What are the Key Facts of Poland?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Poland |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Warsaw |
|
Largest City |
Warsaw |
|
Coordinates |
52.000000, 20.000000 |
|
Area |
120,733 sq. mi ( 312,696 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,908 mi ( 3,071 km) |
|
Coastline |
273 mi ( 440 km) |
|
Currency |
Polish złoty (PLN) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Slovakia, Germany, Czechia, Russia, Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine |
|
Population |
38,386,000 (2019 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Polish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
11 November |
|
National Anthem |
“Mazurek Dabrowskiego” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Andrzej Duda |
|
Prime Minister |
Mateusz Morawiecki |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 31,343.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 15,424.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.865 (2017), Rank: 33 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Polska Agencja Kosmiczna POLSA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
20 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
306 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+48 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.pl |
Where is Poland?
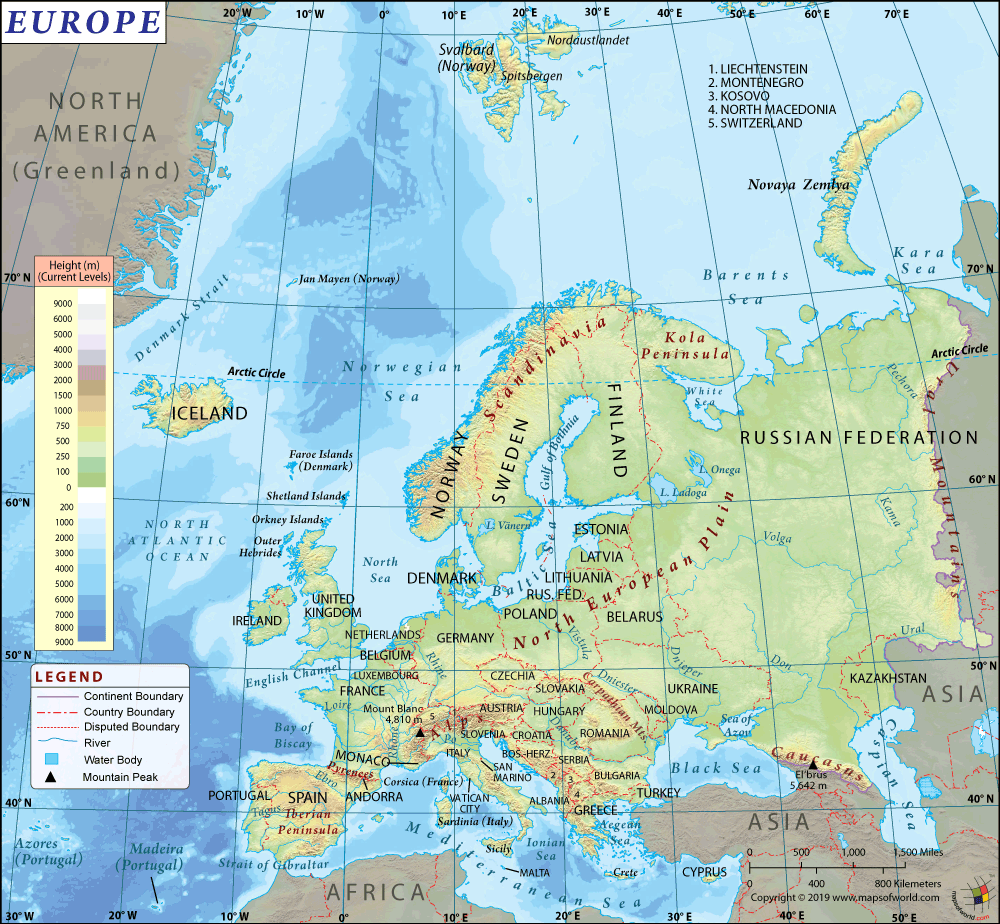
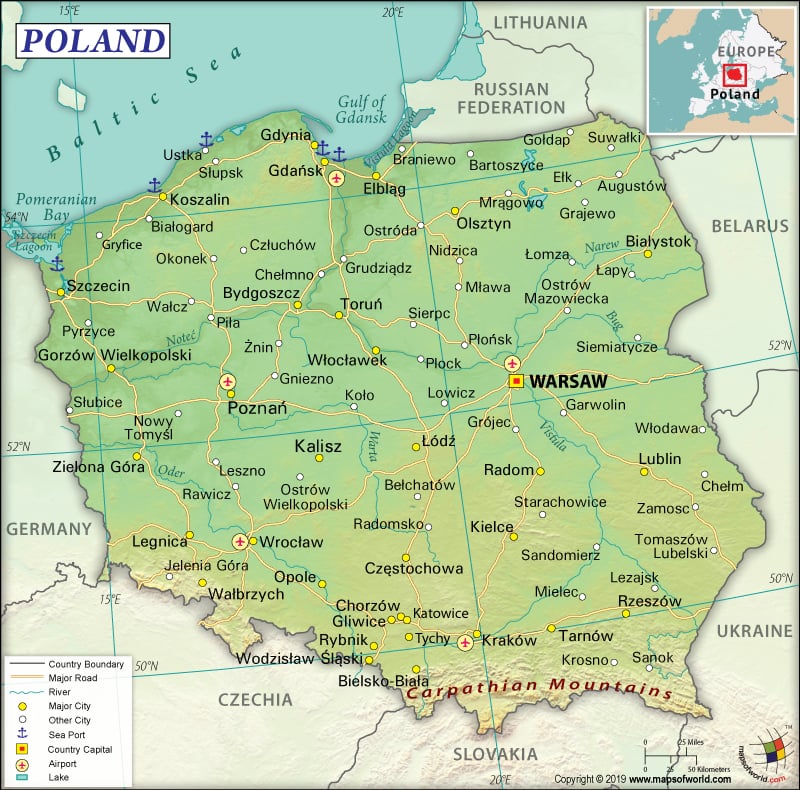
Poland is a Central European country that is located in the east of Germany. It is bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north. Check out this – Map of Poland and Other 26 Related Polish Maps for more maps and info about Poland.
What is the Geography of Poland?
The total area of Poland is 312,696 sq. km (120,733 sq. mi), out of which 304,255 sq. km (117,474 sq. mi) is land area and 8,430 sq. km (3,255 sq. mi) is water area. There is a 3,071 km (1,908 mi) long land boundary that is shared with 7 countries. The land boundary is shared with Czech Republic (796 km or 495 m to the south), Slovakia (541 km or 336 mi to the south), Ukraine (535 km or 332 mi to the east), Germany (467 km or 290 mi to the west), Belarus (418 km or 260 mi to the east), Kaliningrad Oblast region of Russia (210 km or 130 mi to the north), and Lithuania (104 km or 65 mi to the north).
The terrain is characterized mainly by the flat plain. However, along the southern border, the mountains are present. The mean elevation of the country is 173 m (568 ft). While Rysy at 2,499 m (8,199 ft) is the highest elevation point in the country, the lowest point is located near Raczki Elblaskie at -2 m (-7 ft). The major mountains in Poland are Rysy, Mięguszowiecki Szczyt Wielki, Miedziane, Kozi Wierch, Svinica, etc. Some of the major rivers in Poland are Vistula, Warta, Narew, Bug, Oder, etc.
A lowland plain starts from the Baltic Sea and blends into sandy beaches/dunes. The Central Lowlands are dominated by flat fertile farmlands. Hilly regions are located in the northern regions of the country. As you move towards the south, the land starts rising into the hilly uplands, which are located at the front of the Carpathian and Sudetic Mountain Ranges. The Tatra Mountains have the tallest peaks. In the far northeastern parts, many small lakes are situated, making Poland the second country having the most density of lakes.
A fairly smooth coastline is situated in front of the Baltic Sea in the north of Poland. In some areas of these coastlines, sand dunes are situated, which are indented by scattered low-rising cliffs. The landscape rises gently from the Baltic lowlands to the hilly areas that are predominantly tree-covered. In the northeastern parts of Poland, higher elevations are present.
River valleys dominate the Central Lowlands. These valleys blend into the more hilly areas, situated to the Vistula River’s south. A mountainous region is located in the southern third of Poland. The elevated part of the Carpathian Mountains (Tatra Mountains) and the Sudetes are the major ranges in this part of the country. 21 mountains in the country have an elevation of more than 2,000 m (6,600 ft).
The southern part of Poland consists of a natural desert known as the Bledow Desert, which is one of the five deserts present in Europe. This desert is spread across a total area of 32 sq km (12 sq mi) and some of its dunes are as high as 30 m (98 ft).
The climate in Poland can be categorized as temperate, having relatively warm summers and cold winters. The oceanic air currents from the west influence this climatic condition greatly. Other air currents affecting this climate include chilling polar air from Russia and Scandinavia and sub-tropical air from the southern parts.
Poland’s climate gets cold and frosty weather with the temperature plunging below 0 °C (32 °F) during the winter season. This is because of the domination of the polar-continental fronts here. That’s why sometimes heavy snowfall also takes place.
During summertime as well as autumn, warm weather prevails for many days. Dry, sub-tropical, and continental air mass influence this climatic condition. The Baltic Coast gets the highest amount of sunshine during summer. However, it is the Carpathian Mountains that get maximum sunlight during the winters.
6 °C to 8.5 °C (42.8 °F to 47.3 °F) is the average annual air temperature in Poland. 500 mm to 700 mm (20 in to 28 in) is the annual rainfall level, out of which snow constitutes just 5-20%. The altitude determines the climatic condition in the mountains throughout the year. During summertime, the temperature revolves within 20-25 °C (68-77 °F) in Warsaw. This place gets a temperature of 0 °C to -5 °C (32 °F to 23 °F) in winter.
What is the Economy of Poland?
Poland is one of the top-10 economies in the European Union and among the top-20 in the world. In 2018, the nominal GDP grew at a rate of 5.1% to reach US$ 585,816 million. Its main export items are cars, vehicle parts, seats, video displays, other furniture, etc.
The main imports of Poland are crude petroleum, vehicle parts, cars, office machine parts, packaged medicaments, etc. In 2017, it exported US$212 billion value of items and imported US$223 billion value of items. Poland had a negative trade balance of US$11.6 billion.
The unemployment rate was 5.1% in September 2019. The rate of poverty (defined as the Poverty headcount ratio at US$5.50 per day) has come down significantly from 4.6% in 2013 to 2.1% in 2016.
What is the Transportation System of Poland?
Poland has a pretty developed transport system. 420,000 km (260,976 sq mi) roadways are there, out of which 291,000 km (180,819 mi) are paved and 129,000 km (80,157 mi) are unpaved. There is 19,231 km (11,950 mi) long railway track, out of which 18,836 km (11,704 mi) is standard-gauge and 395 km (245 mi) is broad-gauge. 3,997 km (2,484 mi) long navigable waterway (on rivers and canals) is present in Poland. While Swinoujscie, Gdynia, and Gdansk are the major seaports, Szczecin on the River Oder is the main river port. There are 148 merchant marine vessels. 126 airports are there in Poland, out of which 87 have paved and 39 have unpaved runways.
What International Organizations is Poland part of?
UN, IMF, ILO, NATO, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, ESA, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC, Arctic Council (observer), BSEC (observer), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OIF (observer)
Related Links: