What are the Key Facts of Mali?
-
Official Name
Republic of Mali
Continent
Africa
Capital
Bamako
Largest City
Bamako
Coordinates
17.000000, -4.000000
Area
478,841 sq. mi ( 1,240,192 sq. km)
Land Boundaries
4,914 mi ( 7,908 km)
Coastline
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked
Currency
West African CFA franc (XOF)
Neighboring Countries
Niger, Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, Algeria
Population
19,329,841 (2018 Census )
Official Languages
French
Major Religion
Islam
National Day
22 September (Independence Day)
National Anthem
“Le Mali”
Form of Government
Unitary semi-presidential republic
President
Ibrahim Boubacar Keïta
Prime Minister
Soumeylou Boubèye Maïga
GDP per capita (PPP)
$ 2,312.6 (World Bank, 2018)
GDP per capita (nominal)
$ 901.4 (World Bank, 2018)
HDI
0.427 (2017), Rank: 182
Literacy Rate (%)
35.47 (UNESCO, 2018)
Space Agency
NA
Military Expenditure Ranking
88 (SIPRI, 2017)
No. of Olympic Medals
0 (as of 2018)
Driving Side
right
Calling Code
+223
Time Zone
UTC+0 (GMT)
Internet TLD
.ml
Where is Mali?
Mali is a landlocked country, located in the interior of Western Africa. It is located in the north of Guinea, Burkina Faso, and Cote d’Ivoire; west of Niger; and southwest of Algeria.
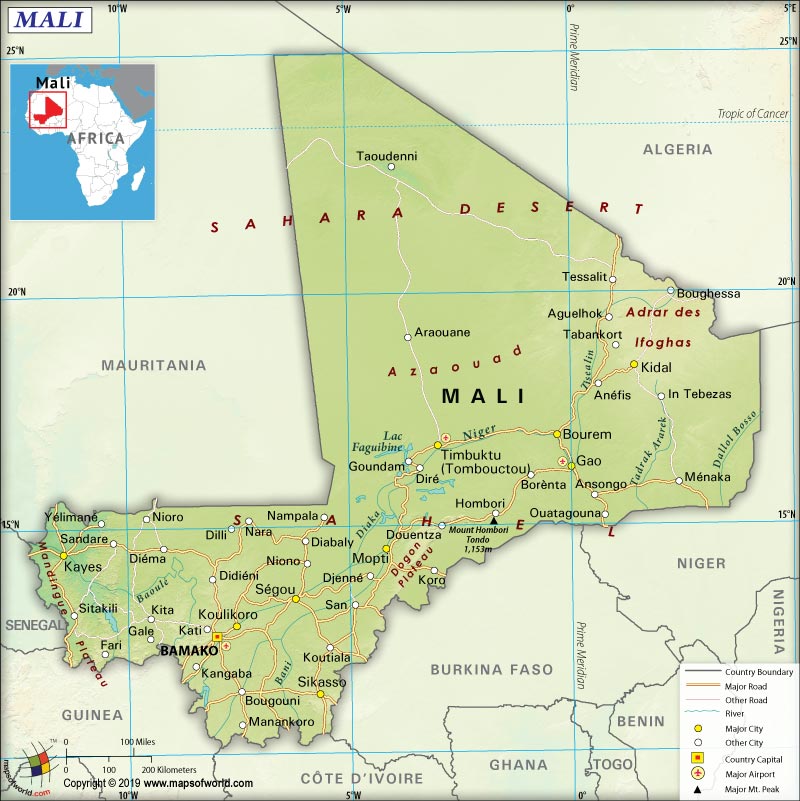
What is the Geography of Mali?
