What are the Key Facts of Honduras?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Honduras |
|
Continent |
North America |
|
Capital |
Tegucigalpa |
|
Largest City |
Tegucigalpa |
|
Coordinates |
15.000000, -86.500000 |
|
Area |
43,433 sq. mi (112,492 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
979 mi ( 1,575 km) |
|
Coastline |
511 mi ( 823 km) |
|
Currency |
Lempira (HNL) |
|
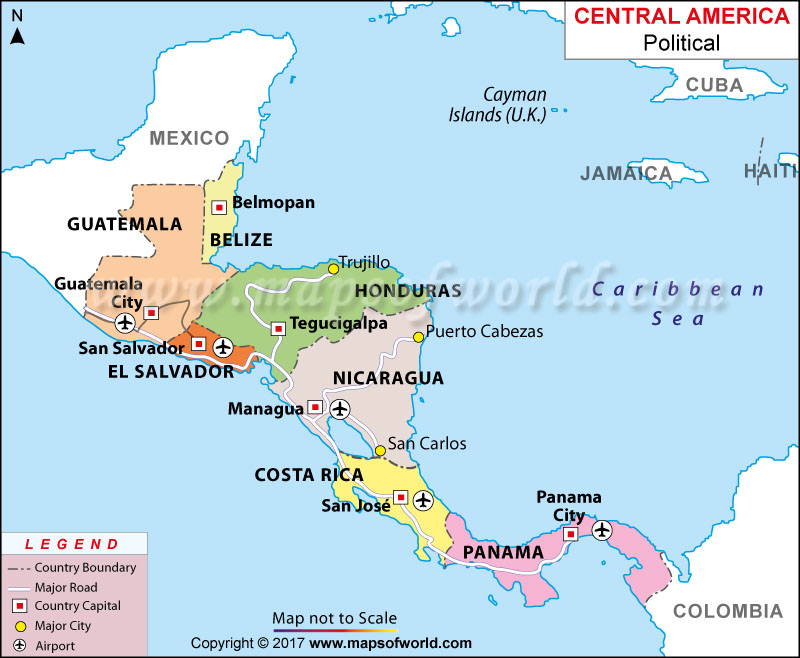
Neighboring Countries |
Guatemala, El Salvador, Nicaragua |
|
Population |
9,112,867 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
15 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Himno Nacional de Honduras” |
|
Form of Government |
Presidential republic |
|
President |
Juan Orlando Hernández |
|
Vice President |
Ricardo Álvarez Arias |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 5,129.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 2,482.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.617 (2017), Rank: 133 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
87.21 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
93 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+504 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−6 (CST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.hn |
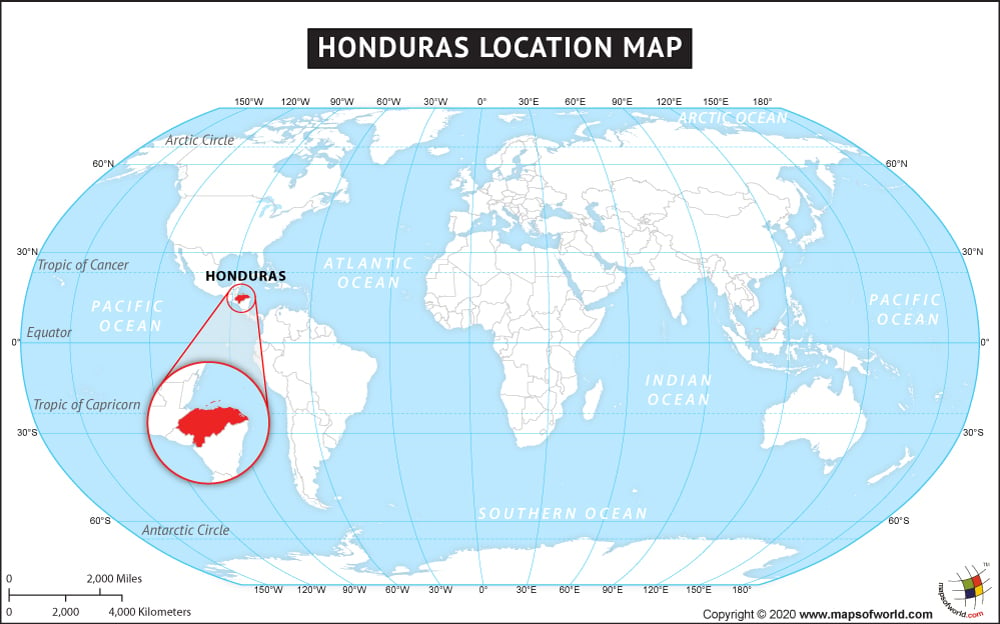
Where is Honduras?
Honduras is situated in Central America and borders both the Caribbean Sea as well as the Gulf of Fonseca.
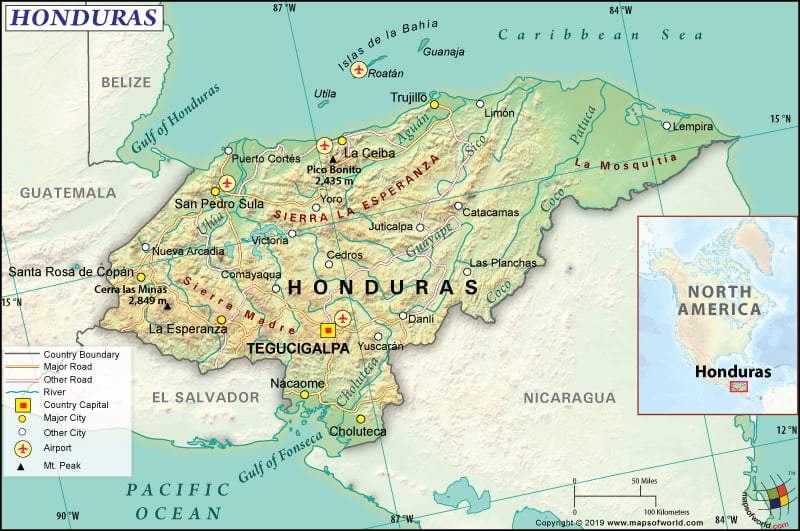
What is the Geography of Honduras?
