What are the Key Facts of Gabon?
|
Official Name |
Gabonese Republic |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
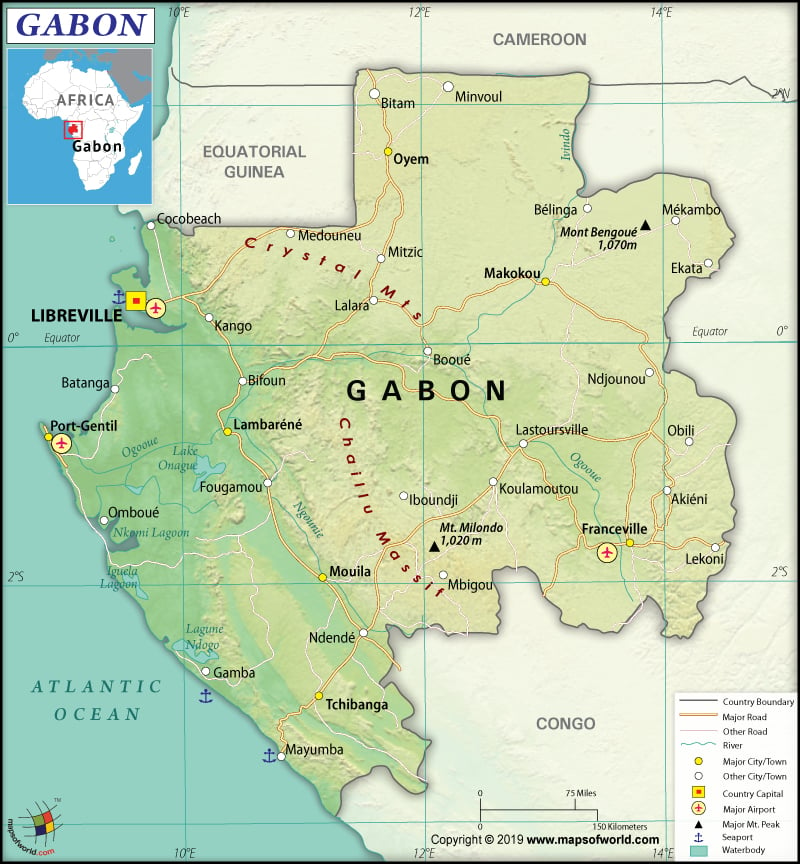
Capital |
Libreville |
|
Largest City |
Libreville |
|
Coordinates |
-1.000000, 11.750000 |
|
Area |
103,347 sq. mi ( 267,667 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
2,026 mi ( 3,261 km) |
|
Coastline |
550 mi ( 885 km) |
|
Currency |
Central African CFA franc (XAF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea |
|
Population |
1,979,786 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
French |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
17 August (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“La Concorde” |
|
Form of Government |
Presidential republic |
|
President |
Ali Bongo Ondimba |
|
Prime Minister |
Julien Nkoghe Bekale |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 17,912.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 8,029.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.702 (2017), Rank: 110 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
107 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
1 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+241 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (WAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.ga |
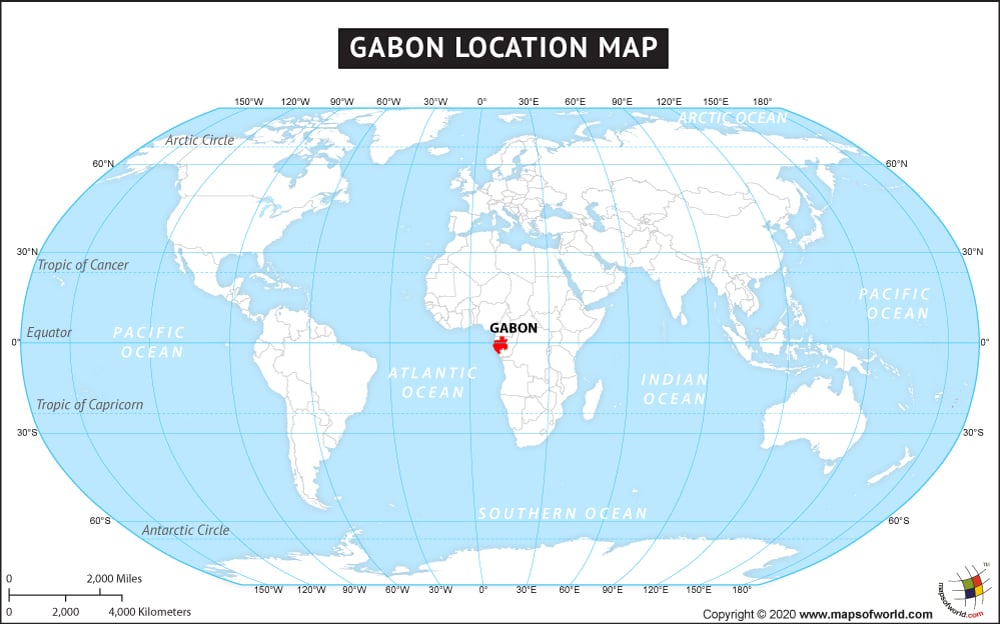
Where is Gabon?
