
Map of Lithuania
| Official Name | Republic of Lithuania |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Vilnius |
| Largest City | Vilnius |
| Coordinates | 56.000000, 24.000000 |
| Area | 25,200 sq. mi ( 65,300 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 978 mi ( 1,574 km) |
| Coastline | 56 mi ( 90 km) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Neighboring Countries | Belarus, Latvia, Poland, Russia |
| Population | 2,791,903 (2019 est. ) |
| Official Languages | Lithuanian |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 6 July (Statehood Day), 16 Feb (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Tautiska giesme” |
| Form of Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| President | Gitanas Nausėda |
| Prime Minister | Saulius Skvernelis |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 33,252.7 (World Bank, 2017) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 19,089.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.858 (2017), Rank: 35 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 72 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 25 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +370 |
| Time Zone | UTC+2 (EET), Summer (DST) UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Internet TLD | .lt |
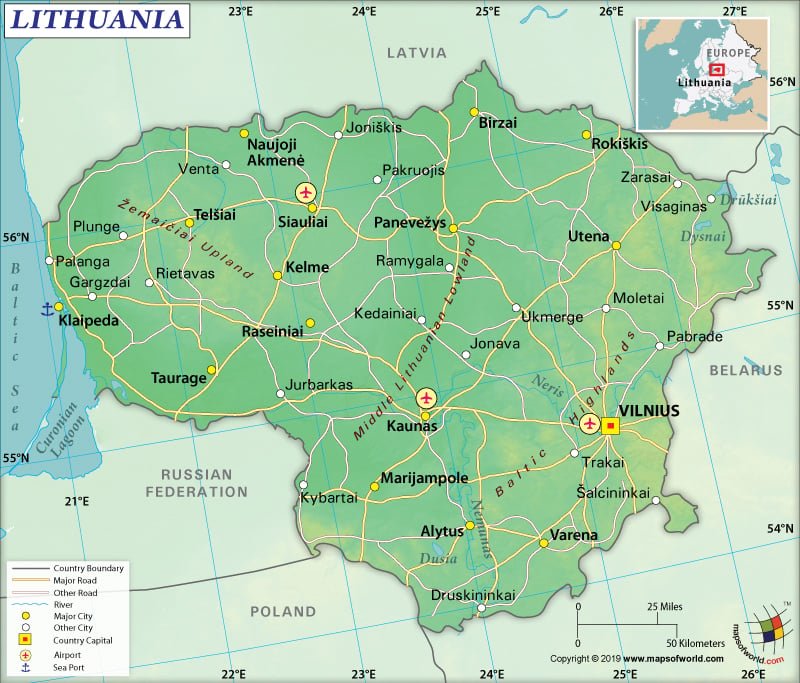
Lithuania is a European country located in the Baltic region. It is located along the Baltic Sea’s southeastern shore and in the east of Denmark and Sweden. Europe’s geographic center is located 26 km (16 mi) north of Vilnius (Lithuania’s capital city).
The country shares its borders with Russia’s Kaliningrad Oblast (261 km or 162 mi) to the southwest, Poland (104 km or 65 mi) to the south, Belarus (640 km or 398 mi) to the east and south, and Latvia (544 km or 338 mi) to the north.
Lithuania is spread over a total area of 65,300 sq. km (25,212 sq. mi). While 62,680 sq. km (24,201 sq. mi) is land area, 2,620 sq. km (1012 sq. mi) is water area. The total boundary of Lithuania is 1,549 km (963 mi). The sandy coastline is 90 km (56 mi) long. However, just 38 km (24 mi) face the Baltic Sea. Curonian sand peninsula shelters the rest of the coast.
At the north European plain’s edge, Lithuania is located. The last ice age’s glaciers have smoothed the landscape, which consists of both highlands and moderate lowlands. The terrain comprises mixed forest zone covers (covering more than 33% of the landforms) as well as numerous lakes and wetlands.
While the highest elevation point of the country is Aukstojas at 294 m (965 ft), the lowest point is the Baltic Sea. The mean elevation is 110 m (361 ft). Juozapinė Hill is the main mountain of Lithuania. Longest rivers of Lithuania are Nemunas, Neris, Venta River, Minija, Merkys, Šventoji, Šešupė, Nevėžis, etc. The largest, deepest, and longest lakes of the country are Drūkšiai, Tauragnas, and Asveja respectively.
Lithuania’s climate is relatively mild and ranges from maritime-to-continental. While in January, the average temperature hovers around −2.5 °C (27.5 °F), in July it remains around 16 °C (61 °F) in the coastal areas.
During summer, the average temperature remains around 20 °C (68 °F) in the daytime and 14 °C (57 °F) in the nighttime. However, a temperature as high as 30-35 °C (86-95 °F) is also not uncommon. During winter, −20 °C (−4 °F) temperature is common. However, extremely cold winter occurs mainly in the eastern and coastal areas of the country. While −34 °C (−29 °F) is the winter extreme in the coastal regions, the temperature may reach −43 °C (−45 °F) in eastern Lithuania.
The annual average rainfall in the Samogitia highlands, coastal regions, and eastern part of the country is 900 mm (35.4 in), 800 mm (31.5 in), and 600 mm (23.6 in) respectively. Snowfall is common in Lithuania, taking place during October-to-April. Sleet generally falls during September-to-May. Severe storms are common in the coastal areas of Lithuania but rare in the eastern parts.
Lithuania is a high-income economy. The services sector contributes 68.3% to the GDP, followed by the industrial (28.5%) and agricultural (3.3%) sectors. Around 74% of the GDP in Lithuania is generated by exports and the main export partners are EU, CIS, Russia, Poland, Latvia, Sweden, Estonia, and the UK. The main export items are foods/agricultural products, plastics & chemical products, mineral products, machinery & appliances, and wood & furniture.
An interesting feature of Lithuania is the flat tax rate. While income and corporate taxes are 15% each, the implicit capital tax rate is just 9.8% (which is the lowest in the European Union). There are seven Free Economic Zones. IT industry is growing by leaps and bounds, thanks to the simplified procedures to obtain e-money and payment institution. In fact, an international-level Blockchain Centre (the first of its kind in Europe) has been launched in Lithuania in 2018.
The nominal GDP of Lithuania in 2018 was US$53.251 billion and the economic growth rate was 3.49% (World Bank). The country is a member of NATO, Schengen, EU, and OECD. The unemployment rate of Lithuania was 6.01% in 2018, while more than 22% of the total population was estimated to be living in poverty in 2014 (World Bank data). Rapidly ageing population, emigration of skilled workers, and weak public spending efficiency in education and healthcare pose challenges for the economy.
Lithuania’s transport system is mainly based upon the networks of roads and rails. Transport is the 3rd largest sector in the economy of Lithuania.
Railways are spread over a total of 1,768 km (1,099 mi), out of which 1,746 km (1,085 mi) is broad gauge (only 122 km or 76 mi is electrified) and the rest (22 km or 14 mi) is a standard 1.435-m gauge. Railways are used predominantly (over half) for inland freight transport. The total network of roads available in Lithuania is 84,166 km (52,298 mi), out of which 72,297 km (44,923 mi) is paved and 11,869 km (7,375 mi) is unpaved. Just 312 km (194 mi) is an expressway.
There are 61 airports in the country, out of which 22 have paved runways and 39 have unpaved runways. Vilnius International Airport is the main airport, counted among the 100 largest airports of the European Union. Other important airports of Lithuania are Palanga International Airport, Kaunas International Airport, and Šiauliai International Airport.
441 km of waterways are also there and they can be navigated throughout the year. Klaipeda is the major seaport that not only serves the passengers but also acts as the main LNG terminal. Butinge is the main oil terminal of Lithuania. The merchant marine is also quite developed in the country. There are 61 such ships, out of which 28 are general cargo, 3 container ships, 2 oil tankers, and 28 others.
UN, WTO, WHO, Australia Group, BA, BIS, NSG, CBSS, IMF, CD, CE, EAPC, ILO, EBRD IMO,, ECB, EIB, EU, FAO, Interpol, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, UNESCO, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IOC, IOM, Schengen Convention, IPU, ISO, UNCTAD, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NIB, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), UN Security Council (non-permanent), ITUC (NGOs), OIF (observer), OAS (observer)
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…