Honduras is spread across a total area of 112,492 sq. km (43,433 sq. mi), out of which 111,890 sq. km (43,201 sq. mi) is land area and the rest 200 sq. km (77 sq. mi) is water area. It has 1,575 km (979 mi) long land boundary and 823 km (511 mi) long coastline (669 km or 416 mi with the Caribbean Sea and 163 km or 101 mi with the Gulf of Fonseca).
In the first place, Honduras shares its land boundaries with three neighboring countries: Nicaragua 940 km (584 mi), El Salvador 391 km (243 mi), and Guatemala 244 km (152 mi). This Central American country has a mean elevation of 684 m (2,244 ft). While Cerro Las Minas is the highest elevation point at 2,870 m (9,416 ft), the lowest elevation point is sea level at the Caribbean Sea. Other major mountains of Honduras are Cerro El Pital, Pico Bonito, Cerro El Aguacate, etc.
In addition, the terrain in Honduras consists of 3 major topographical regions. Most of the landscape is dominated by a vast plateau of hills and mountains in the interior. Other two topographical regions in the country are the Pacific lowlands located along the fringes of the Gulf of Fonsesca and the Caribbean lowlands.
Equally important, the interior hills are forested. A series of rivers and fertile valleys crisscross the Sierra Madre Mountains. The sandy beaches are located in front of the Sierra Madre Mountains. The entire northern coastline is covered by the Caribbean lowlands. A broad stretch of mangrove swamps, lagoons, and thick jungle is there in the Mosquito Coast. The Gulf of Fonseca is surrounded by the Pacific lowlands. Near the coast, the land becomes a bit swampy.
A wide array of islands and cays are present in the Caribbean Sea such as the Swan Islands, Isla de la Bahia, and Cayos Cocinos. Tigre and Zacate are dormant volcanic islands, which are located in the Gulf of Fonseca.
The most important rivers are Ulúa, Choluteca River, La Quebradona, etc. The only significant lake in the country is Yojoa. In the northeastern parts of the country, the Caratasca Lagoon is located.
While the lowlands have a subtropical climate, the mountain regions have temperate weather. The temperature in the mountain areas ranges from 16 ˚C (61 ˚F) to 20 ˚C (68 ˚F). The coastal areas in the north have a very hot climate. Rainfall takes place throughout the year. The climate is tempered by the offshore breezes and the sun shines strongly. While May-to-October is the wet season, November-to-April is the dry season in Honduras.
In contrast, the temperature at the Bay Islands varies from 24 ˚C (75 ˚F) to 34 ˚C (93 ˚F). In this island, rainy season persists from July-to-January. Maximum rainfall takes place from October-to-early-January. The temperature in the southern Pacific Coast ranges from 28 ˚C (82 ˚F)-to-32 ˚C (90 ˚F). The Caribbean hurricane season (January-to-June) mainly affects the Honduran mainland. Both the Caribbean coast of the country and the Bay Islands generally get the tail end of these hurricanes/tropical storms.
What is the Economy of Honduras?
As a matter of fact, Honduras is one of the poorest countries in the Central American region. It suffers from high levels of income inequality and underemployment. The economy is heavily dependent upon the trade with the USA and inward remittances.
Further, the main export items of the country are coffee, bananas, automobile wire harnessing, and apparel. After signing the US-Central America-Dominican Republic Free Trade Agreement, the FDI has increased. Around 15% of the total FDI in the country comes from the US alone. However, political insecurity, high rate of crime/corruption, and lack of personal security have restricted the adequate inflow of FDI in the country.
In 2018, the nominal GDP grew at 3.7% to reach US$23.803 billion. In 2017, it grew by 4.9%. The average unemployment rate during 1974-2018 was 5.11%. It was 5.7% in 2018. 2016 figures show that over 66% of the total population in Honduras lives in poverty. In fact, 1-out-of-5 persons in rural areas earn less than US$1.90 per day, which means that these people live in extreme poverty.
What is the Transportation System of Honduras?
Honduras has 14,742 km (9,160 mi) of roadways available in the country, out of which 3,367 km (2,092 mi) are paved and 11,375 km (7,068 mi) are unpaved. The coffee industry uses an additional stretch of 8,951 km (5,562 mi) roadways.
699 km (434 mi) of railway tracks are also available. 465 km (289 mi) of waterways are available too, which are most suitable for navigation by the small crafts. The major seaports of the country are La Ceiba, Tela, San Lorenzo, and Puerto Cortes. Honduras has 550 merchant marine ships. There are 103 airports available in Honduras, of which 13 have paved runways and 90 have unpaved runways.
What International Organizations is Honduras part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, BCIE, Petrocaribe, Union Latina, NAM, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMO, Interpol, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, SICA, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (candidate country), IOC (suspended), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), LAIA (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), ISO (subscriber), WCO (suspended)
Related Links: