
Map of China which lies in the Continent of Asia
| Official Name | People’s Republic of China |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Beijing |
| Largest City | Shanghai |
| Coordinates | 35.000000, 105.000000 |
| Area | 3,705,407 sq. mi ( 9,596,961 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 13,954 mi ( 22,457 km) |
| Coastline | 9,010 mi ( 14,500 km) |
| Currency | Renminbi (yuan; ¥) (CNY) |
| Neighboring Countries | Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, and North Korea. Maritime Neighbors: Taiwan, South Korea, Japan |
| Population | 1,403,500,365 (2016 est. ) |
| Official Languages | Standard Chinese or Mandarin |
| Major Religion | Majority of Non-religious/Chinese folk religion |
| National Day | 1 October (National Day) |
| National Anthem | “Yiyongjun Jinxingqu” |
| Form of Government | Unitary one-party socialist republic |
| President | Xi Jinping |
| Vice President | Wang Qishan |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 18,210.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 9,770.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.752 (2017), Rank: 86 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 96.84 (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | China Manned Space Agency (CMSA), China National Space Administration (CNSA) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 2 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 608 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +86 |
| Time Zone | UTC+8 (China Standard Time) |
| Internet TLD | .cn |
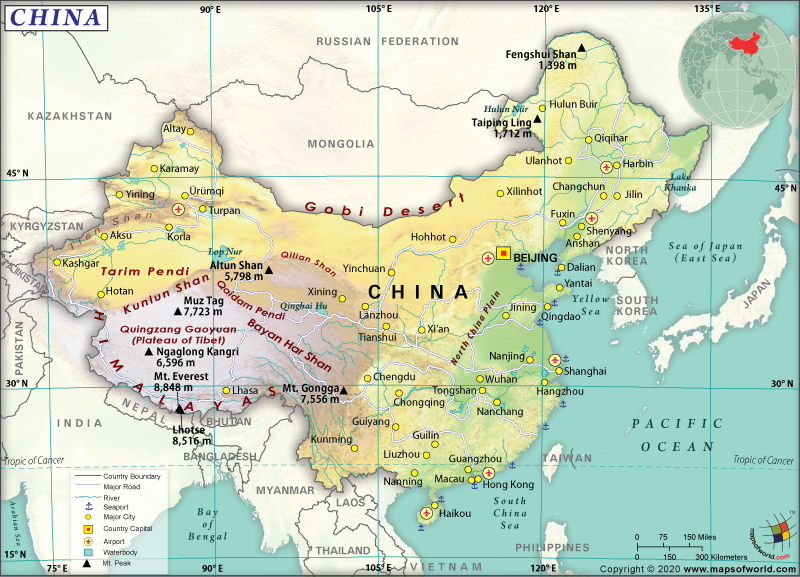
China is an Eastern Asian country that is located between Vietnam and North Korea, bordering the South China Sea, Yellow Sea, Korea Bay, and the East China Sea.
The flag of China, formally the People’s Republic of China, is red with five golden stars in the canton, one of them large, and the other four in an arc around it. Red is a traditional color of communism, representing the communist revolution. The stars symbolize the Chinese people, united under the country’s central leadership. The larger star represents the Communist Party, and the four small stars are the social classes of China.
China is spread across a total area of 9,596,961 sq. km (3,705,407 sq. mi), out of which 9,326,410 sq. km (3,600,947 sq. mi) is land area and 270,550 sq. km (104,460 sq. mi) is water area. This East Asian country has a 22,457 km (13,954 mi) long land boundary and a 14,500 km (9,010 mi) long coastline.
The People’s Republic of China shares its border with 13 countries: Russia (northeast) 4,133 km or 2,568 mi, Russia (northwest) 46 km or 29 mi, India 2,659 km or 1,652 mi, Burma 2,129 km or 1,323 mi, Kazakhstan 1,765 km or 1,097 mi, Nepal 1,389 km or 863 mi, North Korea 1,352 km or 840 mi, Vietnam 1,297 km or 806 mi, Kyrgyzstan 1,063 km or 661 mi, Tajikistan 477 km or 296 mi, Bhutan 477 km or 296 mi, Laos 475 km or 295 mi, and Afghanistan 91 km or 57 mi.
The mean elevation of China is 1,840 m (6,037 ft). While Mount Everest at 8,848 m (29,029 ft) is the highest point of the country, Turpan Pendi at -154 m (-505 ft) or 154 m (505 ft) below sea level is the lowest point. Some of the major mountains of China are Yellow Mountain, Mount Song, Mount Lu, Jade Dragon Snow Mountain, Mount Emei, Mount Tai, and Mount Hua.
China has an extremely diverse terrain. The landscape mainly includes mountains and high plateaus. While the western part of the country has deserts, high plateaus, and mountains, the eastern and central parts include hills, deltas, and broad plains.
The country’s southwestern border is adorned by the most elevated mountain range in the world, the Himalayas. The Chinese border with the Russian Federation in the far northeast has high mountains. Along the border with Mongolia, the Gobi Desert runs from west to east. The topography includes sand desert, low mountain foothills, and plateaus. The arid Turpan Depression (the country’s lowest elevation point and also the 3rd lowest elevation point on the surface of the earth) is located in the western parts of China.
Thousands of rivers from the higher elevations in the west drain the country. The country’s major rivers are the Yangtze River, Yellow River, Heilongjiang River, Pearl River, Brahmaputra River, Lancang River, Tarim River, Nujiang River, etc.
The People’s Republic of China is so big that the climate varies from region to region. The northern regions of China (which includes the capital city Beijing) have hot and dry summers and freezing cold winters. Frequent bouts of rainfall take place in the northern and central regions of the country (which includes Chengdu). This is coupled with cold winters and hot summers. The climatic condition in the southeast is characterized by semi-tropical summers and cool winters. Lots of rainfall takes place in this area. The central, western, and southern regions of China are prone to flooding.
There are 6 temperature zones in the country they are Cold-temperate zone (Harbin), Warm-temperature Zone (Beijing), Temperature Zone (Xian), Subtropical Zone (Shanghai, Guangzhou, Chengdu, Hong Kong), Tropical Zone (Haikou), and Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Temperate Zone (Lhasa).
While July and August are the hottest months of the year, December and January are the coldest months. While the highest average temperature in China is 31 °C (88 °F), the lowest average temperature is -10 °C (14 °F). The average annual temperature of China is 11.8 °C (53 °F).
May-to-September is the usual rainy season. Based on the rainfall, the regions can be divided into 4 parts: dry, semi-dry, semi-wet, and wet areas. Spring (March and April) or autumn (September and October) are the best time to visit China.
The People’s Republic of China has grown over the years to become a global economic giant, the 2nd largest in terms of nominal GDP and the largest in terms of purchasing power parity. They follow a socialist market economy with the public sector accounting for a bigger share of the national economy along with a burgeoning private sector. 129 out of the 500 largest companies in the world are headquartered in China. In 2018, the Chinese economy grew at a rate of 6.6% to reach a nominal GDP of US$ 13.608 trillion. It has grown by an average of 9.49% in the last 30 years (1989-2019).
The major export items of China are phone system devices, computers & their parts/accessories, integrated circuits, processed petroleum oils, automobile parts/accessories, semiconductors, TV receivers/monitors/projectors, lamps, lighting, etc. In 2018, the country exported US$2.494 trillion in value goods. It is a 10.2% increase in 2018 over 2017.
The major imports of the People’s Republic of China are electrical machinery/equipment, mineral fuels, machinery, all kinds of apparatus (including medical, technical, and optical), vehicles, organic chemicals, ores, precious metals/gems, copper, etc. In 2018, the country imported a US$2.135 trillion value of goods. It is a 15.8% increase in 2018 over 2017. Therefore, this economic behemoth had a trade surplus of 0.359 trillion in 2018.
The annual unemployment rate in this country in 2018 was 3.8%, marginally less than 3.9% in 2017. Due to impressive economic and social development gains, China has drastically decreased the population of people living in poverty. The recent National Bureau of Statistics data shows that the rate of poverty in China dropped from 10.2% to 1.7% in the last 6 years (thereby lifting 82.39 million poor out of poverty). By the end of 2018, 16.6 million people were living below poverty in this country. In comparison to 2017, the poverty rate in China has dropped by 1.4% in 2018. Around 13.86 million people have been lifted out of poverty in 2018 vis-à-vis 2017.
It is on track of eliminating poverty (as per the current poverty standard of China which considers $416 per year or about US$1.10 per day as the poverty line instead of the World Bank’s poverty line of just under US$700 per year or US$1.90 per day) by 2020.
If the “upper middle income” international poverty line of US$5.50 per day is considered, there are around 373.1 million people living below this level.
China’s transportation system has improved dramatically in the last few decades. The main transport networks crisscrossing the country are airports, highways, trains, waterways, ports, and subways.
There are 507 airports in the country, out of which 463 have paved runways and 44 have unpaved runways. 1,279 air routes are there in the country, out of which 1,035 are domestic and 244 are international routes. The General Administration of Civil Aviation of China (CAAC) manages the air aviation industry.
The most reliable and popular airliners in this country are Air China Limited, Shanghai Airlines, Shandong Airlines, Shenzhen Airlines, Hainan Airlines, Southern Airlines, Xiamen Airlines, Sichuan Airlines, and Eastern Airlines. 47 heliports are also there in China.
Almost all the cities, towns, and countryside are connected by highways. There are 4,960,600 km (3,082,374 mi) long roadways available in the country. While 4,338,600 km (2,695,881 mi) is paved, 622,000 km (386,493 mi) is unpaved. 136,500 km (84,817 mi) of expressways are available in the country.
110,000 km (68,351 mi) long navigable waterways are available in China. It has 4,610 merchant marine ships. The major seaports are Shanghai, Qinhuangdao, Dalian, Qingdao, Ningbo, Tianjin, and Shenzhen. This country boasts of having 7 of the 10 largest container ports.
The railway transportation system is significantly developed in this Asian giant. There are 131,000 km (81,400 mi) of standard gauge train tracks, out of which 80,000 km (49,710 mi) is electrified. While 102,000 km (63,380 mi) is a traditional railway facility, 29,000 km (18,020 mi) is a high-speed railway.
WTO, IMF, UN, ADB, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, APEC, NSG, ARF, BIS, BRICS, CDB, CICA, EAS, FAO, FATF, G-20, G-5, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, OPCW, PCA, SCO, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, UNSC (permanent), PIF (partner), ASEAN (dialogue partner), ICC (national committees), AfDB (non-regional member), Arctic Council (observer), G-24 (observer), IOM (observer), LAIA (observer), NAM (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), SAARC (observer), OAS (observer), SICA (observer)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…