What are the Key Facts of Kuwait?
|
Official Name |
State of Kuwait |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Kuwait City |
|
Largest City |
Kuwait City |
|
Coordinates |
29.500000, 45.750000 |
|
Area |
6,879 sq. mi (17,818 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
295 mi (475 km) |
|
Coastline |
310 mi (499 km) |
|
Currency |
Kuwaiti dinar (KWD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Iraq, Saudi Arabia. Maritime Neighbor: Iran |
|
Population |
4,207,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
25 February (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Al-Nasheed Al-Watani” |
|
Form of Government |
Constitutional monarchy (emirate) |
|
Emir |
Sabah Ahmad al-Sabah |
|
Prime Minister |
Sabah Khalid al-Sabah |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 51,912.0 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 32,032.0 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.808 (2019), Rank: 57 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
96.06 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
26 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
965 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.kw |
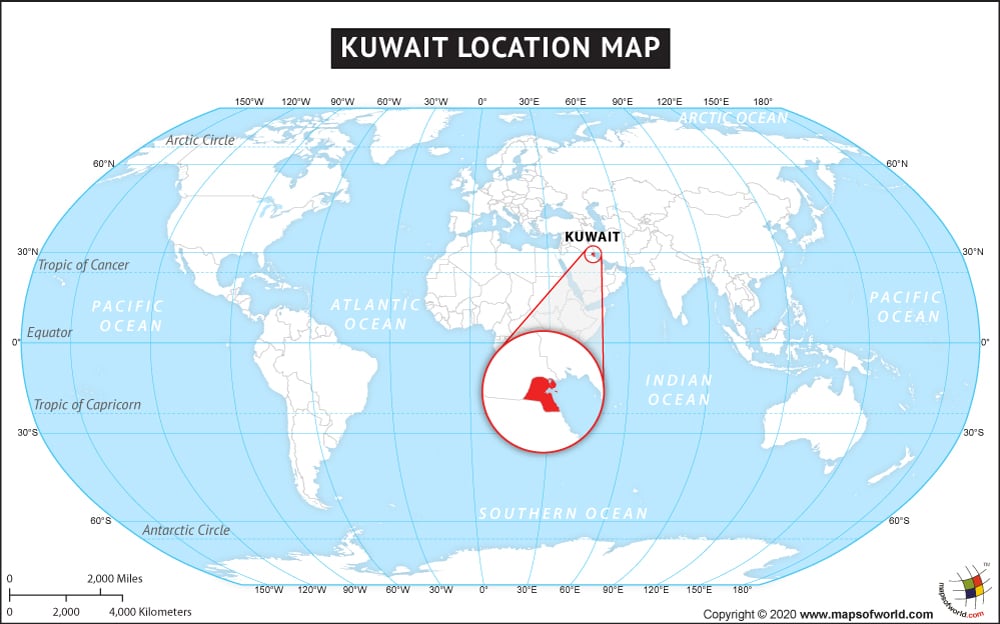
Where is Kuwait?
Kuwait (whose official name is the State of Kuwait) is a Western Asian country located in Eastern Arabia’s northern edge and at the tip of the Persian Gulf.
Flag of Kuwait
The flag of Kuwait is a rectangular flag, twice as long as it is wide, and is divided horizontally into three bands of green, white, and red from top to bottom. Along the left, or hoist side, a black trapezoid angles inward from the outer corners to the outsides of the white band, where it flattens. Each of the colours on the flag has a symbolic meaning, and together, they make up the pan-Arab colours, a combination of colours that are used throughout the Arab world.
What is the Geography of Kuwait?
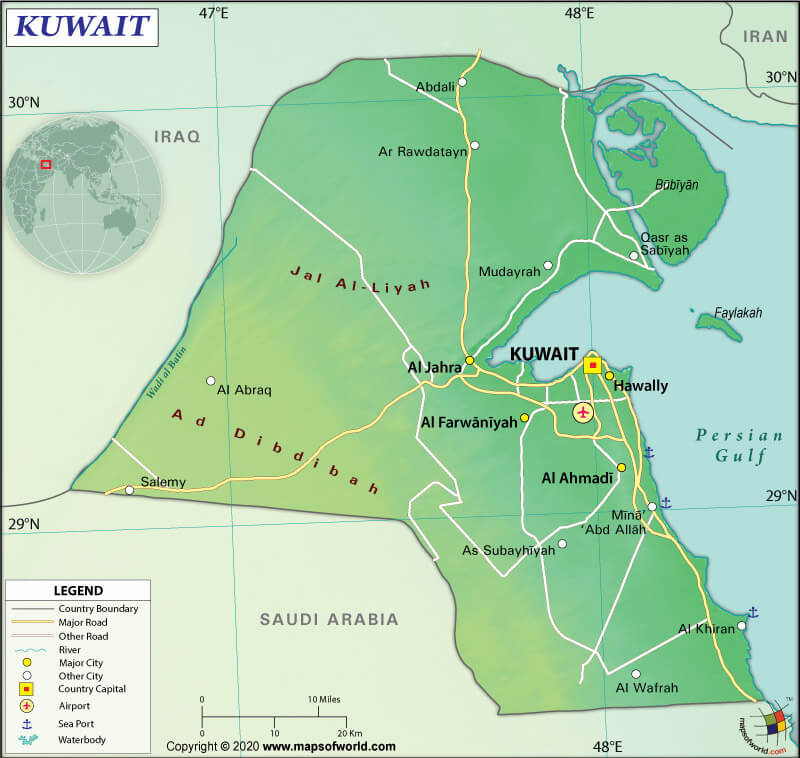
Kuwait spreads across a total area of 17,818 sq. km (6,879 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 17,818 sq. km (6,879 sq. mi) is land and 0 sq. km (0 sq. mi) is water.
The State of Kuwait’s total land boundary is .475 km (295.2 mi) long. It shares its border with Iraq (254 km or 157.8 mi) to the north and Saudi Arabia (221 km or 137.3 mi) to the south. The country has a 499 km (310.1 mi) long coastline.
The mean elevation of Kuwait is 108 m (67.1 ft). The highest point is an unnamed point at 300 m (984.3 ft). It is located 3.6 km (2.2 mi) to the west of Al-Salmi Border Post. The lowest point is the Persian Gulf at 0 m (0 ft).
The country has a flat to slightly undulating desert plain, mostly covered by flat and sandy Arabian Desert.
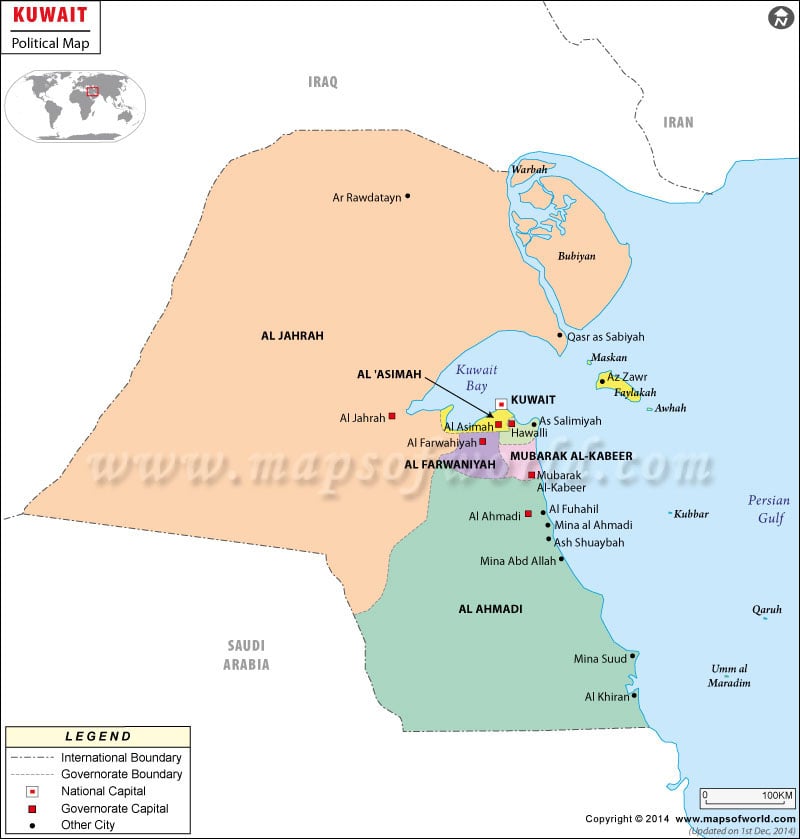
There are 9 islands in Kuwait: Bubiyan Island, Warbah Island, Failaka Island, Miskan Island, Umm an Namil Island, Auhah Island, Umm al Maradim Island, Kubbar Island, and Qaruh Island.
Bubiyan Island is the largest of them all with 860 sq. km (330 sq. mi) area. With the help of a 2,380 m long (7,808 ft) bridge, this island has been connected to Kuwait.
Just a minuscule land area (0.6% of the total land area) is considered arable. Vegetation is found only along the coastline. Kuwait City is located on a natural deep-water harbour, Kuwait Bay.
Jal Az-Zor is only one national park in Kuwait. Some of the major nature reserves in the country are Al-Khairan, Dawhat Al Zorq, Failaka island, Getty reef, Indies Rock, Jahra pool, Mud Flats, Naval Base reef, etc. Burgan field has a proven oil reserve of around 70 billion barrels (1.1×1010 m3) total capacity.
The highest mountains in Kuwait are Khashm Ghuḑayy, Al’ Awjah, and Jabal al Banāyā. There is no permanent river or lake in the country. Many wadis or desert basins in Kuwait get filled with water during the winter rains. The most important water bodies are Wadi al Batin (Kuwait River), Wadi al Batin (Kuwait River), Bahrat al Mirfi, etc.
What is the Climate of Kuwait?
The climate of the country can be characterized as arid. A huge temperature difference can be found between the summer and winter seasons.
The summer season in Kuwait lasts for an extended period of time, punctuated by dust storms. These northwesterly winds mainly blow during March-April, covering the cities in the sand. It remains more humid during late summer.
The daily high temperature in the country during the summer season ranges from 42 to 48 °C (108-118 °F). However, the highest ever temperature recorded in the country was 54.0 °C (129.2 °F) on July 21, 2016, at Meribah. This temperature is also the highest ever temperature recorded in Asia and the 3rd highest one in the world.
The hot weather gets over by October-end, and the colder winter weather starts to set in. During this time of the year, the temperature goes as low as −6 °C (21 °F) at night. However, during the daytime, the temperature hovers around 10–17 °C (50–63 °F). Brief but strong thunderstorms take place mainly during this time. As the temperature drops below 5 °C (41 °F), frost starts occurring.
Compared to other Persian Gulf countries (including UAE, Qatar, and Bahrain), the winter remains colder in Kuwait. This is mainly because of its location, which is in the farther north. Cold winds blow from upper Iraq and Iran, which also make the winter colder in the country.
Precipitation in the country usually takes place during October-April, mostly in November. The average annual rainfall varies within 75-150 mm (2.95-5.91 inches). However, a year’s actual rainfall ranges much more, right from 25 mm (0.98 inches) to 150 mm (2.95-5.91 inches).
What is the Economy of Kuwait?
The economy of Kuwait is a wealthy and relatively open economy. It is one of the richest countries in the world. Kuwait is heavily dependent on its oil export, which accounts for 92% of total export revenues, 90% of government income, and more than 50% of GDP.
Kuwait has a huge oil reserve, which is around 102 billion barrels (accounting for over 6% of the world’s total oil reserves). The officials of Kuwait plan to increase their oil production by 4 million barrels per day by 2020.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of the country increased by 0.412%, and it grew to US$134.761 billion. Kuwait’s export and import values in 2018 were US$63.6 billion and US$34 billion, respectively. It has a positive trade balance of US$29.6 billion.
Major export items are Crude Petroleum, Refined Petroleum, Petroleum Gas, Acyclic alcohol, and Cyclic Hydrocarbons. Major imports of the country are Cars, Broadcasting Equipment, Gold, Packaged Medicaments, and Jewellery.
The unemployment rate in this Middle Eastern country was 2.18% in 2019. No data on Kuwait’s poverty rate or poverty count is available to UNICEF, World Bank, or CIA World Factbook. However, a World Bank report says that Kuwait has “no extreme poverty and no forced unemployment.”
What is the Transportation System of Kuwait?
Kuwait has seven airports. While four have paved runways, 3 are unpaved runways. The major airports are Kuwait International Airport (Kuwait City), Ahmed Al Jaber Airport (Ahmed Al Jaber), Ali Al Salem Air Base, etc. There are four heliports in the country.
There are 5,749 km (3572.3 mi) long roadways available, out of which 4,887 km (3036.6 mi) are paved, and 862 km (535.6 mi) are unpaved. There is no railway in the country. Major seaports are Ash Shu’aybah, Mina’ al Ahmadi, Ash Shuwaykh, Mina’ ‘Abd Allah, and Az Zawr (Mina’ Sa’ud).
What are International Organizations in Kuwait Part of?
WTO, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, BDEAC, CAEU, CD, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, AfDB (nonregional member), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), Paris Club (associate), WFTU (NGOs), UN Security Council (temporary)
Related Maps: