
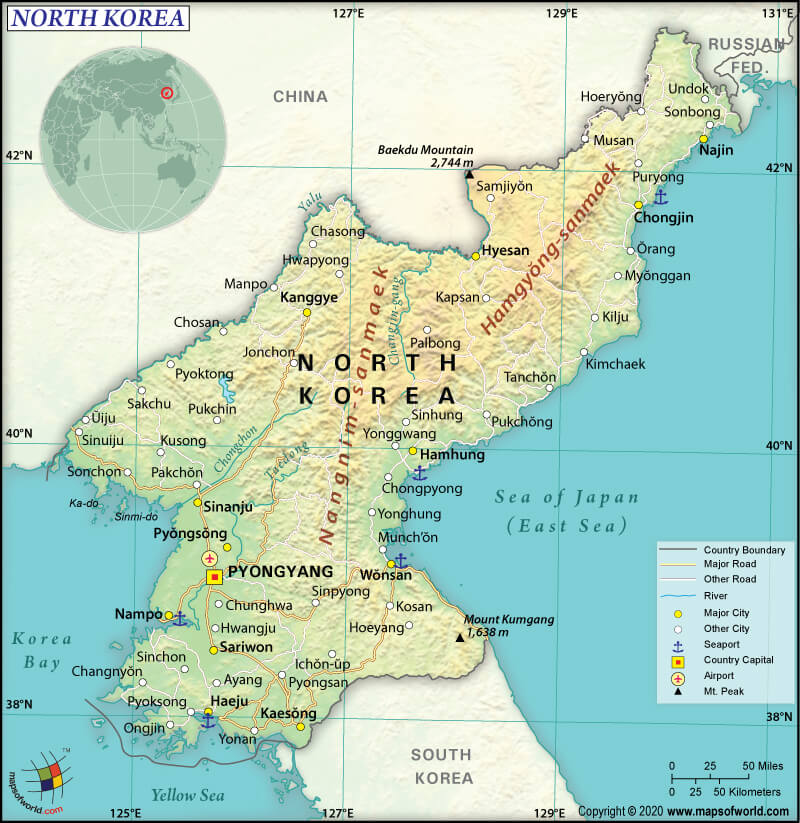
Map of North Korea which lies in the Continent of Asia
| Official Name | Democratic People’s Republic of Korea |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Pyongyang |
| Largest City | Pyongyang |
| Coordinates | 40.000000, 127.000000 |
| Area | 46,540 sq. mi (120,540 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 999 mi ( 1,607 km) |
| Coastline | 1,550 mi ( 2,495 km) |
| Currency | Korean People’s won (₩) (KPW) |
| Neighboring Countries | South Korea, China, Russia |
| Population | 25,368,620 (2016 est.) |
| Official Languages | Korean |
| Major Religion | Majority not religious |
| National Day | 15 August (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Aegukka” |
| Form of Government | Unitary one-party republic |
| Supreme Leader | Kim Jong-un |
| President of Assembly Presidium | Choe Ryong-hae |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | NA (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | NA (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | NA |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | National Aerospace Development Administration (NADA) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 56 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +850 |
| Time Zone | UTC+9 (Pyongyang Time) |
| Internet TLD | .kp |
North Korea is located in Eastern Asia, between China and South Korea. It occupies the Korean Peninsula’s northern half. It borders the Sea of Japan as well as the Korea Bay.
To begin with, North Korea is spread across a land area of 120,540 sq. km (46,540 sq. mi), out of which 120,408 sq. km (46,490 sq. mi) is land and the rest 130 sq. km (50 sq. mi) is water. It has a 1,607 km (999 mi) long land boundary and a coastline of 2,495 km (1,550 mi). North Korea shares its land boundaries with three countries: China (1,352 km or 840 mi) to the north, South Korea (237 km or 147 mi) to the south, and Russia (18 km or 11 mi) to the northeast.
Further, the North Korean landforms are mostly dominated by medium-sized mountain ranges as well as large hills that are separated by deep and narrow valleys. Wide coastal plains are present along the west coast. Narrow plains rise to the mountains along the coastline of the Sea of Japan. The western coastline of the country has many small islands.
Furthermore, the highest elevation point of North Korea is Paektu-san (2,744 m or 9,003 ft), which is situated on Baekdu volcanic mountain (located along the Chinese border in the north). The lowest elevation point of North Korea is sea level at the Sea of Japan. The mean elevation point of the country is 600 m (1,969 ft).
North Korea’s major mountains include Paektusan, Myohyangsan, Kumgangsan, Chilbosan, And Kuwolsan. Most important rivers of the country are Yalu, Tumen, Bukhan, Taedong, Imjin, Chongchon, and Changja.
Moreover, the climate of North Korea can be categorized as a combination of continental and oceanic climates. As per Köppen climate classification scheme, DPRK’s climate is considered as having a humid continental climate, where the summers remain warm and the winters remain cold and dry. The short rainy season is also there in the summer and it is known as ‘changma’.
Another key point is that winter season persists for a longer period of time and it is characterized by severe cold. The northern and northwestern winds blowing from Siberia lead to snowstorms in the country. Clear sky persists throughout the winter season. The northern, mountainous regions get the harshest winter. In January, the average daily high and low temperatures in the capital city Pyongyang remain −3 °C and −13 °C (27 °F and 9 °F) respectively.
The southern and southeastern monsoon winds bring in moist air from the Pacific Ocean, which causes the summer to remain humid, hot, rainy, and short. Besides winter and summer, there are two transitional seasons: spring and autumn. During these seasons, the weather remains pleasant. The temperature remains mild and the winds remain variable. In August, the average daily high and low temperatures in Pyongyang remains 29 °C and 20 °C (84 °F and 68 °F) respectively.
Most of the rainfall takes place during June-to-September. Typhoons affect the Korean peninsula regularly, especially during the summertime or in early autumn.
The North Korean economy is one of the most centralized and closed economies of the world. Since 2012, the economy has witnessed certain degree of liberalization. North Korea had a nominal GDP of US$17.36 billion in 2017. The GDP contracted by -4.10% in 2018.
Around 65% of the estimated 12.6 million labor force of DPRK is employed in the industrial and services sector. In terms of iron ore and coal production, North Korea is far ahead of its southern neighbor. Some of the major industries of the country are machine building, military equipment, textiles, metallurgy, mining, chemicals, tourism, and food processing.
As a matter of fact, most of the companies operating in the special economic zones and Special Administrative Regions of DPRK belong to China. Over 100 South Korean companies are working in the Kaesong Industrial Region SEZ, thereby employing around 52,000 North Korean workers. Over 80% of the external trade of the country takes place with China, followed by just over 3% trade with India.
While 43.4% of the total North Korean population is malnourished (as per the Global Hunger Index), 70% of the total population depends upon food aid.
Public transport is the lifeline of North Korea. The most important aspect of transport is that most of the road transport is electrically powered. The trolleybuses, subways, and tram lines are all electrified.
North Korea has 25,554 km (15,879 mi) of roadways, out of which only 724 km (450 mi) are paved and the rest 24,830 km (15,429 mi) are unpaved. 7,435 km (4,620 mi) of railways are also there in the country and all of them are standard gauge. There are 82 airports across DPRK. While 39 airports have paved runways, 43 have unpaved runways. 23 heliports are also there in the country.
The waterways are also moderately developed. Total 2,250 km (1,398 mi) of waterways are there in North Korea. The major seaports are Ch’ongjin, Hungnam, Haeju, Wonsan, Sonbong, Songnim, and Namp’o.
UN, WHO, ARF, FAO, UNESCO, G-77, WIPO, ICAO, UNCTAD, ICRM, UNIDO, IFAD, UNWTO, IFRCS, NAM, IHO, UPU, IMO, WMO, IMSO, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…