
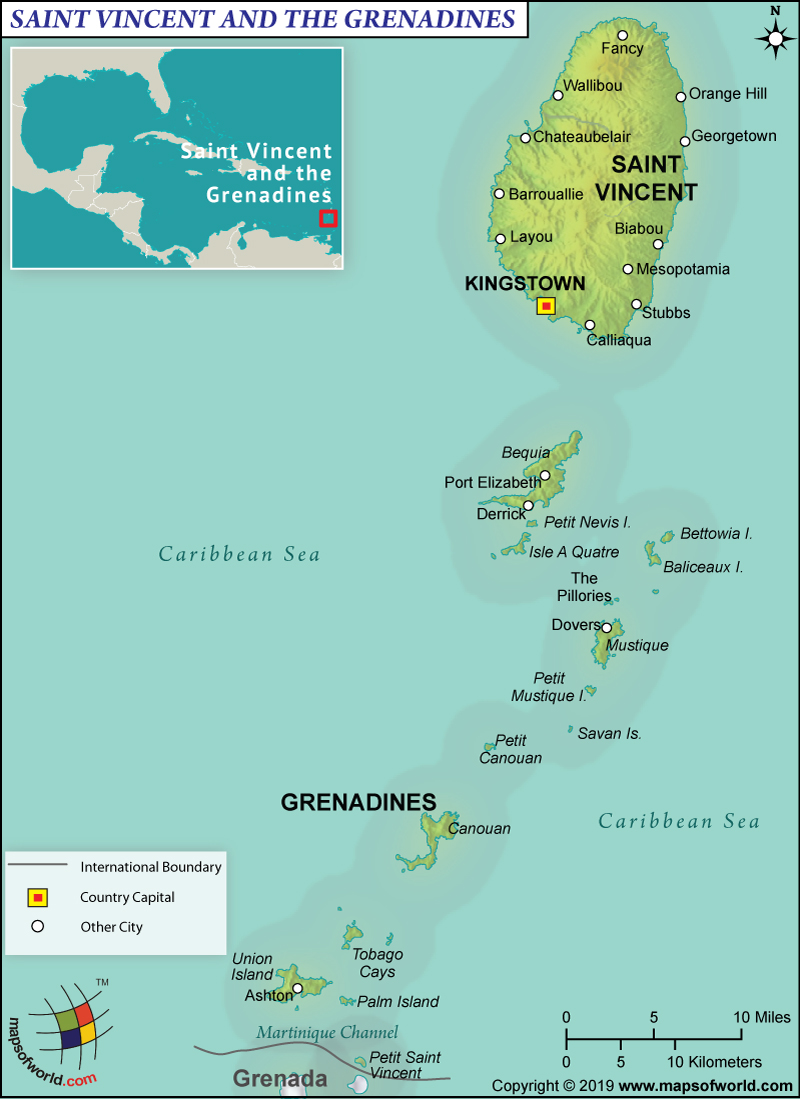
Map of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines which lies in Caribbean
| Official Name | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines |
| Continent | Caribbean |
| Capital | Kingstown |
| Largest City | Kingstown |
| Coordinates | 13.250000, -61.200000 |
| Area | 150 sq. mi (389 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 0 mi ( 0 km) |
| Coastline | 52 mi ( 84 km) |
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (XCD) |
| Neighboring Countries | Maritime Neighbor: St. Lucia, Barbados, Grenada |
| Population | 109,643 (2016 est.) |
| Official Languages | English |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 27 October (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “St. Vincent! Land So Beautiful!” |
| Form of Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Monarch | Elizabeth II |
| Prime Minister | Ralph Gonsalves |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $12,307.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 7,377.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.723 (2017), Rank: 99 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 0 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | left |
| Calling Code | +1 784 |
| Time Zone | UTC-4 |
| Internet TLD | .vc |
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a Caribbean Island located to the north of Trinidad and Tobago between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
The total area of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is 389 sq. km (150 sq. mi), out of which Saint Vincent is spread over 344 sq. km (133 sq. mi). The entire area is land area and there is no water area in the country. It has an 84 km (52 mi) long coastline and no land boundary.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines consist of around 32 islands along with hundreds of islets, stretching around 48 mi (77 km) south to Grenada. Saint Vincent is the big island in the country. It has a volcanic origin. Almost the entire terrain is rugged and mountainous. There is very little level ground in the country. Lush forests cover the terrain.
La Soufriere (located in the northern parts of the Saint Vincent Island) is the highest elevation point in the country at 1,234 m (4,049 ft). The other major mountain in the country is Grand Bonhomme. The Caribbean Sea is the lowest elevation point in the country at 0 m (0 ft).
Some of the main islands of the Grendalines are Union Island, Petit Saint Vincent, Isle D’Quatre, Mustique, Mayreau, Canouan, Balliceau, and Bequia. There are more than 600 rocky islets and all of them are low-lying and ringed by coral reefs. The mountain slopes on the Saint Vincent Island is drained by some very small rivers. Some of them are Colonarie River, Caratal River, Wallibou River, etc.
The climate in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is tropical, which is characterized by hot and humid weather round the year.
Starting from January to mid-April, the climate remains relatively cool and dry. During this period of the year, constant northeast trade winds blow steadily at moderate intensity. The June to December climate remains hot, humid, and rainy. The northeast trade winds blow during the June-December period too but they are more irregular during this time of the year, thereby increasing sultriness of the climate.
The frequency of rainfall and the temperature increases gradually between mid-April and late May, the time period just before the start of the hot and rainy season.
The extent of rainfall is abundant in Kingstown, which is around 2,000 mm (78 in) every year. During June-November, over 200 mm (8 in) of rainfall takes place. February-April is the period when the extent of rainfall is less than 100 mm (4 in).
The Grendaline islands get less amount of rainfall, which is less than 1,500 mm (60 in) per year. Rainfall takes place across the year and it is generally accompanied by intense thunderstorms for a short period of time.
The country receives abundant sunshine throughout the year. During January-April, the water temperature remains around 27 °C (81 °F). The same remains around 29 °C (84 °F) during August-September. February-April is the best time to visit Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is a lower-middle-income economy, which is mainly dependent upon tourism, agriculture, construction activities, and remittances. A small but thriving offshore banking sector (fully adopting the international regulatory standards) is there in the country. Most of the labor force works in either banana production or tourism. The economy grew by 2.6% in 2018, expanding the nominal GDP to US$813.09 million.
The economy had a negative trade balance of US$113 million in 2017. While it exported $258 million of goods, it imported $372 million of goods. The main export items were petroleum gas, special purpose ships, coated flat-rolled iron, passenger/cargo ships, etc. The major items imported by Saint Vincent and the Grenadines are jewelry, refined petroleum, wheat, cars, poultry meat, etc.
The rate of employment in the country is significantly high. In 2018, it was 19.76%. The rate of poverty in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is also very high. Around 30% of the population lives in poverty.
The transport system in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is limited and the most popular mode of transport inside the main islands is taxis. Bus services are also available. These buses are very affordable but usually remain crowded. Here are 6 major airports in the country, out of which 5 have paved runways and 1 has an unpaved runway. Argyle International Airport is the new international airport of the country, opened on February 14, 2017. Ferries and boats are the most popular ways of island-hopping. Kingstown is the major seaport and there are 889 merchant marine ships in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.
UN, IMF, Petrocaribe, ILO, ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OECS, OPANAL, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WTO, WFTU (NGOs), ISO (subscriber)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…