
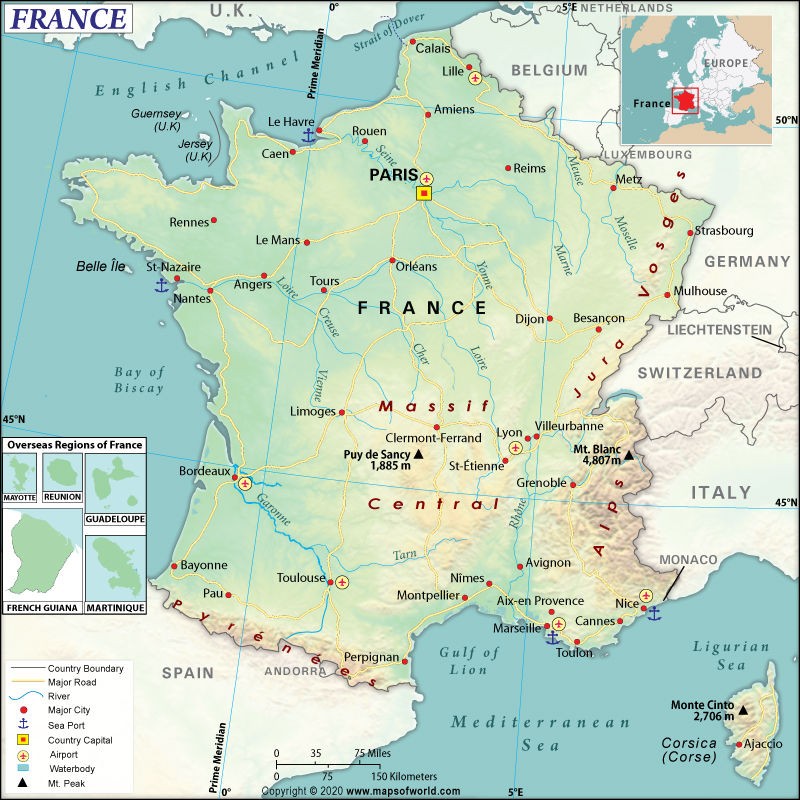
Map of France which lies in the continent of Europe
| Official Name | French Republic |
| Continent | Europe (Metropolitan France) |
| Capital | Paris |
| Largest City | Paris |
| Coordinates | 46.000000, 2.000000 |
| Area | 247,368 sq. mi ( 640,679 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 2,464.5 mi ( 3,966.2 km) |
| Coastline | 2,129 mi ( 3,427 km) |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR), CFP franc (XPF) |
| Neighboring Countries | Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Monaco, Spain, Andorra, United Kingdom |
| Population | 66,998,000 (2019 est. ) |
| Official Languages | French |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 14 July (Bastille Day) |
| National Anthem | “La Marseillaise” |
| Form of Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic |
| President | Emmanuel Macron |
| Prime Minister | Jean Castex |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 45,877.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 41,463.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.901 (2017), Rank: 24 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | Centre national d’études spatiales (CNES) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 6 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 840 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +33 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Internet TLD | .fr |
France is the largest country in western Europe.
France is divided into 13 metropolitan regions after its Parliament passed a law in 2016 reforming the total number of regions. In addition, five regions of France are overseas, and away from the main or metropolitan part of France. These five regions are French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Réunion. France also has other overseas territories like French Polynesia that are considered collectivities. Regions are administratively divided into 102 departments, then further into arrondissements (342), cantons, and finally communes or municipalities. Paris, Lyon, and Marseille are three of the major communes in France which are also located on the map France and these communes are divided into municipal arrondissements. Check this Map of France and Other 76 Related French Maps for more maps and info about France.
Metropolitan France is located in western Europe. It borders the English Channel and the Bay of Biscay. Metropolitan France is situated in the southeast of the United Kingdom and in between Spain and Belgium. It also borders the Mediterranean Sea between Spain and Italy.
French Guinea is in the northern part of South America. It borders the North Atlantic Ocean between Suriname and Brazil. Guadeloupe, an overseas French region, is in the Caribbean, southeast of Puerto Rico. It is a set of islands located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Martinique is yet another Caribbean island (another French region) located between the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. It is part of the Lesser Antilles, which is situated in the north of Trinidad and Tobago.
Mayotte (a department and region of France) is an archipelago that is located in the southern part of the Indian Ocean. It is situated around halfway between the northern parts of both Mozambique and Madagascar. Reunion Island, a French department, is located in the southern part of Africa in the Indian Ocean. It is situated in the east of Madagascar.
Metropolitan France shares land borders with Luxembourg and Belgium (in the northeast direction), Switzerland and Germany (in the eastern direction), Monaco and Italy (in the southeast), Andorra (in the south), and Spain (in the southwest).
Here is France’s Physical Map showing all the physical features of the country.
Except for the northeastern part, natural boundaries and geographic features roughly delineate most of the land borders. Rhine River is situated to the east, the Pyrenees to the south, and the Alps as well as the Jura to the southeast. France is spread over a total area of 643,801 sq. km (248,573 sq. mi), out of which 640,427 sq. km (247,240 sq. mi) is land and 3,374 sq. km (1303 sq. mi) is water. The total coastline of France is 4,853 km (3016 mi).
Most of the terrains in metropolitan France include flat plains with hills rolling gently in the northern and western parts. The southern part of France is mountainous, which includes the Pyrenees. In the eastern parts of the country, you will find the Alps.
French Guiana mainly has low-lying coastal plains that rise to the hills as well as small mountains. Most of Guadeloupe has a volcanic origin. It consists of Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, and 7 other islands. While Basse-Terre has volcanic origin having mountains in the interior, Grande-Terre has low limestone formation. All the other 7 islands have a volcanic origin.
Martinique has mountainous terrain, an indented coastline, and a dormant volcano. Mayotte has undulating terrains in general along with ancient volcanic peaks as well as deep ravines. Reunion mostly has a rugged and mountainous terrain. Along the coast of Reunion, the lowlands are fertile.
While the highest elevation point is Mont Blanc at 4,810 m (15,781 ft), the Rhone River delta lies at -2 m (6.5 ft below sea level). The mean elevation of France is 375 m (1230 ft). The major mountains and peaks of France are The French Alps, The Massif Central and the Auvergne Mountains, The Pyrenees, Corsica, The Vosges, Morvan Massif in Burgundy, and The Jura.
The two largest rivers of France are The Loire River (1,005 km or 625 mi long, the biggest river in terms of length) and The Rhone River (the biggest river in terms of depth/volume). Other major rivers are The Seine, The Dordogne, Garonne, and Gironde. The major lakes are Lake Geneva, Bourget Lake, Serre-Ponçon Lake, Lake Annecy, and Der-Chantecoq Lake.
The climate of metropolitan France generally has mild summers and cool winters. However, along the Mediterranean, the summers are hot, and winters are mild. North-to-northwesterly winds known as mistral blow occasionally. These winds are strong, cold, and dry.
Seasonal temperature variation in French Guiana is little, thanks to the tropical climate. The place remains hot and humid. Guadeloupe and Martinique have subtropical tempered climates and moderately high humidity. June to October is the rainy season in Guadeloupe and Martinique. Both these islands are vulnerable to devastating cyclones. Mayotte, as well as Reunion, has a tropical climate (hot and humid). While November to April is the rainy season, May-to-November is cool and dry.
France is one of the largest economies in the world. Its nominal GDP was US$2.778 trillion, and the GDP growth rate was 3 % in 2018 (World Bank). In the European Union, France is the third-largest economy, after Germany and the United Kingdom. It is also a member of the G-7 countries and the Eurozone. France was among the first eleven countries of the EU that came together to launch the Euro in 1999. French franc (₣) was completely replaced with Euro banknotes and coins in 2002.
The French economy is a mixed economy that includes private enterprises, state enterprises, and significant government intervention. The French government keeps considerable influence over the major sectors of the economy such as the infrastructural sector, telecommunications, nuclear power, aircraft, electricity, and railways. However, there is a slow but steady tilt towards corporatization of defense, banking, insurance, telecom, and airliners industries where the government has considerable clout.
The diversified economy of France has a core chemical industry, which not only contributes significantly to the country’s economic growth but also helps other manufacturing activities to grow. The aerospace industry is also highly developed.
Other major economic components of the economy include tourism, fashion, and other industries. One of the leading technology hubs is located in Sophia Antipolis. While France is one of the largest exporters/importers of the world, it is also the 3rd largest recipient of FDI among the OECD countries.
The financial, banking, and insurance sector is vibrant in the country. NYSE Euronext group’s French branch (Euronext Paris) is the second-largest stock exchange market in Europe (only after the London Stock Exchange). While AXA (a French insurance company) is the largest insurance company in the world, major banks of the country include BNP Paribas, Société Générale group, and the Crédit Agricole.
Out of the 30.25 million labor force, 4.95% are unemployed (World Bank, 2018). Most of the labor force is engaged in the services sector (71.8%), followed by industry (24.3%) and agriculture (3.8%). Reports say around 8.8 million people in France were living under the poverty line in 2017. The poverty rate in France in 2017 was 13.5%. The worst affected sections of the French population by poverty are elderly women, single mothers, and foreigners.
France’s transportation system is known for having the densest networks of roads and railway lines in the world. For every 100 sq. km (38.61 mi) of area, you will find 146 km (90.72 mi) of road and 6.2 km (3.85 mi) of railway lines. Airways and waterways are also highly developed.
The roadways are extremely developed in France. Around 950,000 km (590,000 mi) of the road is there. 30,500 km (18,952 mi) of major trunk roads are available in the country. 365,000 km (226,800 mi) is covered by the routes départementales. In Europe, France is the country most dependent on cars. Urban bus services are also very popular, especially because of the flat-rate charge. These services are available in the cities and suburbs too. However, they are limited in rural areas.
France has 29,901 km (18,580 mi) of railway lines, which are mostly governed and operated by the national railway company SNCF (Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer français). The railway system accounts for around 10% of the total passenger travel. Rapid transit services or metro services are available in six French cities – Paris, Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Lille, and Rennes. Modern tram or light rail networks are also there in the many major French cities including Lyon, Paris, Nantes, Strasbourg, Saint-Étienne, Montpellier, and Toulouse.
France has the largest network of natural and man-made waterways in Europe. 8,500 km (5,300 mi) of waterways are present in the country, where the navigable sections (6,700 km or 4,200 mi) are managed by the French navigation authority, VNF. The most popular navigable rivers of France are Rhône, Seine, and Loire. The navigable sections in Brittany Canals and River Somme are managed locally. 20% of the waterway network is suitable for boats carrying out more than 1,000 tons of operation.
More than 1,400 ships are there under the management of French companies. There are 55 merchant marine ships that have over 1,000 gross register tonnage sizes. The most important harbors and seaports of the country are Bayonne, Brest, Boulogne-sur-Mer, Bordeaux, Fos-sur-Mer, Dunkerque, Cherbourg-Octeville, Calais, and many more.
There are around 30 registered air carriers in France. The country has around 478 airports, out of which 288 have paved runways and 199 unpaved runways.
WTO, UN, UNSC (permanent), NATO, IMF, OECD, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, Paris Club, EITI (implementing country), ICC (national committees), PIF (partner), IGAD (partners), Australia Group, ILO, BDEAC, BIS, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, Union Latina, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, FZ, NSG, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, Interpol, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, IMSO, InOC, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NEA, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, SPC, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), ADB (non-regional member), AfDB (non-regional member), Arctic Council (observer), BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), OAS (observer), SELEC (observer)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…