Mali is spread over a total area of 1,240,192 sq. km (478,841 sq. mi), out of which 1,220,190 sq. km (471,118 sq. mi) is land area and 20,002 sq. km (7,723 mi) is water area. This West African country has a 7,908 km (4,914 mi) long boundary. The border is shared with seven countries: Mauritania (2,236 km or 1,389 mi), Algeria (1,359 km or 844 mi), Burkina Faso (1,325 km or 823 mi), Guinea (1,062 km or 660 mi), Niger (838 km or 521 mi), Cote d’Ivoire (599 km or 372 mi), and Senegal (489 km or 304 mi). The country has no coastline as it is landlocked. Here is Mali Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
The major mountains of Mali are Hombori Tondo, Barkoussou, Kera, Tandarmi Tondo, etc. The two main rivers of Mali are Niger and the Sénégal. Other important water bodies of the country are Bara Issa, Issa Ber, Bafing, Bakoye Rivers, Gorgol River, and many more.
The significant part of Mali’s landscape is covered by savanna grassland. While moving to the northern direction, the grassland rolls into higher plateaus. The northeast region is dotted by the rugged hills having elevations of more than 1,000 m (3,280 ft). Desert or semi-desert covers around 65% of the country’s terrains.
While Hombori Tondo is the highest elevation point of the country at 1,155 m (3,789 ft), Senegal River is the lowest elevation point at 23 m (75 ft). The mean elevation of Mali is 343 m (1,125 ft).
There are three kinds of climatic conditions found in Mali: desert climate, semi-desert climate, and tropical climate.
The desert climate is mainly found in the northern parts of the country, where the Sahara desert is located. The vast northern area gets scorching hot summer. The winter season remains pleasant with the average temperature ranging from 15-to-20 °C (59-to-68 °F). The winter month also witnesses colder nights, sometimes reaching freezing point.
The central part of Mali gets a semi-arid climate, which is influenced by the climate of the Sahel desert. June-to-September is the rainy season in this part of the country. The extent of rainfall hovers within 100-to-600 mm (4-to-23.5 in) per year. The average temperature hovers around or remains above 20 °C (68 °F) in January. The temperature normally exceeds 40 °C (104 °F) during April-June, the hottest months in this region. Heavy downpour in the monsoon brings down the temperature by a few degrees.
The southern parts of Mali get the tropical climate, which is influenced by the savanna. This region gets more rainfall (over 600 mm or 23.5 in) per year and the rainy season continues from May to October. December-to-February is the best time to visit Mali.
What is the Economy of Mali?
Mali is among the 25 poorest nations in the world. For revenue, the economy is mainly dependent upon the gold mining and export of agricultural products. Around 80% of the export earnings of the country come from the export of gold and cotton. Another important component of the economy is foreign aid. In 2018, the nominal GDP of Mali was US$17,197 million and it grew at a rate of 4.9% (slower than the 5.4% growth rate of 2017).
The economy of Mali has a negative balance of trade. 2017 figures show that it exported US$2.31 billion worth of products and imported $4.56 billion worth of products. It gave rise to a negative trade balance of US$2.25 billion. The major export items are gold, prepared/raw cotton, bovine, sheep, and goats. The major import items are refined petroleum, cement, packaged medicaments, rice, and light pure woven cotton.
The unemployment rate has increased from 3.99% in 1998 to 9.57% in 2018. Mali is one of the poorest nations in the world. The UN’s Human Development Index shows that Mali ranked 182nd out of the 188 countries in 2018. Almost 90% of the people living in rural areas are poor. The incidence of poverty has increased due to the continued double whammy: drought and political conflict.
What is the Transportation System of Mali?
Mali has an extensive network of roadways, which is currently 139,107 km (86,437 mi) long. The country also has a significantly large extent of waterways. 1,800 km (1,118 mi) of roadway is present in the country. However, commercial vessels are not able to operate in the dry years and in the months just before the rainy season on the River Niger. Koulikoro is the major river port on the River Niger.
593 km (368 mi) long railway network is available in Mali. There are 25 airports present in the country, out of which 8 have paved runways and 17 have unpaved runways. Bamako’s Senou International Airport is the main airport of the country.
What International Organizations is Mali part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, Interpol, ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WAEMU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (compliant country), WADB (regional), WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs)
Related Link: