal |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Dakar |
|
Largest City |
Dakar |
|
Coordinates |
14.000000, -14.000000 |
|
Area |
75,955 sq. mi (196,722 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,668 mi (2,684 km) |
|
Coastline |
330 mi (531 km) |
|
Currency |
West African CFA franc (XOF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
The Gambia, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Mauritania. Maritime neighbors: Cabo Verde |
|
Population |
16,296,360 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
French |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
4 April (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Pincez Tous vos Koras, Frappez les Balafons” |
|
Form of Government |
Presidential republic |
|
President |
Macky Sall |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 3,535.6 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,446.8 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.514 (2019), Rank: 166 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
51.90 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
99 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
1 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
221 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC (GMT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.sn |
Where is Senegal?
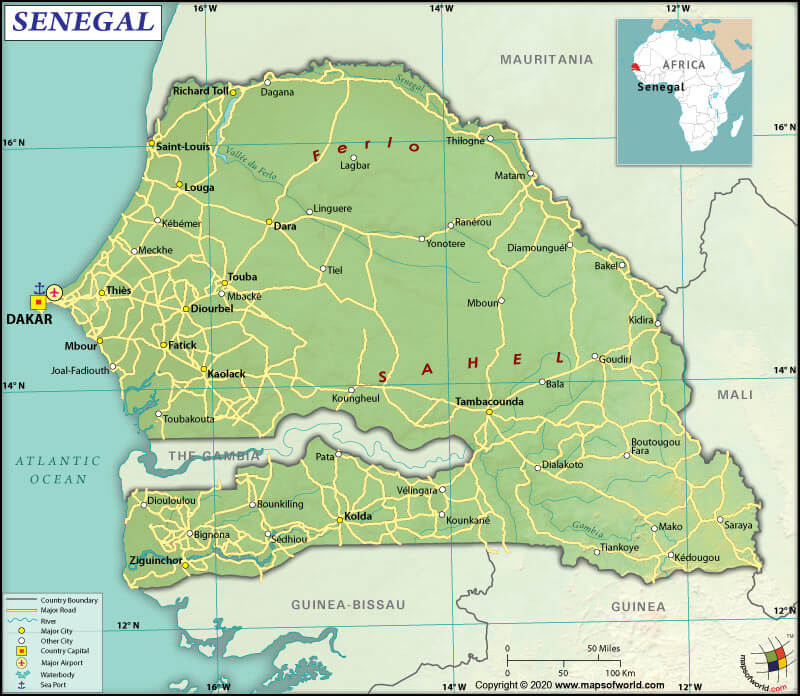
Senegal (whose official name is the Republic of Senegal) is a West African country located between Mauritania and Guinea-Bissau, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean.
What is the Geography of Senegal?
Senegal spreads across a total area of 196,722 sq. km (75,955 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 192,530 sq. km (74,336 sq. mi) is land and 4,192 sq. km (1,619 sq. mi) is water.
The total land boundary of Senegal is 2,684 km (1,667.8 mi) long. It is shared with five countries: The Gambia (749 km or 465.4 mi; surrounded by Senegal from three sides), Mauritania (742 km or 461.1 mi) to the north, Mali (489 km or 303.9 mi) to the east, Guinea (363 km or 225.6 mi) to the southeast, and Guinea-Bissau (341 km or 211.9 mi) to the southwest.
Senegal has a 531 km (330 mi) long coastline. The Atlantic Ocean bounds the country from the west. The mean elevation of the country is 69 m (226.4 ft). While the highest point is an unnamed elevation (which is located around 2.8 km or 1.7 mi southeast of Nepen Diaka) at 648 m (2,126 ft), the lowest point is the Atlantic Ocean at 0 m (0 ft).
Senegal’s terrain is predominantly characterized by rolling sandy plains of the western Sahel. It rises to foothills as you start moving towards the southeast. The highest mountains in Senegal are Sambaya (Kédougou), Inndia (Tambacounda), Nion Médina (Kédougou), Toukanaya (Tambacounda), Bansifara (Kédougou), etc.
You will also find small pockets of tropical rainforest and mangroves nestled in the savannah dominating the landscape. Prominent landforms of Senegal, besides rolling plains, are plateaus, foothills, deserts, freshwater lakes, and rivers.
Major rivers in the country are Senegal, Casamance, Gambia, Saloum, and Siné. While the largest lake in the country is Lac de Guiers or Guiers Lake (an artificially controlled lake), the most prominent natural lake is a shallow saltwater lake called Lac Rose (also called Lake Retba or Pink Lake). Lac Rose is unique because it is one of the few lakes in the world with naturally pink-colored water.
What is the Climate of Senegal?
Two seasons are found in the country. While one is a rainy season, the other is dry. The rainy season starts in May and continues till November in Senegal. This season is tropical, hot, and humid. Strong southeast winds blow during these months.
The dry season lasts for five months from December to April. It is characterized by a hot and dry climate along with the occurrence of harmattan wind. Dry and humid seasons take place because of northeast winter winds as well as southwest summer winds.
The yearly rainfall level in Senegal’s capital, Dakar, is around 600 mm (24 in). Most of the rainfall takes place during June-October. During this time, the average maximum temperature revolves around 86.0 °F (30 °C), and the average minimum temperature revolves around 75.6 °F (24.2 °C). The average maximum and minimum temperatures during December-February revolve around 78.3 °F (25.7 °C) and 64.4 °F (18 °C), respectively.
The temperature in the interiors of the country is higher than along the coastal areas. While the average daily temperature in coastal cities such as Dakar remains around 73.8 °F (23.2 °C), the average daily temperature in the interior cities such as Kaolack and Tambacounda in May remains around 86.0-90.9 °F (30-32.7 °C). The temperature along the border with Mali, such as Tambacounda, can reach as high as 129.2 °F (54 °C).
The amount of rainfall increases significantly as you move towards the south. In some Senegal areas, the annual precipitation level can exceed 1,500 mm (59.1 inches). The average yearly precipitation is as low as 250 mm (10 inches) in the extreme north. However, in extreme southern coastal areas, the average annual precipitation is as high as 1800 mm (71 inches).
What is the Economy of Senegal?
Senegal’s economy is driven by five sectors, including mining, tourism, construction, agriculture, and fisheries. The country is also working on its oil explorations. Their main foreign currency earners are the export of phosphate, fertilizer, agricultural products, and fishes.
The nominal GDP of Senegal grew at an annual rate of 5.271% to US$23.578 billion in 2019. The export and import values of the country in 2018 were US$3.89 billion and US$11.1 billion, respectively. In 2018, Senegal had a negative trade balance of -$7.23 billion.
The major exports are Gold, Refined Petroleum, Phosphoric Acid, Non-fillet Frozen Fish, and Cement. The major imports of Senegal are Refined Petroleum, Crude Petroleum, Rice, Cars, and Wheat.
As per modeled ILO estimate, the unemployment rate (percentage of the total labor force) was hovering around 10% during 2006-2011. However, it came down to 6.757% in 2015. The unemployment rate was 6.604% in 2019.
United Nations’ World Food Programme’s report says that more than 1/3rd of Senegal’s population (39%) lives in poverty. Chronic poverty is experienced by 75% of the families in Senegal.
What is the Transportation System of Senegal?
The country has 20 airports, out of which nine have paved runways, and 11 have unpaved runways. Major airports are Blaise Diagne International Airport (Dakar), Léopold Sédar Senghor International Airport (Dakar), Cap Skirring Airport (Cap Skirring), Ziguinchor Airport (Ziguinchor), etc.
The total roadways in the country are 16,665 km (10,355.2 mi) long, out of which 6,126 km (3,806.5 mi) is paved, and 10,539 km (6,548.6 mi) is unpaved. The country has 241 km (149.8 mi) of expressways. Senegal has 906 km (563 mi) long narrow-gauge railways, out of which 713 km (443 mi) was operational in 2017.
Dakar is the major seaport of the country. There are 32 merchant marine vessels in the country, out of which 4 are general cargo, 1 is an oil tanker, and 27 are other types of vessels.
What International Organizations is Senegal Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, UNESCO, WHO, ILO, ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WAEMU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, CPLP (associate), EITI (candidate country), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), WADB (regional), WFTU (NGOs)