What are the Key Facts of Lebanon?
| Official Name | Lebanese Republic |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Beirut |
| Largest City | Beirut |
| Coordinates | 33.833333, 35.833333 |
| Area | 4,036 sq mi (10,452 sq km) |
| Land Boundaries | 301 mi (484 km) |
| Coastline | 140 mi ( 225 km) |
| Currency | Lebanese pound (LBP) |
| Neighboring Countries | Syria, Israel |
| Population | 6,859,408 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | Arabic |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | 22 November (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Kulluna lil-watan” |
| Form of Government | Unitary confessionalist parliamentary republic[ |
| President | Michel Aoun |
| Prime Minister | Hassan Diab |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 13,058.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 8,269.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.757 (2017), Rank: 80 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 95.07 (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 53 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 4 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | 961 |
| Time Zone | UTC+2(EET), Summer (DST) UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Internet TLD | .lb |
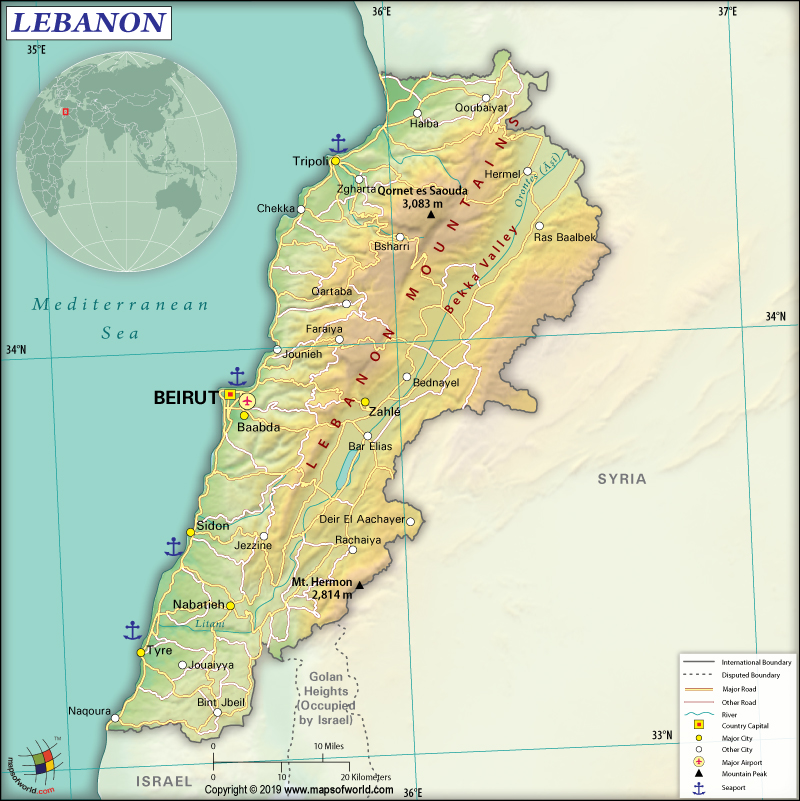
Where is Lebanon?
Lebanon is a Middle Eastern country that is located between Syria and Israel. It also borders the Mediterranean Sea. Lebanon shares its borders with Syria to the east and north, Cyprus to the west across the Mediterranean Sea, and Israel to the south.
What is the Geography of Lebanon?
Lebanon is the smallest country on the mainland Asian continent. It is spread across a total area of 10,400 sq km (4,015 sq mi), out of which 10,230 sq km (3,950 sq mi) is the land area and 170 sq km (66 sq mi) is water area. The Lebanese Republic has 484 km (301 mi) long land boundary, out of which 403 km (250 mi) is shared with Syria, and 81 km (50 mi) is shared with Israel. The country has a 225 km (140 mi) long coastline.
The Lebanese landscape consists of a narrow coastal plain: Bekaa Valley or El Beqaa separates Lebanon and Anti-Lebanon Mountains. The mean elevation of the country is 1,250 m (4,101 ft). While Qornet es Saouda at 3,088 m (10,131 ft) is the highest elevation point of the country, the lowest elevation point is the Mediterranean Sea at 0 m (0 ft).
Besides Qornet es Saouda, the other significant mountains in Lebanon are Tallet el Ouata, Tallet Ouâdi er Rjoûm, Er Rahal, Ez Znânîr, etc. Some of the most important rivers of the country are Litani, Beirut, Nahr-al-Kalb, Hasbani, Damour, Abraham, Zahrani, and many more.
There are four significant landforms in the country that run in parallel belts from the northern part to the southern part. These four major regions are Lebanon Mountains, the coastal strip, the Anti-Lebanon Mountains (located along the Syrian border), and the Bekaa Valley.
The peaks of the mountain are rocky and rugged. These peaks characteristically have green meadows and sparse forests containing cedars. The hills located inland come down sharply into the Beqaa Valley, which was formed by the tectonic plate. This valley is the Jordan Rift Valley’s northernmost extension.
The most popular landform of Lebanon is the Mediterranean coast having sandy beaches as well as amazing historical sites.
A Mediterranean climate prevails in Lebanon. This climatic condition is characterized by hot and short summers that continue for a long time of the year. The winters are cold and rainy. The climate prevails for a shorter period of time.
Lebanon has a unique location which influences its climate — located between the eastern Mediterranean area, which is humid and the African continent, which is arid. January is the coldest month of the year, having an average temperature of 5-10 °C (41-50 °F). August is the hottest month of the year, having an average temperature of 18-38 °C (64.4-100.4 °F).
A hot, dry southerly wind blows during summertime which increases the daily temperature to above 40 °C (104 °F). These winds are generally very strong and can also take the form of sandstorms. Most of the rainfall (around 70%) takes place during November-March. June-August is the rainless period.
What is the Economy of Lebanon?
Lebanon is a free market economy. It doesn’t restrict foreign investment but suffers from a wide range of economic impediments such as corruption, high taxes/tariffs/fees, complex customs procedures, arbitrary licensing decisions, inadequate IPR protection, and archaic legislation. Banking and tourism are the main growth sectors of the Lebanese economy.
In 2018, the nominal GDP of Lebanon increased by just 0.2% to reach US$56.639 billion. The main exports of the economy are computers, gold, jewellery, scrap copper/iron, etc. Major imports of Lebanon are cars, refined petroleum, raw iron bars, gold, packaged medicaments, etc. In 2017, Lebanon had a US$16.9 billion negative trade balance. While it exported $3.91 billion of goods, it imported $20.8 billion of goods.
The rate of unemployment in Lebanon was 6.20% in 2018. UNDP’s 2016 Rapid Poverty Assessment in Lebanon shows that 1/3rd of the population, translating to around 1.5 million individuals, lives in poverty (below US$4 per day).
What is the Transportation System of Lebanon?
The transportation system of Lebanon consists of both advanced Beirut International Airport and poor roadways. There is 21,705 km (13,487 mi) roadway in the country. Some of the major road networks are Beirut – Bhamdoun Al Mhatta – Chtaura – Masnaa, Beirut – Sidon – Sour – Naqoura, Beirut – Byblos – Tripoli – Aarida, Tripoli – Bcharre – Baalbek, Chtaura – Zahle – Baalbek – Qaa, etc. Frequent bus connections are there with neighbouring Syria. Service or taxis are top-rated too.
Just 401 km (249 mi) long railway network is available, out of which 319 km (198 mi) is standard-gauge and 82 km (51 mi) is narrow-gauge. However, none of them is operational because of the long-drawn wars during the 1980s and 2006.
Lebanon has eight airports and one heliport; the most significant of all is the Beirut Rafic Hariri International Airport. Other military airports of the country are Wujah Al Hajar Air Base, Rayak Air Base, and Rene Mouawad Air Base. Tripoli and Beirut are the major airports in Lebanon.
What International Organizations is Lebanon part of?
UN, NAM, WHO, ILO, UNESCO, IMF, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), WTO (observer), OAS (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Maps:

