What are the Key Facts of Montana?
|
State |
Montana |
|
State Capital |
Helena |
|
Largest City |
Billings |
|
Coordinates |
47°N 110°W |
|
Nickname(s) |
“Big Sky Country”, “The Treasure State” |
|
Postal Abbreviation |
MT |
|
Area |
147,040 sq. mi (380,800 sq. km) |
|
Highest Point |
Granite Peak, 12,807 ft (3,903.5 m) |
|
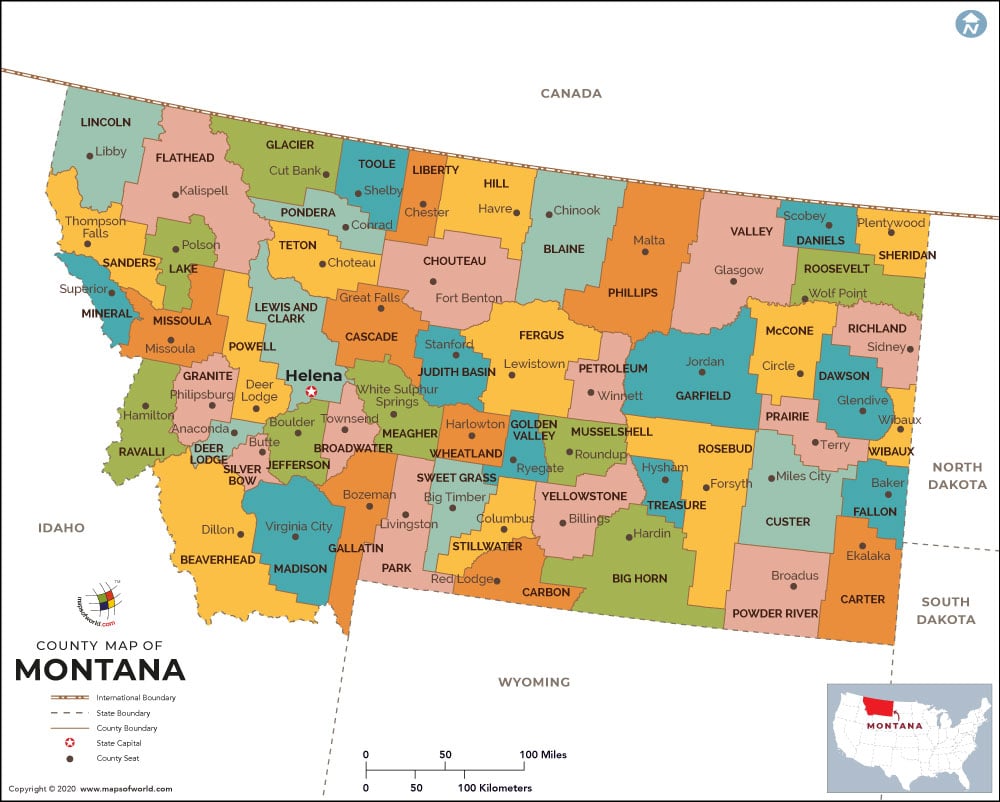
Number of Counties |
56 |
|
Neighboring States |
North Dakota, South Dakota, Wyoming, Idaho |
|
Population |
1,062,305 (2018) |
|
Date of Entering the Union |
November 8, 1889 |
|
State Anthem |
“Montana” |
|
Governor |
Steve Bullock (Democratic Party) |
|
Lieutenant Governor |
Mike Cooney (Democratic Party) |
|
U.S. Senators |
Jon Tester (Democratic Party), Steve Daines (Republican) |
|
U.S. House Delegation |
Jon Tester (Democratic Party), Steve Daines (Republican), Greg Gianforte (Republican) |
|
GDP (Millions of Dollars) |
50327 |
|
Demonym |
Montanan |
|
Time Zones |
UTC-07:00 (Mountain), Summer (DST) UTC-06:00 (MDT) |
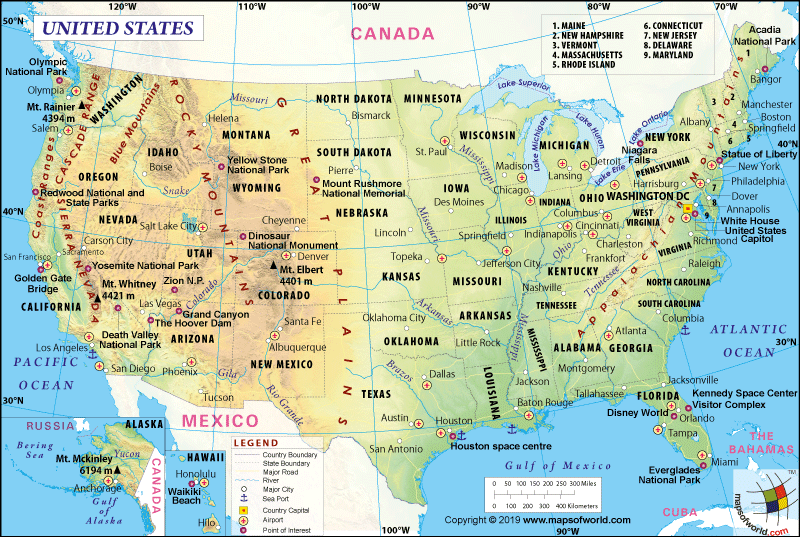
Where is Montana?
Montana (the 41st state that was admitted to the union on November 8, 1889) is located in the Northwestern USA. It is bordered by South Dakota and North Dakota (to the east), Wyoming (to the south), and Idaho (to the west), and three provinces of Canada (Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia) to the north.
What is the Geography of Montana?
Montana is spread across a total area of 147,040 sq. mi (380,800 sq. km), making it the fourth largest state among the 50 US states. The land area is spread across 145,552 sq. mi (376,980 sq. km), the water area is spread across 1,491 sq. mi (3,862 sq. km). Montana is around 559 mi (899.6 km) long from east-to-west and 321 mi (516.6 km) wide from north-to-south.
