What are the Key Facts of El Salvador?
|
Official Name |
Republic of El Salvador |
|
Continent |
North America |
|
Capital |
San Salvador |
|
Largest City |
San Salvador |
|
Coordinates |
13.833333, -88.916667 |
|
Area |
8,124 sq. mi (21,041 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
367 mi ( 590 km) |
|
Coastline |
191 mi ( 307 km) |
|
Currency |
United States dollar (USD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Honduras, Guatemala. Maritime Neighbor: Nicaragua |
|
Population |
6,344,722 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
15 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Himno Nacional de El Salvador” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Nayib Bukele |
|
Vice President |
Félix Ulloa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 8,317.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 4,058.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.674 (2017), Rank: 121 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
97.98 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
106 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+503 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−6 (CST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.sv |
Where is El Salvador?
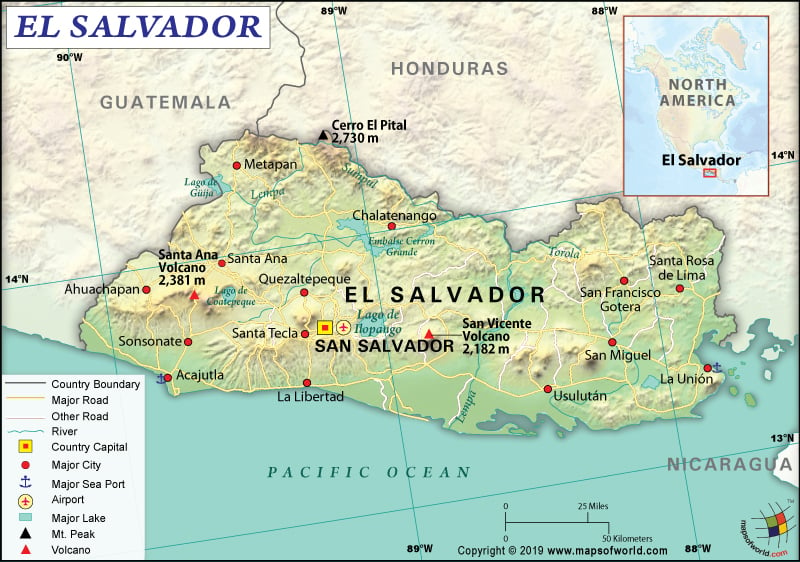
El Salvador is a Central American country that is located between Honduras and Guatemala, bordering the North Pacific Ocean. Check this El Salvador Map and Other 21 Related Salvadoran Maps for more maps and info about El Salvador.
What is the Geography of El Salvador?
El Salvador is spread across a total area of 21,041 sq. km (8,124 sq. mi), out of which 20,721 sq. km (8,000 sq. mi) island area and the rest 320 sq. km (124 sq. mi) is water area. The country has a 590 km (367 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with Honduras by 391 km (243 mi) and Guatemala by 199 km (124 mi). The Republic of El Salvador has a 307 km (191 mi) long coastline.
Cerro El Pital is the highest elevation point of the country at 2,730 m (8,957 ft) and the Pacific Ocean at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of the country is 442 m (1,450 ft). The major mountains of El Salvador are Santa Ana Volcano, Volcán de San Vicente, Volcán de San Miguel, Volcán de Izalco, Volcán de San Salvador, etc.
The terrain of El Salvador mainly consists of mountains. The landscape also has a central plateau and a narrow coastal belt. Two parallel mountain ranges border the central plateau. The Sierra Madre Mountains run along the Honduran border in the northern part of the country.
As you move to the southern direction, the land starts lowering into a coastal plain. From west to east, there is a scattered chain of over twenty volcanic stretches from west to the east. Though many volcanoes are still active, major eruptions hardly take place.
Hundreds of rivers are there in the country. Some of them are Lempa River, Paz River, Copinula River, Banderas River, etc. Lempa is the most important river in El Salvador, which rises in the Honduran mountains, flows across the central plateau towards the south, and empties into the Pacific Ocean.
There are many volcanic lakes present in the interior and they are all ringed by mountains. Lake Ilopango is one of the largest lakes, located in the eastern direction of the capital city of San Salvador. Cerrone Grande Reservoir is the largest manmade lake in the country, which is formed after the creation of a hydroelectric dam on the Lempa River.
El Salvador has a tropical climate, which remains hot throughout the year. This climatic condition prevails mainly along the narrow coastal belt and at an elevation below 1,000 m (3,300 ft). There is a little difference in temperature with the change in seasons.
There are two prominent seasons in the country: the rainy season and dry season. While the rainy season continues from May to October, the dry season continues from November to April. Heavy rainfall and high humidity are the only significant climatic changes found during the rainy season. It remains muggy during the rainy season.
The climate remains temperate in the uplands. Mountains, volcanoes, and plateaus are found in the inland areas of El Salvador. The weather remains cooler at higher altitudes.
The cloud forests are found mainly at intermediate altitudes. The weather gets colder at higher altitudes, especially above 2,000 m or 6,500 ft. At this altitude, the winter nights can become colder. Snow on the top of Cerro El Pital can be found during November-March.
A cool wind from the USA known as the Norte affects the country’s weather sometimes. Cool weather can prevail both in the evening as well as the night in the plains due to the Norte wind. This wind can make the night cold and bring down the lows to around 10 °C (50 °F).
What is the Economy of El Salvador?
El Salvador has one of the top-5 largest economies in the region. In 2018, the nominal GDP grew at a rate of 2.5% (marginally higher than 2.3% in 2017) to reach US$26.057 billion. The per capita GDP was US$4,058 in 2018, higher than the US$3,787 in 2017. Remittances play an important role in economic growth. It accounted for 18% of the GDP.
The country had a US$ 4,832,773,689 trade deficit in 2017. While it exported US$10,592,788,531, it imported US$ 5,760,014,842 of goods and services. The main export items are Knit/crochet clothing/accessories, plastics/plastic-made products, paper/paper items, sugar/sugar confectionery, mineral fuels (including oil), etc. El Salvador’s major import items are raw materials, fuels, capital goods, consumer goods, foodstuffs, electricity, etc.
The unemployment rate has come down from 7.05% in 2010 to 6.4% in 2018. The country has witnessed a moderate poverty reduction, thanks to the low economic growth of the country. In fact, rural poverty has remained high. Considering US$5.5 per day poverty line, the poverty rate has declined from 39% to 31% during 2007-to 2016. Considering US$3.2 per day poverty line, extreme poverty has decreased from 15% to 10% during 2007-to 2016.
What is the Transportation System of El Salvador?
El Salvador has 9,012 km (5,600 mi) of the roadway, out of which 5,341 km (3,319 mi) is paved and 3,671 km (2,281 mi) are unpaved. Rio Lempa River is the navigable river in the country. Small crafts can be used for partial navigation. While Puerto Cutuco is the major seaport, Acajutla offshore terminal is the oil terminal of El Salvador. Only 13 km (8 mi) of narrow-gauge railway track is available. There are 68 airports present in the country, out of which only 5 have paved runways and the other 63 have unpaved runways. There are two heliports too.
What International Organizations is El Salvador part of?
WTO, UN, UNESCO, Union Latina, IMF, Interpol, BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-11, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, SICA, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ISO (correspondent), ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), NAM (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link:
