
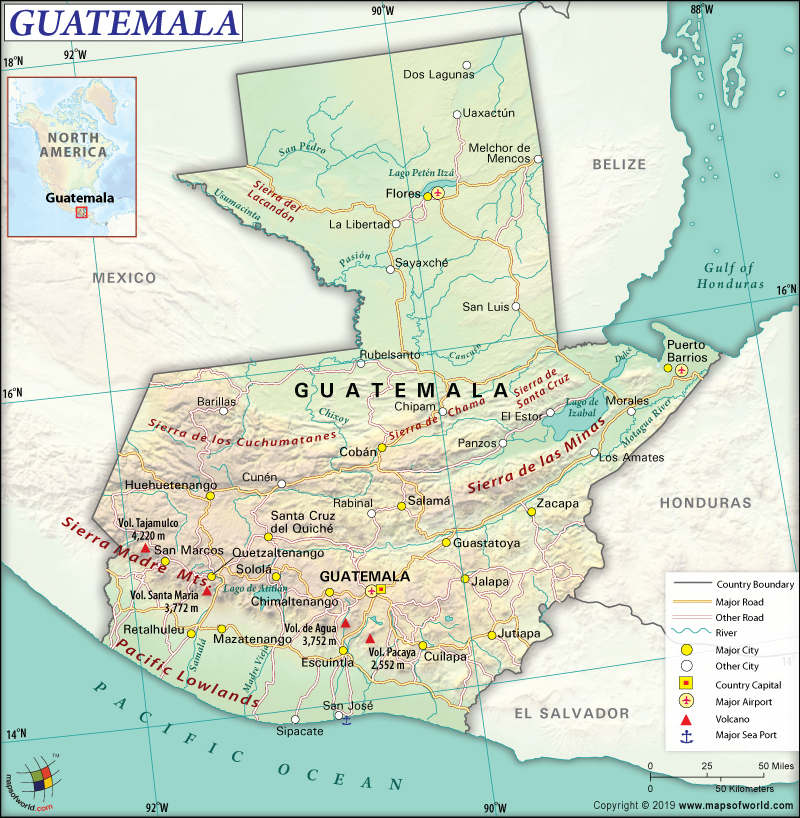
Map of Guatemala which lies in the Continent of North America
| Official Name | Republic of Guatemala |
| Continent | North America |
| Capital | Guatemala City |
| Largest City | Guatemala City |
| Coordinates | 13.000000, -85.000000 |
| Area | 42,042 sq. mi (108,889 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,036 mi ( 1,667 km) |
| Coastline | 249 mi ( 400 km) |
| Currency | Quetzal (GTQ) |
| Neighboring Countries | Honduras, El Salvador, Belize, Mexico |
| Population | 17,263,239 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | Spanish |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 15 September (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Himno Nacional de Guatemala” |
| Form of Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| President | Alejandro Giammattei |
| Vice President | Jafeth Cabrera |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 8,447.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 4,549.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.65 (2017), Rank: 127 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 81.29 (UNESCO, 2014) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 103 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 1 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +502 |
| Time Zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| Internet TLD | .gt |
Guatemala is a Central American country. It borders the North Pacific Ocean between Mexico and El Salvador. Guatemala also borders the Caribbean Sea between Belize and Honduras.
The total area of Guatemala is 108,889 sq. km (42,042 sq. mi), out of which 107,159 sq. km (41,374 sq. mi) is land area and 1,730 sq. km (668 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 1,667 km (1,036 mi) long border, which is shared with Mexico (958 km or 595 mi), Belize (266 km or 165 mi), Honduras (244 km or 152 mi), and El Salvador (199 km or 124 mi). Guatemala has a 400 km (249 mi) long coastline.
This Central American country is divided into 3 regions by two east-west trending mountain chains. These three regions are the highlands (mountainous), the Pacific Coast at the southern parts of the country, and the vast Peten lowlands in the northern parts of Guatemala. The major landforms in this country are rolling hills, deep river valleys, plateaus, and many volcanoes (out of which some are active).
The northwestern Cuchumatanes Mountains and the Sierra Madre Mountains (mainly volcanic ranges) in the east and south are separated by the central highlands of Guatemala.
The northern third of Guatemala is covered by a limestone plateau called Peten, which is again covered by grasslands and tropical rainforest. The Gulf of Honduras’s swampy edges is located in front of the Atlantic lowlands. Other important characteristic features of Guatemala are rivers of the Pacific Lowlands, volcanic sand beaches, and grassy farmland. Motagua, Sarstun, Polochic, Dulce, and Usumacinta are the main rivers of Guatemala. The most important lake in the country is Lake Izabal.
Volcan Tajumulco has a height of 4,220 m (13,845 ft), which is not only the highest elevation point of Guatemala but also entire Central America. The Pacific Ocean at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest point of the country. The mean elevation is 759 m (2,490 ft). The major mountains of the country are Volcán Tajumulco, Volcán de Agua, Volcán de Fuego, Volcán Santa María, Volcán de Acatenango, etc.
The climate in Guatemala is tropical. While the lowlands remain hot throughout the year, the mountainous regions remain cooler. With an increase in altitude, the temperature becomes cooler. A cooler mass of air from the US reaches Guatemala during December-March, which drives down the temperature to around 13/15 °C (55/59 °F) in the plains and below 10 °C (50 °F) in Guatemala City.
Guatemala is one of the most populous Latin American countries, whose economy is highly dependent upon agricultural sector. Over 30% of the total labor force is dependent upon the agriculture and this sector accounts for around 13.5% of the GDP. The main agricultural items exported by the country include bananas, coffee, sugar, and vegetables. Remittances play an important part in the economy. It is the leading remittance receiving nation in entire Central America. Remittances from the large expatriate community account for 1/10th of Guatemalan GDP and 2/3rd of the exports & imports. In 2018, the nominal GDP of Guatemala grew at a rate of 3.1% to reach US$78,460.45 billion.
The Guatemalan economy had a negative trade balance of US$3.5 billion in 2017. While the country exported around US$10 billion of goods and services, it imported around US$13.5 billion of goods and services. The main export items are coffee, bananas, palm oil, raw sugar, knit sweaters, etc. The main imported items of the country are refined petroleum, packaged medicaments, light rubberized knitted fabric, cars, broadcasting equipment, etc.
Guatemala has a highly skewed income distribution. Reports say 20% of the upper-income bracket of the population accounts for around 51% of the total consumption. The largest economy in Central America has the worst problems of poverty, child and maternal mortality rates, high incidence of malnutrition, and wide urban-rural gap. The indigenous areas are the most deprived ones in the country.
World Bank reports say that the poverty rate decreased from 56% to 51% during 2000-2006. However, it again increased to 59.3% in 2014. In fact, 23% of the total population is still living in extreme poverty. Though 52% of the total population in Guatemala is indigenous people, 79% of them live in poverty. 40% of the indigenous population in Guatemala lives in extreme poverty. Further data shows that 8 out of 10 children from the indigenous community suffer from acute malnutrition.
There are 17,621 km (10,949 mi) of roadways in Guatemala, out of which 7,489 km (4,653 mi) are paved and 10,132 km (6,296 mi) are unpaved. Guatemala has 990 km (615 mi) of waterways, out of which 260 km (162 mi) remains navigable round the year. An additional 730 km (454 mi) can be navigated only during the high-water season.
The major seaports are Santo Tomas de Castilla and Puerto Quetzal. The country has nine merchant marine ships. Though there is 800 km of narrow gauge railway network is there in Guatemala, they are not operational anymore. There are 291 airports in Guatemala, out of which 16 have paved runways and 275 have unpaved runways.
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, UNESCO, BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-24, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNISFA, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (compliant country), ICC (national committees), ICCt (signatory), ITUC (NGOs), ISO (correspondent), LAIA (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…