
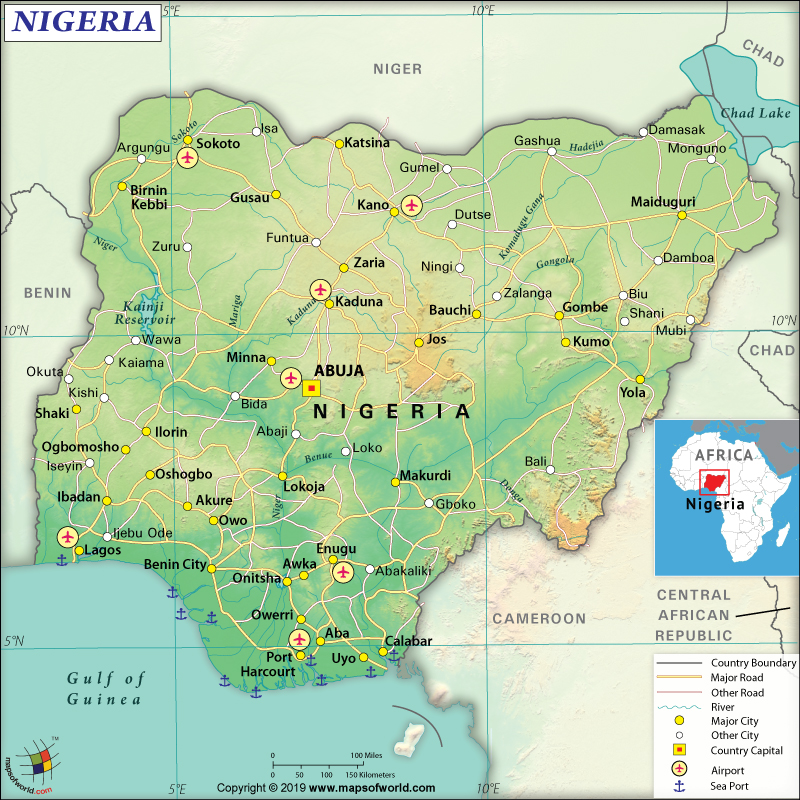
Map of Nigeria which lies in the Continent of Africa
| Official Name | Federal Republic of Nigeria |
| Continent | Africa |
| Capital | Abuja |
| Largest City | Lagos |
| Coordinates | 10.000000, 8.000000 |
| Area | 496,000 sq. mi ( 923,768 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 2,782 mi ( 4,477 km) |
| Coastline | 530 mi ( 853 km) landlocked |
| Currency | Naira (₦) (NGN) |
| Neighboring Countries | Cameroon, Chad, Niger, Benin |
| Population | 200,962,417 (2019 est.) |
| Official Languages | English |
| Major Religion | Islam and Christianity |
| National Day | 1 October (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Arise Oh Compatriots, Nigeria’s Call Obey” |
| Form of Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic |
| President | Muhammadu Buhari |
| Vice President | Yemi Osinbajo |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 5,980.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 2,028.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.532 (2017), Rank: 157 |
| Literacy Rate | 62.02 % (2018, UNESCO) |
| Space Agency | National Space Research and Development Agency |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 60 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 25 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +234 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1 (WAT) |
| Internet TLD | .ng |
Nigeria is a Western African country that borders the Gulf of Guinea between Cameroon and Benin.
Nigeria is spread across a total area of 923,768 sq. km (496,000 sq. mi), out of which 910,768 sq. km (351,649 sq. mi) is land area and the rest 13,000 sq. km (5,019 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 4,477 km (2,782 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with 4 countries: Cameroon (1,975 km or 1,227 mi) in the east, Niger (1,608 km or 999 mi) in the north, Benin (809 km or 503 mi) in the west, and Chad (85 km or 53 mi) in the northeast. The country has an 853 km (530 mi) long coastline along the Gulf of Guinea.
This Western African country has a mean elevation of 380 m (1,247 ft). While the highest elevation point is Chappal Waddi at 2,419 m (7,936 ft), the lowest elevation point is the Atlantic Ocean at 0 m (0 ft). The major mountains of Nigeria are Maisajeh Hill, Tsaunin Kura, Tsaunin Ukuru, Tsaunin Yeru, Tsaunin Mainono, etc.
There are 4 major drainage basins in Nigeria: The Niger River Basin Drainage System, The Lake Chad Inland Drainage System, The Atlantic Drainage System (east of the Niger), and The Atlantic Drainage System (west of the Niger). Some of the major rivers and tributaries of this country are Niger River, Ouémé River, Ogun River, Osun River, Oli River, etc. A part of the Lake Chad is available in Nigeria.
Nigeria has diverse landform. It includes southern lowlands, which merge with the hills at the center of the country as well as plateaus. While the mountains are located in the southeast part of the country, the plains are situated in the north. The southern coasts are characterized by swamps and mangrove forests. As one moves inland, there are more hardwood forests.
The most expansive region of the country is formed by the Niger and Benue River valleys. Hills and mountains punctuate the Mambilla Plateau. The vast savannah fills up the area between the far north and far south. In this savannah, there are three distinct zones and they are Sahel savannah, Sudan savannah, and the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic. The Sahel savannah is situated in the northeast where rain falls sparsely.
The climate in Nigeria is tropical. Based on the location, the climate remains variable rainy and dry. In the southeastern parts of the country, the weather remains predominantly hot and wet across the year. However, the climate becomes dry in the southwestern parts of the country or inland areas. The northern and western parts of Nigeria have a savanna climate, which has both marked wet and dry seasons. In the far northern parts, a steppe climate is found.
The Nigerian economy is the largest economy in Sub-Saharan Africa. In 2018, the nominal GDP grew at a rate of 1.9% (much higher than that of 0.8% in 2017) to US$397.270 billion. This West African country’s economy is mainly dependent upon oil product and export. 65% of the Nigerian government’s income comes from the country’s oil and gas sector.
The heavy reliance on petroleum has led the economy to a recession in 2016 due to a fall in international oil prices. With the rise in oil prices in 2017 followed by stabilization of output, the GDP growth became positive.
The World Bank has categorized Nigeria as a lower middle-income economy. However, the economy is plagued with a lack of infrastructure, inadequate power supply, restrictive trade policies, unreliable dispute resolution mechanisms, the ineffective judicial system, and high level of corruption.
The United States is the largest trading partner of the Nigerian economy. In fact, the US is the largest foreign investor in this Sub-Saharan African country. Besides oil, the other main industries of the country are construction, cement, beverages, food processing, textiles, apparels, etc. Nigeria is a trade surplus economy.
The National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) said that the unemployment rate during Q3 2018 (till the end of Sept’18) was 23.1%, which is 5% more than the 18.1% a year earlier. World Poverty Clock shows that in September 2019, over 94 million Nigerians live in extreme poverty. Reports say the economy should grow by around 5-6% rate for lifting people out of poverty.
Nigeria’s transportation system is mainly dependent upon roadways, railways, and moderately developed waterways. There is 195,000 km (121,167 mi) of roadways present in the country, out of which 60,000 km (37,282 mi) are paved and 135,000 km (83,885 mi) is unpaved.
In Nigeria, 3,798 km (2,360 mi) long railway tracks are there. While 3,505 km (2,178 mi) of tracks are narrow gauge, the rest 293 km (182 mi) are standard gauge. The airway facility is pretty developed too. There are 54 airports in the country, out of which 40 have paved runways and just 14 have unpaved ones. 5 heliports are also there.
8,600 km (5,344 mi) of waterways are there. Most of the waterways are concentrated in Niger and Benue Rivers. Waterway navigation also takes place in smaller rivers and creeks. The major seaports of the country are Bonny Inshore Terminal, Lagos, and Calabar. The country has 576 merchant marine ships.
WTO, IMF, UN, Interpol, UNESCO, ILO, NAM, ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, D-8, ECOWAS, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNITAR, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), EITI (compliant country), OAS (observer)
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…