
Map of Pakistan which lies in the Continent of Asia
| Official Name | Islamic Republic of Pakistan |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Islamabad |
| Largest City | Karachi |
| Coordinates | 30.000000, 70.000000 |
| Area | 307,374 sq mi ( 796,095 sq km) |
| Land Boundaries | 4,237 mi ( 6,819 km) |
| Coastline | 650 mi ( 1,046 km) |
| Currency | Pakistani rupee (₨) (PKR) |
| Neighboring Countries | India, Afghanistan, Iran |
| Population | 212,742,631 (2017 census) |
| Official Languages | English, Urdu |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | 14 August (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Qaumi Tarana” |
| Form of Government | Federal parliamentary constitutional republic |
| President | Arif Alvi |
| Prime Minister | Imran Khan |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 5,543.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 1,472.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.562 (2017), Rank: 150 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | Pakistan Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 18 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 10 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | left |
| Calling Code | +92 |
| Time Zone | UTC+5 (PST) |
| Internet TLD | .pk |
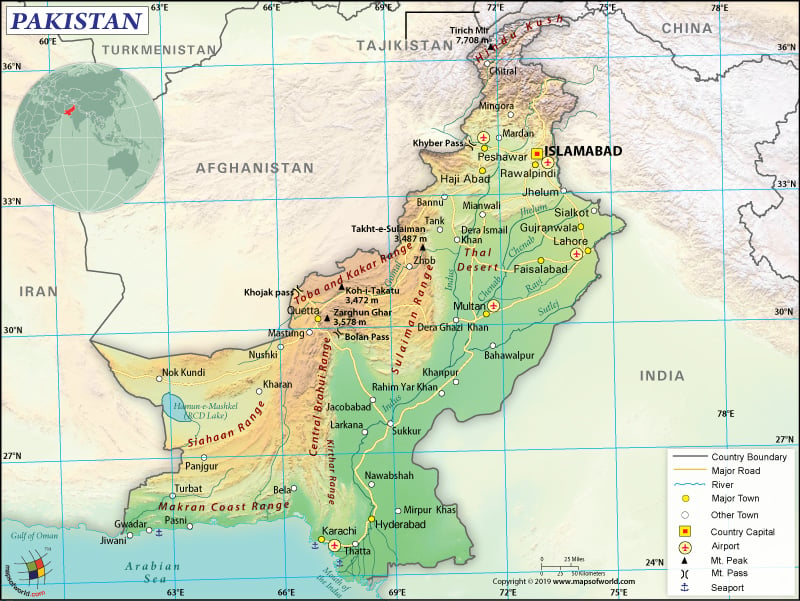
Pakistan is located in southern Asia, just above the tropic of Cancer. It is bordered to the south by the Arabian Sea, India to the east and north, and Iran and Afghanistan to the west.
To begin with, Pakistan is spread across a total area of 796,095 sq. km (307,374 sq. mi) (excluding the illegally occupied territories of India) out of which 770,875 sq. km (297,637 sq. mi) is land area and 25,220 sq. km (9,737 sq. mi) is water area. It shares a 6,819 km (4,237 mi) long border with 3 neighboring countries: India (3,190 km or 1,982 mi), Afghanistan (2,670 km or 1,659 mi), and Iran (959 km or 596 mi). Pakistan has a 1,046 km (650 mi) long coastline.
The average elevation of the country is 900 m (2953 ft). While the highest point is the K2 mountain at 8,611 m (28,251 ft), the lowest elevation point is the sea level at the Arabian Sea. Other major mountains in the country are Nanga Parbat, Gasherbrum I & II, Broad Peak, Broad Peak Central, etc. The most notable rivers are the Indus River, Chenab, Sutlej, and others.
Generally, there are 3 major geographical regions in Pakistan: the highlands in the northern parts of Pakistan, the Indus River plain in eastern and central Pakistan, and the Balochistan Plateau in western and southern Pakistan. The Thar Desert is located in the eastern parts of the country.
For instance, Karakoram, Pamir, and Hindu Kush mountain ranges (including the highest mountain peaks such as K2 and Nanga Parbat) are located in the northern highlands. The Indus River is 1,609 km (1,000 mi) long and its tributaries are the lifelines of Pakistan. In the Punjab and Sindh provinces, a large expanse of alluvial plains can be found.
Additionally, as Pakistan is located just above the tropic of Cancer, it comes within the temperate zone. The climatic conditions vary from tropical to temperate. In the coastal areas, arid climatic condition is prevalent. While the monsoon gets adequate rainfall, the dry season gets lesser rainfall.
Moreover, the extent of rainfall per year varies significantly (from less than 10 inches to more than 150 inches) in accordance with the various regions in Pakistan. While the coastal areas along the Arabian Sea generally remain warmer, the mountainous ranges (such as Karakoram Range having snow-capped ridges) in the far north remain cold throughout the year.
Therefore, 4 seasons are found in Pakistan. Winter season prevails from December to February. The temperature remains mild, characterized by a cool and dry climate. Spring season lasts from March to May. It is characterized by a hot and dry climate. The rainy season lasts from June to September, followed by the retreating monsoon from October to November.
In 2018, Pakistan’s nominal GDP was US$312.57 billion and it was growing at an annual rate of 5.43%. The accommodative fiscal and monetary policies have fuelled higher consumption, generating the requisite growth of the economy.
However, these policies have also widened the macroeconomic imbalances. In 2018, both the current account deficit and the fiscal deficit (excluding foreign grants) increased to 6.1% and 6.6% respectively. Exports have suffered while there is a steady increase in imports. This has led to an increased trade deficit. Also, the Pakistani Rupee’s cumulative depreciation during the period from July 2018 to March 2019 was 13.9%.
The service sector contributes 61.2% to the GDP, followed by the industrial (20.3%) and the agricultural (18.5%) sectors. However, the worrying feature is that around 37.4% of the labor force is still involved in agriculture, which is significantly more than that of the industrial sector (24%). Only 38.6% of the labor force is involved in services.
From July 2018 – January 2019, large-scale manufacturing (accounting for 65% of the total industrial output) has fallen by 2.3%. The unemployment rate was hovering around 5.7% in 2017-18. The country has reduced poverty significantly in the last decade (from 50.4% in 2005-06 to 24.3% in 2015-16). But, Pakistan’s Economic Survey 2018 has revealed that the extent of poverty reduction has been more prominent in urban areas than the rural ones.
The transport industry in Pakistan accounts for over 10% of the GDP. The most important transportation in the country is roadways. The total length of roadways is 263,775 km (163,902 mi), out of which only 185,063 km (114,993 mi) is paved (including expressways of 708 km or 440 mi). A substantial part of the roadways is still unpaved.
There are 151 airports available in Pakistan, out of which 108 have paved runways and 43 have unpaved runways. 23 heliports are also present. Only 11,881 km (7,383 mi) of railway tracks are there in Pakistan. While most of them are broad gauge (11,492 km or 7,141 mi), only 389 km (242 mi) are narrow gauge railway tracks. The country has two major seaports: Karachi and Port Muhammad Bin Qasim.
WTO, IMF, ADB, NAM, ARF, WHO, C, SAARC, CICA, ILO, CP, UN, D-8, ECO, UNESCO, FAO, UNCTAD, G-11, G-24, G-77, UNHCR, IAEA, IBRD, UNIDO, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, Interpol, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, OIC, OPCW, PCA, SACEP, UNAMID, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ASEAN (dialogue partner), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), SCO (observer), OAS (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…