
Map of Guinea which lies in the Continent of Africa
| Official Name | Republic of Guinea |
| Continent | Africa |
| Capital | Conakry |
| Largest City | Conakry |
| Coordinates | 11.000000, -10.000000 |
| Area | 94,926 sq. mi (245,857 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 2,514 mi (4,046 km) |
| Coastline | 199 mi (320 km) |
| Currency | Guinean franc (GNF) |
| Neighboring Countries | Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Senegal, Sierra Leone |
| Population | 12,771,250 (World Bank, 2019) |
| Official Languages | French |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | 2 October (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Liberte” |
| Form of Government | Presidential republic |
| President | Alpha Condé |
| Vice-President | Ibrahima Kassory Fofana |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 2,670.3 (World Bank, 2019) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 1,064.1 (World Bank, 2019) |
| HDI | 0.466 (2019), Rank: 174 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 32.00 (UNESCO, 2014) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 111 (SIPRI, 2019) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 0 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | 224 |
| Time Zone | UTC (GMT) |
| Internet TLD | .gn |
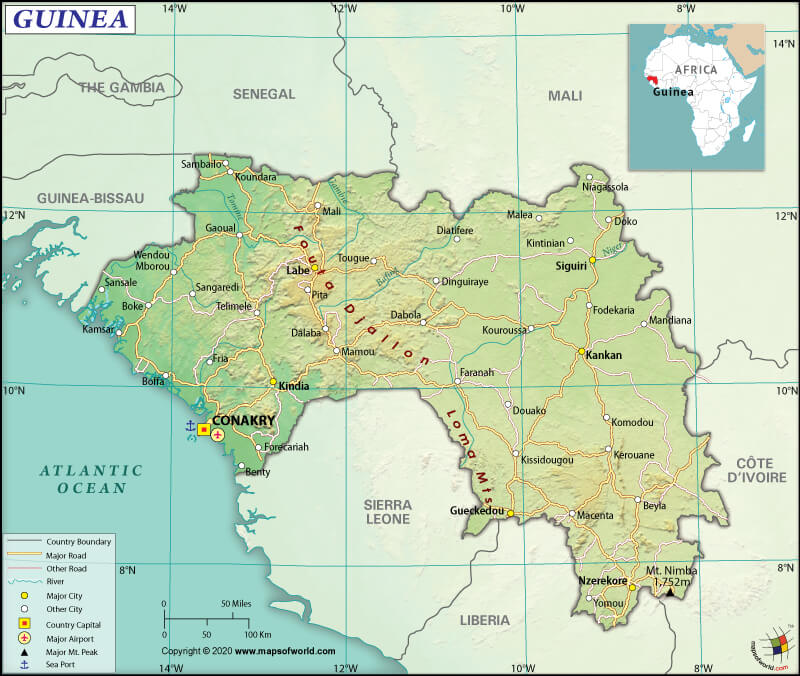
Guinea (whose official name is the Republic of Guinea and formerly known as French Guinea) is a West African country located between Guinea-Bissau and Sierra Leone, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean.
As “Guinea” is the eponymous region, many other countries in that region also share the name such as Guinea-Bissau and Equatorial Guinea. That’s why Guinea is also called Guinea-Conakry to distinguish it from other countries and the name of the eponymous region.
Guinea spreads across a total area of 245,857 sq. km (94,926 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 245,717 sq. km (94,872 sq. mi) is land and 140 sq. km (54 sq. mi) is water.
The total land boundary of Guinea is 4,046 km (2,514.1 mi) long. Guinea shares its borders with 6 countries: Mali (1,062 km or 659.9 mi) to the north-east, Cote d’Ivoire or Ivory Coast (816 km or 507 mi) to the east, Sierra Leone (794 km or 493.4 mi) to the south-west, Liberia (590 km or 366.6 mi) to the south, Guinea-Bissau (421 km or 261.6 mi) to the north-west, and Senegal (363 km or 225.6 mi) to the north.
Guinea has a 320 km (198.8 mi) long coastline coast. The North Atlantic Ocean borders the country along the southwestern coast. The mean elevation of the country is 472 m (1,548.6 ft). While the highest point is Mont Nimba at 1,752 m (5,748 ft), the lowest point is the Atlantic Ocean at 0 m (0 ft).
Guinea’s terrain is characterized by flat coastal plain and hilly-to-mountainous landforms in the interior. There are four geographic regions in the country: Guinea Highlands, Upper Guinea, the Fouta Djallon, and Lower Guinea.
To the northeast of Conakry Mount, Kakoulima Massif is located. Its height is around 998 m (3,273 ft). Tamgué is the highest elevation point in the Fouta Djallon highlands with 1,538 m (5,046 ft).
Guinea’s highest mountains are Mont Nimba, Mount Kakulima, Kambo, Belakaniaré, Bonkoui, and many more.
Guinea is the origination point of more than twenty rivers in West Africa. Some of the country’s major rivers are the Niger River, Bafing, Bakoye, Gambia River, Sankarani, Milo, Tinkisso, Konkouré, Fatala, Kolenté, Saint Paul River, Moa River, Rio Nunez, and others.
A tropical climate is found in Guinea. While it remains dry during the winter season, it receives lots of rainfall during the summer season due to the south-west monsoon. The coastal region gets annual precipitation of around 4,000 mm (155 in).
In the capital city, Conakry (located in the coastal area), the rainy season lasts from May to November. However, the cities in the east, such as Kankan, receive rainfall from May to October.
The winter season starts in December and continues till February. It remains predominantly hot, dry, and sunny. Harmattan, a north-east wind, blows during the winters. This wind blows from the desert and carries dust and sand particles. The average maximum temperature during winter season hovers around 90-93 °F (32-34 °C). However, it can peak at 104 °F (40 °C).
The southern region of Guinea receives the first showers. However, the heat gets more intense in the central and northern parts of the country. During the spring season, the ocean breeze and higher altitude in the south-central inland areas mitigate the coastal regions’ temperature.
Guinea’s economy is dependent mainly on agriculture and mining of natural resources (such as bauxite, high-grade iron ore, diamonds, and gold). US Geological Survey’s estimate says that the country houses around 1/4th of the world’s total bauxite reserves. There is considerable potential for growth in agriculture, fishing, and uranium mining.
The unfavorable factors restricting Guinea to grow at its full potential are political instability, consistently high level of corruption over the years, lack of government transparency, inefficiency, low international commodity prices, and the Ebola virus epidemic.
The nominal GDP of Guinea grew at an annual rate of 5.577% to US$13.59 billion in 2019. The export and import values of the country in 2018 were US$5.77 billion and US$4.26 billion, respectively.
The major exports are Gold, Aluminium Ore, Petroleum Gas, Aluminum Oxide, and Non-fillet Frozen Fish. Guinea’s major imports are Rice, Refined Petroleum, Packaged Medicaments, Rolled Tobacco, and Rubber Footwear.
The unemployment rate increased from 4.2% in 2018 to 4.3% in 2019. The poverty rate in Guinea is around 55% even though the country has the highest per capita income in the African continent. Around 20% of the population lives in extreme poverty.
Guinea has 16 airports, out of which 12 have paved runways, and 4 have unpaved runways. Major airports are Conakry International Airport (Conakry), Faranah Airport (Faranah), Tata Airport (Labe), etc.
The total roadways in Guinea are 44,301 km (27,527.7 mi) long, out of which 3,346 km (2079.1 mi) is paved, and the rest 40,955 km (25448.3 mi) is unpaved. Guinea has 1,086 km (674.8 mi) long railways, out of which 279 km (292.7 mi) is a standard gauge and 807 km (501.4 mi) is a narrow gauge.
1,300 km (807.8 mi) long navigable waterway is present in Guinea. The major seaports are Conakry and Kamsar. There are just two merchant marine vessels in Guinea.
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, ILO, UNESCO, ACP, AfDB, AU, ECOWAS, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WIPO, WMO, EITI (compliant country), ISO (correspondent), ITUC (NGOs)
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…