The mean elevation of Montana is 3,400 ft (1036.3 m) above sea level. Granite Peak is the highest elevation point in the state at 12,799 ft (3,901.1 m) above sea level, and the Kootenai River is the lowest elevation point at 1,800 ft (548.6 m) above sea level.
The major peaks and mountains in this state are Granite Peak, Granite Peak-Northwest Peak, Mount Wood, Mount Wood-West Peak, Castle Mountain, Castle Mountain-Northwest Peak, Whitetail Peak, Silver Run Peak, Castle Rock Spire, Silver Run Peak-East Peak, Tempest Mountain, Mount Peal, Castle Rock Mountain, Beartooth Mountain, Bowback Mountain, Mount Villard, Mount Wood-Northwest Peak, Mount Hague, Glacier Peak, and Mont Villard-West Peak. All of these peaks belong to the Beartooth Mountain range.
One per cent of the total area is occupied by the water bodies. The longest rivers in Montana are the Missouri River, Milk River, Yellowstone River, Kootenai River, Bighorn River, Powder River, Clark Fork, Musselshell River, Tongue River, and the Frenchman River. The major lakes in the state are Fort Peck Lake, Lake Koocanusa, Hungry Horse Reservoir, Canyon Ferry Lake, Flathead Lake, Hebgen Lake, Bowman Lake, Swan Lake, Ennis Lake, Mystic Lake, and Echo Lake.
Montana has a significant geographical, topographical, and altitudinal diversity. In general, the landforms can be divided into two parts: Eastern Montana (covering 3/5th of the state, mainly consisting of the Great Plains) and Western Montana (covering 2/5th of the state, mainly consisting of the Rocky Mountain Region).
The Great Plains consist of high, gently rolling landform that is interrupted by hills as well as broad river valleys. The badlands are found in southeast Montana, which is characterized by columns of varied colors (yellow, red, white, and brown) natural stones.
Western Montana consists of flat and grassy valleys. Trees such as pine, spruce, fir, and other evergreen plants cover the Rocky Mountain Region. The northern valleys (1-5 miles or 1.6-8 km wide) are narrower than the southern valleys (30-40 miles or 48.3-64.4 km wide). Clear, cold lakes are characteristic features of the Montana Rocky Mountains.
The Continental Divide passes through the Rocky Mountain Region in Montana. It separates waters that flow into the Pacific Ocean (to the west) and the Atlantic Ocean (to the east). The Missouri River system drains into the Gulf of Mexico, Columbia River system to the Pacific Ocean and three rivers (St. Marys, Bellys, and Waterton Rivers) to Hudson Bay.
What is the Climate of Montana?
Montana has a varied climate, thanks to the vast variation in landform, altitude, and geography. A semiarid, continental climate is found in the eastern part of the state.
The Continental Divide affects the climate considerably. The western side of the continental divide gets a modified northern Pacific Coast climate, which is characterized by cooler summers and milder winters. This area gets a longer growing season as well as less wind. During the winter season, the valleys in the western part of the divide get low clouds and fogs. This phenomenon is generally not found in the east.
While daytime average temperature revolves around 28 °F (−2.2 °C) in January, it remains 84.5 °F (29.2 °C) in July. Mountainous regions in the west and central parts of the state get snowfall in all months of the year. In the months of July and August, snowfall is rare in these areas.
Cold continental air coming from Canada usually brings cold spells in winter. It causes a significant drop in temperature within a period of 24-hours. Air flows from the southwest at a steady pace of 25-50 mph (40-80 km/h), which are called “Chinooks.” They can warm up some parts (especially east of the mountains in the state) and increase temperature up to 50-60 °F (10.0-15.6 °C) for ten days or more.
The yearly average precipitation level revolves around 15 inches (380 mm). Western Montana receives significantly more precipitation than the east. While the average precipitation level is around 34.70 inches (881 mm) in the west, the same in the eastern valleys is around 11-11.45 inches (279-291 mm). The mountainous areas receive more than 100 inches (2,500 mm) of precipitation. Heavy snowfall takes place during September-May with the heaviest being during November-March.
What is the Economy of Montana?
The economy of Montana is dependent mainly upon services, agriculture, energy production, mining, and forestry. Around 1/3rd of the total workforce in the state is employed in the service sector. The two most important industries in Montana that have become important are outdoor recreation and high-technology industries.
Some of the biggest cattle ranches are present in Montana and the most important livestock product is beef. Around 1/3rd of the total agricultural income of the state comes from crop production. The most important crops produced are wheat, barley, hay, sugar beets, potatoes, beans, and fruits (such as black cherries).
The total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for Montana in 2018 was US$50,326.6 million (a steady and significant increase from US$36,862.5 in 2008). The Per Capita Personal Income in the state dropped from US$35,253 to US$34,260 during 2008-2009 (especially because of the recessionary pull-downs). However, it has increased steadily over the years to reach US$47,538 in 2018.
Unlike many other states with frequent ups and downs, the Median Household Income in Montana has performed in a much steadier manner. During the 2007 recession, it fell from US$43,655 in 2007 to US$40,437 in 2009 and stagnated till 2011 (US$40,277). It started increasing in 2011 to reach US$57,679 in 2018.
The total value of exports and imports in 2018 was US$1,666,403,163 and US$4,692,715,002 respectively, resulting in a trade balance of -US$3,026,311,839. In terms of the total value of exports, imports, and trade balance, Montana’s ranking in 2018 was 47, 40, and 21 respectively.
The major items exported are Oil and Mineral Fuels, Tobacco, Inorganic Chemicals, Industrial Machinery, Natural Minerals and Stone, Precision Instruments, Vegetables, Pharmaceuticals, Motor Vehicles and Parts, and Live Animals. The major import items are Oil and Mineral Fuels, Precious Stones and Metals, Industrial Machinery, Wood, Electrical Machinery, Fertilizers, Motor Vehicles and Parts, Iron and Steel Articles and Organic Chemicals.
Montana’s economy had witnessed faster and stronger economic recovery during the 2007 recession than many other US states.
During the recession, the unemployment rate in the state more than doubled in three years. It increased from 3% in March 2007 to 7.4% in March 2010. The unemployment rate stagnated at that level for one year (until March 2011). After that, it started dropping rapidly and almost halved in 4-years (reached 4.1% in April 2015). Since then the unemployment rate has come down to 3.4% in November 2019 (marginally lower than national US average of 3.5%).
The poverty rate in Montana was 12.5% (127,777 people lived below the poverty line out of the total population of 1,024,513) in 2018. The rate of poverty is more severe among the Native Americans (34%), Asian Americans (19.6%), and Latino population (17.6%) than whites (10.6%) and African Americans (12.7%).
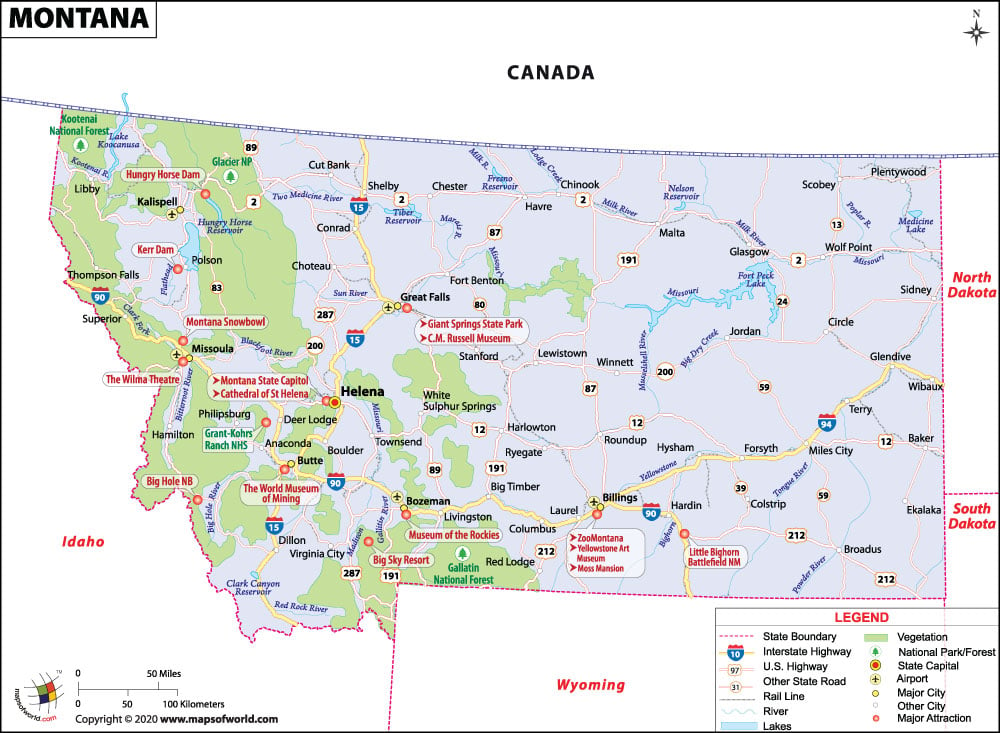
What is the Transportation System of Montana?
A wide array of travel forms is available in Montana. Many international crossings are found in this state (including one rail crossing and 13 road crossings) as Montana shares a long border with Canada. There is around 70,000 miles (112,654 km) of highways present in the state.
The most important interstate (mainline) highways are I-90, I-15, I-94, I-115, and I-315. Besides interstate highways, the Montana Department of Transportation (MDT) also maintains the U.S. Highways in the state. Some of the longest US highways that pass through Montana are US 2, US 12, US 87, US 10, US 191, US 89, US 212, etc. There is an extensive network of state highways too including MT 200, MT 3, MT 59, MT 16, MT 24, MT 13, MT 83 and MT 7.
The major airports in Montana are Bozeman Yellowstone International Airport (in Bozeman), Billings Logan International Airport (in Billings), Missoula International Airport (in Missoula), Glacier Park International Airport (in Kalispell), Great Falls International Airport (in Great Falls), Helena Regional Airport (in Helena), Bert Mooney Airport (in Butte), Yellowstone Airport (in West Yellowstone), Sidney–Richland Municipal Airport (in Sidney), L. M. Clayton Airport (in Wolf Point), Glasgow International Airport (in Glasgow), Dawson Community Airport (in Glendive) and Havre City-County Airport (in Havre).
The passenger rail services are provided by Amtrak. There are 12 railway stations inside Montana. The largest freight railroad transportation service is provided by BNSF Railway, operating around 1,983 miles (3,191 km) of track in the state.
Other common freight carriers are Butte, Anaconda and Pacific Railway (BAP), Central Montana Rail, Inc. (CM), Dakota, Missouri Valley and Western Railroad (DMVW), Mission Mountain Railroad (MMT), Montana Rail Link (MRL), Union Pacific Railroad (UP) and Yellowstone Valley Railroad (YSVR).
Why is Montana called the “The Treasure State?”
The most popular nickname of Montana is “The Treasure State.” It got this name because of its rich mineral reserves (including silver, copper, gold, sapphires, garnets, etc.). The abundant reserves of gold, silver, and other minerals were discovered in the mid-1800s. The standard license plates in Montana started featuring “The Treasure State” or “Treasure State” during 1950-66.
The other nicknames of the state are “Big Sky Country,” “Bonanza State,” “Land of Shining Mountains,” “The Last Best Place,” “The Stub-Toe State,” “The Headwaters State,” and “The Mountain State.”
What is the Origin of the Name of Montana?
Montana was created in 1864 after carving out a large chunk of a land area consisting a significant amount of mountainous terrains. The word “Montana” is derived from the Latinized Spanish word “montaanus,” which means mountainous.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Montana?
Glacier National Park, Little Bighorn Battlefield National Monument, Museum of the Rockies, Big Sky Resort, Helena, The C.M. Russell Museum Complex, The Grizzly and Wolf Discovery Center, The World Museum of Mining, Lewis and Clark Caverns State Park, The Moss Mansion, Gates of the Mountains Wilderness, and The Western Heritage Center to name a few.
Facts About Montana:
1) The state of Montana is nicknamed “The Treasure State” and “Big Sky Country”.
2) The capital city of Montana is Helena and the largest city is Billings.
3) The state encompasses a total area of 147,042 sq miles, which makes it the 4th biggest state of the country.
4) The state of MT was incorporated into the Union on November 8, 1889 and became the 41st state.
5) Montana is bordered by Canada, South Dakota, North Dakota, Idaho, and Wyoming.
6) The official flower is the Bitterroot.
7) The official motto is “Gold and Silver”.
8) The official bird is the Western Meadowlark.
9) The official anthem is “Montana”.
10) The official mammal is the Grizzly Bear.
11) The official butterfly is the Mourning Cloak.
12) Famous natives of the state include Gary Cooper and Martha Raye.
13) Mining and agriculture are two important industries in the state of Montana.
14) The official fish is the Blackspotted Cutthroat Trout.
15) Sited at a height of 12,807 feet, the tallest point in MT is the Granite Peak.
16) The state tree is the gigantic Ponderosa Pine.
17) The state houses various mineral and natural resources such as copper, silver, oil, gold, zinc, manganese, lead, and timber.
18) The variety of mammals found in the state is unparalleled.
19) Miles City is nicknamed as the Cowboy Capital of the World.
20) The official state gemstones are Agate and Yogo Sapphire.