Gabon is located on Central Africa’s west coast. The country has 3,261 km (2,026 mi) long land boundaries, which it shares with the Republic of the Congo (2,567 km or 1,595 mi) on the east and south, Cameroon (349 km or 217 mi) to the north, and Equatorial Guinea (345 km or 214 mi) to the northwest.
What is the Geography of Gabon?
Gabon is spread across a total area of 267,667 sq. km (103,347 sq. mi), out of which 257,667 sq. km (99,486 sq. mi) is land area and 10,000 sq. km (3,861 sq. mi) is water area. It has a coastline that is 885 km (550 mi) long.
Generally, geographical landforms of the country can be divided into 3 regions: a savanna in the far-east and southern parts of Gabon, a hilly mountainous region in the interior, and a narrow coastal plain. Around 85% of the landscape is covered by rainforests. The Central African mangroves are found on the coastal plains. In the east-central regions, hundreds of caves having dolomite and limestone rock formations can be found.
Moreover, Mont Iboundji is the highest elevation point of Gabon at 1,575 m (2,534 ft) and sea level at the Atlantic Ocean is the lowest point. The largest river of Gabon is Ogooué River, which is 1,200 km (746 mi) long.
Besides, the equator passes through Gabon, thereby giving it a typical tropical climate. This climate is characterized by hot and moist weather conditions in the northern and inland areas almost throughout the year. In these regions, a short dry season prevails during June-to-August. During the dry season, the temperature remains comparatively low (especially cool) in the central and southern coastal areas. The far southern areas of Gabon get relatively long dry season, which generally lasts from mid-May-to-mid-September.
Also, January-to-May remains the warmest period in the northern and central parts of the country. The average temperature revolves around 30 °C (86 °F). The temperature drops to around 24/25 °C (75/77 °F) in the central and southern coastal areas during June-to-September. The temperature in the inland areas of Gabon revolves around 27/28 °C (81/82 °F) from June to September.
Usually, the annual rainfall level in Gabon generally remains within 1,500-2,000 mm (60-79 in). However, the northern part of the coast (especially where the country’s capital Libreville is located) receives around 3,000 mm (118 in) rainfall. Near the Equator, especially in the northern inland areas, two rainy seasons can be found: March-to-May and September-to-November. December-February can be called the sunniest period. From June-to-August, the sky often remains cloudy and therefore gets the least amount of sunshine.
What is the Economy of Gabon?
Gabon, an upper-middle-income economy, has a per capita income that is four times that of most sub-Saharan African countries. However, a significant population of the country still lives in poor condition. It is mainly because of the large income inequality.
Earlier, the economy of Gabon was mainly dependent upon exports of timber and manganese. However, after the discovery of fossil fuels, the country has become the 5th largest producer of oil in Africa. The oil sector has become the backbone of the economy, currently contributing 80% of the exports, 60% of the fiscal revenue, and 45% of the GDP. With the decline in oil reserves, the government has started adopting a new economic strategy based on diversification.
In 2015, Gabon’s economy ran into trouble as it recorded fiscal deficit for the first time since 1998. It grew at 2.1% in 2016 but decelerated to a mere 0.6% in 2017, mainly because of the drastic fall in oil revenue coupled with limited expansion of the industrial and service sectors. In 2018, the economic growth recovered marginally to 1.2%, which helped the economy to reach a nominal GDP of US$17.017 billion.
The unemployment rate is over 20%, of which 35% of the youth are unemployed. 40% of the labor force is still dependent on agriculture, contributing to the poverty of the populace. Reports say 5% of the population still lives under the internationally accepted poverty level of US$1.25 per day.
What is the Transportation System of Gabon?
Gabon’s transportation system is moderately developed. The country has 14,300 km (8,886 mi) of total roadways, out of which 900 km (559 mi) are paved and 13,400 km (8,326 mi) is unpaved. There are 44 airports in Gabon, of which 14 have paved runways and 30 have unpaved runways. 649 km (403 mi) long railway network is also present and all of them are standard gauge railway tracks. The waterway is one of the main transportation systems in Gabon. There are 1,600 km (994 mi) of waterways available in the country, of which 310 km (193 mi) is on Ogooue River itself. The three major seaports of the country are Libreville, Port-Gentil, and Owendo. 29 merchant marine ships are there in Gabon.
What International Organizations is Gabon part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, ACP, Interpol, UNWTO, AfDB, UNIDO, AU, BDEAC, IMSO, UNESCO, CEMAC, ISO, WMO, FAO, ITU, FZ, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UNCTAD, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, ITUC (NGOs)