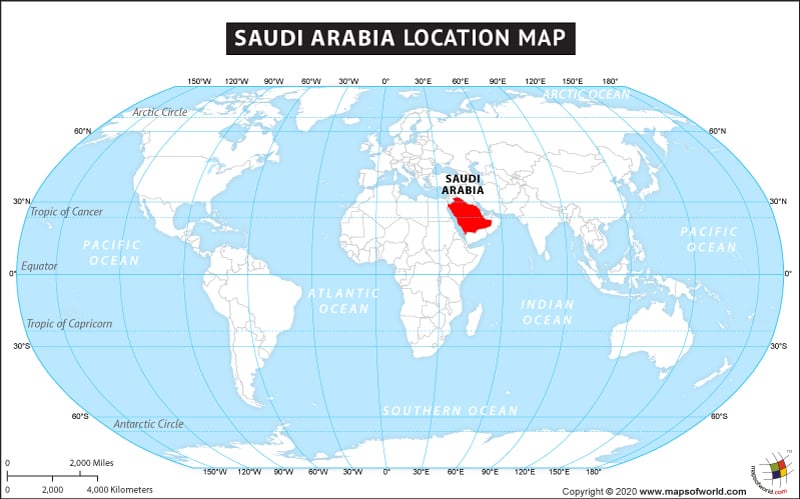
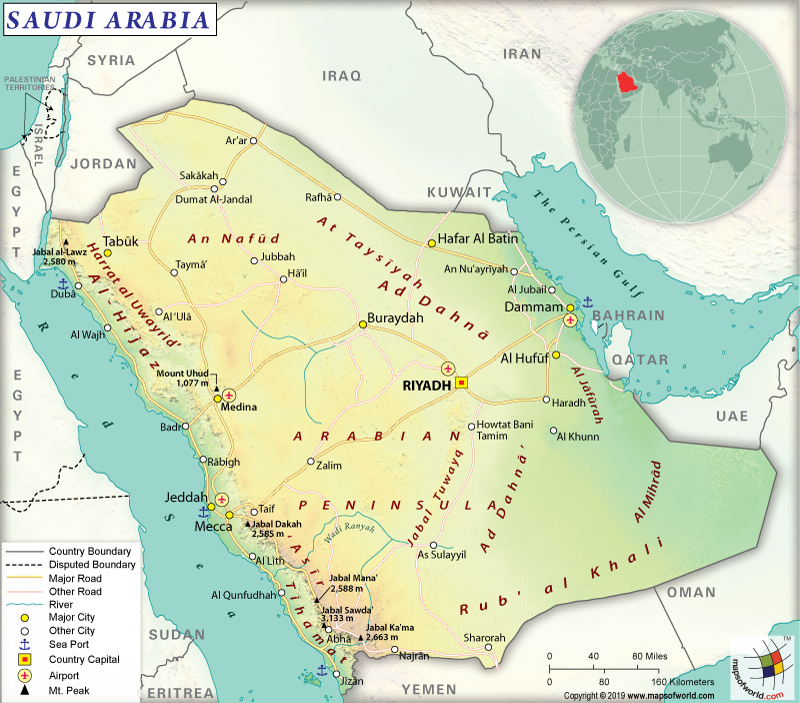
What are the Key Facts of Saudi Arabia?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Riyadh |
|
Largest City |
Riyadh |
|
Coordinates |
25.000000, 45.000000 |
|
Area |
830,000 sq. mi ( 2,149,690 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
2,654 mi (4,272 km) |
|
Coastline |
1,640 mi ( 2,640 km) |
|
Currency |
Saudi riyal (SR) (SAR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
U.A.E, Oman, Yemen, Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain. Maritime Neighbors: Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea |
|
Population |
33,000,000 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
23 September (Saudi National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Aash Al Maleek” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary Islamic absolute monarchy |
|
King |
Mohammad bin Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 55,119.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 23,219.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.853 (2017), Rank: 39 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
95.33 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
Space Research Institute of Saudi Arabia |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
4 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
3 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+966 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.sa |
Where is Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia is a Middle Eastern country that is located to the north of Yemen, bordering the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf.
What is the Geography of Saudi Arabia?
Saudi Arabia is spread across a total area of 2,149,690 sq. km (830,000 sq. mi), out of which the land area is spread over 2,149,690 sq. km (830,000 sq. mi). The country is devoid of any water area. In terms of total area, it is the largest Middle Eastern sovereign country and the fifth largest one in the entire Asian continent.
This country has a 4,272 km (2654 mi) long land boundary. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia shares its borders with seven countries: Yemen (1,307 km or 812 mi), Iraq (811 km or 504 mi), Jordan (731 km or 454 mi), Oman (658 km or 409 mi), UAE (457 km or 284 mi), Kuwait (221 km or 137 mi), Qatar (87 km or 54 mi). As Saudi Arabia borders both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, the country has a 2,640 km (1,640 mi) long coastline.
Additionally, the mean elevation of Saudi Arabia is 665 m (2,182 ft). While the highest elevation point is Jabal Sawda’ at 3,133 m (10,279 ft), the lowest elevation point is sea level at the Persian Gulf. The major mountains of the kingdom are Jabal Sawda, Jabal Ferwa’, Jabal Natfa’, Jabal Warrab, Jebal As-Seqaa, and Jabal Al-Majaz.
While no permanent river flows through the kingdom, there are many wadis (valleys and riverbeds) in the country. Some of the most important ones are Wadi Hanifa (largest Saudi Arabian drainage basin of around 2,500 sq mi near Riyadh), Wadi Sahba, Wadi Rabigh, Wadi Nisah, Wadi Aful, Wadi Hamir, Wadi al Batin, Wadi Al-Rummah, Wadi ad-Dawasir, Al-Kharj, and many more.
As a matter of fact, the major landform of Saudi Arabia is uninhabited desert land. The three major deserts are Rub’ Al Khali Desert (250,000 sq. mi or 647,497 sq. km), An-Nafud Desert (around 40,000 sq mi or 103,600 sq km), and Ad Dahna (800 mi or 1,287 km strip). While the former has the world’s largest mass of sand, the latter is characterized by sand dunes that often exceed 100 ft in height.
Moreover, the landform starts rising from being a desert land to hills/mountains as you move to the west and southwest direction (mostly along the Red Sea’s edges). While Hejaz mountain range is located in the northwest direction of the country, Azir range is situated in the southwest. The two most important water bodies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia are the Red Sea on the west, and the Persian Gulf on the east. A stunning coral reef can be found along the coast of the Red Sea. A large limestone cavern network (having stalactites and helictites) can be found under the desert terrain. One such important cave system is Al Habkah.
Saudi Arabia, except for Asir province, has a harsh and dry desert. Great temperature extremes are the characteristic features of this climatic condition. While daytime witnesses extreme heat, nighttime experiences abrupt temperature drops. Rainfall level throughout the year is very low. The considerable temperature/humidity variation takes place because of the subtropical high-pressure system’s influence. The Saudi Arabian climate has two distinctive differences, depending upon the coastal and interior areas.
During summer, the average temperature revolves around 45° C (113 ˚F). However, many times during this season, the temperature reaches 54° C (129.2 ˚F). Just after sunrise, the heat increases significantly, and the intense heat lingers till sunset. However, after sunset, the nights become surprisingly cool. During the winter season, the atmosphere remains significantly cool, thanks to the high wind-chill factor and almost total absence of humidity. However, the temperature hardly ever falls below 0° C (32 ˚F).
What is the Economy of Saudi Arabia?
To begin with, Saudi Arabian economy is a petroleum-export dependent economy, which propels its growth with the help of the petrodollar from the export of crude oil. Saudi Arabia is the second-largest petroleum producer and the largest exporter in the world. The kingdom possesses around 16% of the total petroleum reserves of the world. Around 87% of the budget revenues, 90% of the export earnings, and 42% of the GDP come from the petroleum sector. Over $34 trillion worth of natural resources can be found in the country.
In 2018, the nominal GDP of the country was US$782.483 billion that grew at 2.215%. Saudi Arabia is currently trying to diversify its economy and lessen its overdependence on petroleum. That’s why it is opening the economy to the private sector. Though the economy is heavily dependent upon a whopping 6 million foreign workers, the administrators are giving more impetus to the employment of local Saudi nationals.
Official data by the General Authority for Statistics (GaStat) shows that in the first quarter of 2019, the unemployment rate fell slightly to 12.5% from 12.7% in Q4 2018. However, the unemployment rate for the total Saudi and non-Saudi population in the country was 5.7% in Q1 2019 in comparison to 6% in Q4 2018. The poverty rate in Saudi Arabia in 2017 was 12.7%, making it the lowest rate of poverty in the Middle East.
What is the Transportation System of Saudi Arabia?
There is an extensive roadway system available in Saudi Arabia. The country has 221,372 km (137,554 mi) of roadways, out of which 47,529 km (29,533 mi) is paved and 173,843 km (108,021 mi) is unpaved. 3,891 km (2,418 mi) of expressways are there in the country.
Some of the major inter-city highways of the kingdom are Dammam-Abu Hadriya-Ras Tanura Highway, Khaybar-Al Ola Highway, Riyadh-Sudair-Al Qasim Highway, Riyadh-Dammam Highway, Taif-Abha-Jizan Highway, Riyadh-Taif Highway, Jeddah-Mecca Highway, Jeddah-Al Leith-Jizan Highway, Medina-Tabuk Highway, etc.
The sea network system is also well developed in Saudi Arabia. This is mainly used for the transportation of petrochemicals. The major seaports of the country are Ad Dammam, Yanbu’, King Abdulla, Jeddah, Al Jubayl, and many more. There are 380 merchant marine ships in Saudi Arabia.
There is 5,410 km (3,362 mi) long railway network available in the country, and all of it is narrow gauge. The air transport facility is also significantly developed. Out of the total 214 airports, 82 airports have paved runways and 132 airports have unpaved runways. Ten heliports are also there in the country.
What International Organizations is Saudi Arabia part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, NAM, Interpol, OPEC, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, BIS, CAEU, CP, FAO, G-20, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, AfDB (nonregional member), ICC (national committees), WFTU (NGOs), IOM (observer), OAS (observer)
Related Links: