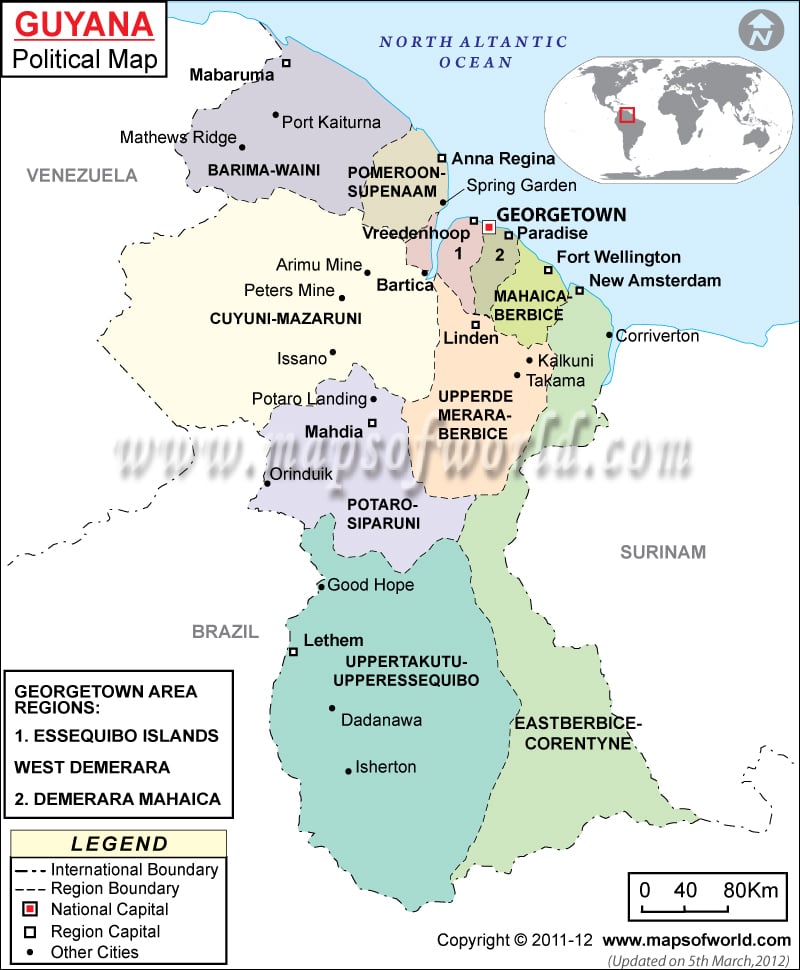
What are the Key Facts of Guyana?
|
Official Name |
Co-operative Republic of Guyana |
|
Continent |
South America |
|
Capital |
Georgetown |
|
Largest City |
Georgetown |
|
Coordinates |
5.000000, -59.000000 |
|
Area |
83,000 sq. mi (214,969 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,822 mi (2,933 km) |
|
Coastline |
285 mi (459 km) |
|
Currency |
Guyanese dollar (GYD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Brazil, Suriname, Venezuela. Maritime neighbors: Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago. |
|
Population |
782,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
English |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
23 February (Republic Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Dear Land of Guyana, of Rivers and Plains” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Mohamed Irfaan Ali |
|
First Vice President |
Mark Phillips |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 10,104.7 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 5,468.4 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.670 (2019), Rank: 123 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
85.03 (UNESCO, 2014) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
133 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
1 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
592 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC-4 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.gy |
Where is Guyana?
Guyana (whose official name is the Co-operative Republic of Guyana) is a South American country located on its northern mainland. For having strong cultural, historical, and political ties with other Anglo-Caribbean countries and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), Guyana is considered a part of the Caribbean region.
What is the Geography of Guyana?
Guyana spreads across a total area of 83,000 sq. mi (214,969 sq. km). Out of the total area, 76,003.8 sq. mi (196,849 sq. km) is land area, and 6996.2 sq. mi (18,120 sq. km) is the water area. In mainland South America, it is the 3rd smallest sovereign state after Uruguay and Suriname.
The Co-operative Republic of Guyana’s total land boundary is 1822.5 mi (2,933 km) long. It shares its border with Brazil (812.8 mi or 1308 km), the south and southwest, Suriname (519.5 mi or 836 km) to the east, and Venezuela (490.3 mi or 789 km) to the west. Guyana shares its border with the Atlantic Ocean to the north. The country has a 285.2 mi (459 km) long coastline.
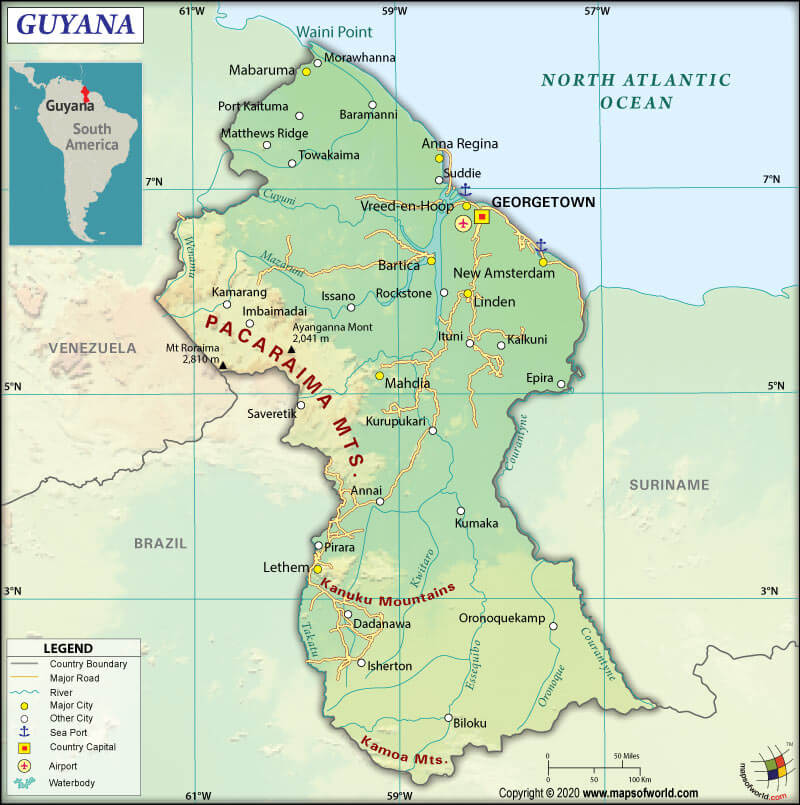
The mean elevation of Guyana is 679.1 ft (207 m). While the highest point is Laberintos del Norte on Mount Roraima at 9104.3 ft (2,775 m), the lowest point is the Atlantic Ocean at 0 ft (0 m).
Guyana’s terrain mainly consists of rolling highlands, low coastal plain, and savanna in the south. The coastal plain occupies around 5% of the country’s total area, but more than 90% of the population lives in this region. This plain is 3.1-3.7 mi (5-6 km) wide, extending from the Courantyne River in the east to the Venezuelan border in the northwest. A barrier of swamps separates the coastal plain and the white sandy hills in the interior region.
To the south of the coastal zone, a belt of white sand is located. This belt is around 93.2-155.3 mi (150-250 km) wide, consisting of low sandy hills interspersed with rocky outcroppings. The white sands support a dense hardwood forest. The abundant reserves of bauxite, gold, and diamond are found in this belt of white sands.
The interior highlands are the most significant part of Guyana. It includes a series of plateaus, flat-topped mountains, and savannahs, extending to the southern borders from the belt of white sands.
The interior highlands’ western part is dominated by the Pakaraima Mountains, where you will find some of the oldest sedimentary rocks in the Western Hemisphere. The tallest peak in Guyana, Mount Roraima, is located in this region.
A broad, rocky area with an elevation of around 1968.5 feet (600 meters), known as the Kaieteur Plateau, is located farther south. On the southern border with Brazil, the low lying Acarai Mountains and 3280.8 ft (1,000-meter) high Kanuku Mountains are situated.
You’ll find grassland, mainly in the interior highlands. The Rupununi Savannah (covering around 9320.6 sq mi or 15,000 sq km), the largest expanse of grassland, is located in southern Guyana.
The Kanuku Mountains split Guyana into northern and southern regions. In the foothills of the Kanuku Mountains and along the Rupununi River, the Amerindian groups carry out cultivation work.
Guyana has 156 mountains, and they are mainly found in the highland regions such as Upper Takutu-Upper Essequibo (52 peaks), Potaro-Siparuni (45 peaks), and Cuyuni-Mazaruni (57 peaks).
The highest mountains are Mount Roraima, Maringma Tepui, Appakaima Mountain, Mount Kukenaam, Morakabang Mountain, etc. While Essequibo River is the longest river, Mainstay Lake is the largest lake in Guyana.
What is the Climate of Guyana?
Guyana has an equatorial lowland climate. Characteristic features of this climate are high temperatures, heavy rainfall with small seasonal differences, high humidity, and high average cloud.
The entire country gets a uniform temperature. The average daily temperature in Georgetown remains within the mid-70s °F and mid-80s °F (mid-to-upper 20s °C). The trade winds near the coastal areas mitigate constant heat and high humidity.
The movement of the intertropical front or doldrums (heavy mainly in the coastal and plateau regions) affects rainfall. The average yearly rainfall varies from 70 inches (1,800 mm) in the interior Rupununi Savanna to 90 inches (2,290 mm) in Georgetown.
There are two wet seasons in Guyana. While the longer one is during April-August, the shorter one is during December-early-February. However, the shorter wet season doesn’t occur in the southern savannas.
Especially when the southeast trade winds parallel the coast, seasonal drought occurs in July and August. Tropical crop production is determined by the variations in the climatic patterns of Guyana.
What is the Economy of Guyana?
The economy of Guyana is mainly dependent upon agriculture and extractive industries. It has seen moderate economic growth in recent years.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Guyana increased by 4.696% to US$4.28 billion. Guyana’s export and import values in 2018 were US$1.72 billion and US$3.99 billion, respectively. It had a negative trade balance of -US$2.26 billion in 2018.
Major export items are Gold, Aluminium Ore, Railway Cargo Containers, Rice, and Raw Sugar. Significant imports of Guyana are Special Purpose Ships, Refined Petroleum, Excavation Machinery, Industrial Fatty Acids, Oils and Alcohols, and Planes, Helicopters, and Spacecraft.
The unemployment rate in this South American country was 11.85% in 2019. 35% of the population in Guyana lives below the poverty line.
What is the Transportation System of Guyana?
Guyana has 117 airports. While 11 have paved runways, 106 have unpaved runways. The major airports of Guyana are Cheddi Jagan International Airport (Georgetown), Eugene F. Correia International Airport (Georgetown/Ogle), Kaieteur International Airport (Kaieteur National Park), etc.
There is 2482.4 mi (3,995 km) long roadways available, out of which 496.5 mi (799 km) are paved, and 1985.9 mi (3,196 km) are unpaved. Waterways are around 205 mi (330 km) long (mainly on Berbice, Demerara, and Essequibo Rivers). Georgetown is the principal seaport. There are 56 merchant marine vessels.
What International Organizations is Guyana Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, UNESCO, ILO, ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ISO (correspondent), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Maps: