What are the Key Facts of Ecuador?
| Official Name | Republic of Ecuador |
| Continent | South America |
| Capital | Quito |
| Largest City | Quito |
| Coordinates | -2.000000, -77.500000 |
| Area | 109,484 sq. mi ( 283,561 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,390 mi ( 2,237 km) |
| Coastline | 1,390 mi ( 2,237 km) |
| Currency | United States dollar (USD) |
| Neighboring Countries | Colombia, Peru |
| Population | 16,385,068 (2016 est.) |
| Official Languages | Spanish, Kichwa (Quichua), Shuar |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 10 August (Independence day) |
| National Anthem | “ Salve, Oh Patria!” |
| Form of Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
| President | Lenín Moreno |
| Vice President | Otto Sonnenholzner |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 11,713.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 6,344.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.752 (2017), Rank: 86 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 94.35 (UNESCO, 2016) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 55 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 2 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +593 |
| Time Zone | UTC−5 / −6 (ECT / GALT) |
| Internet TLD | .ec |
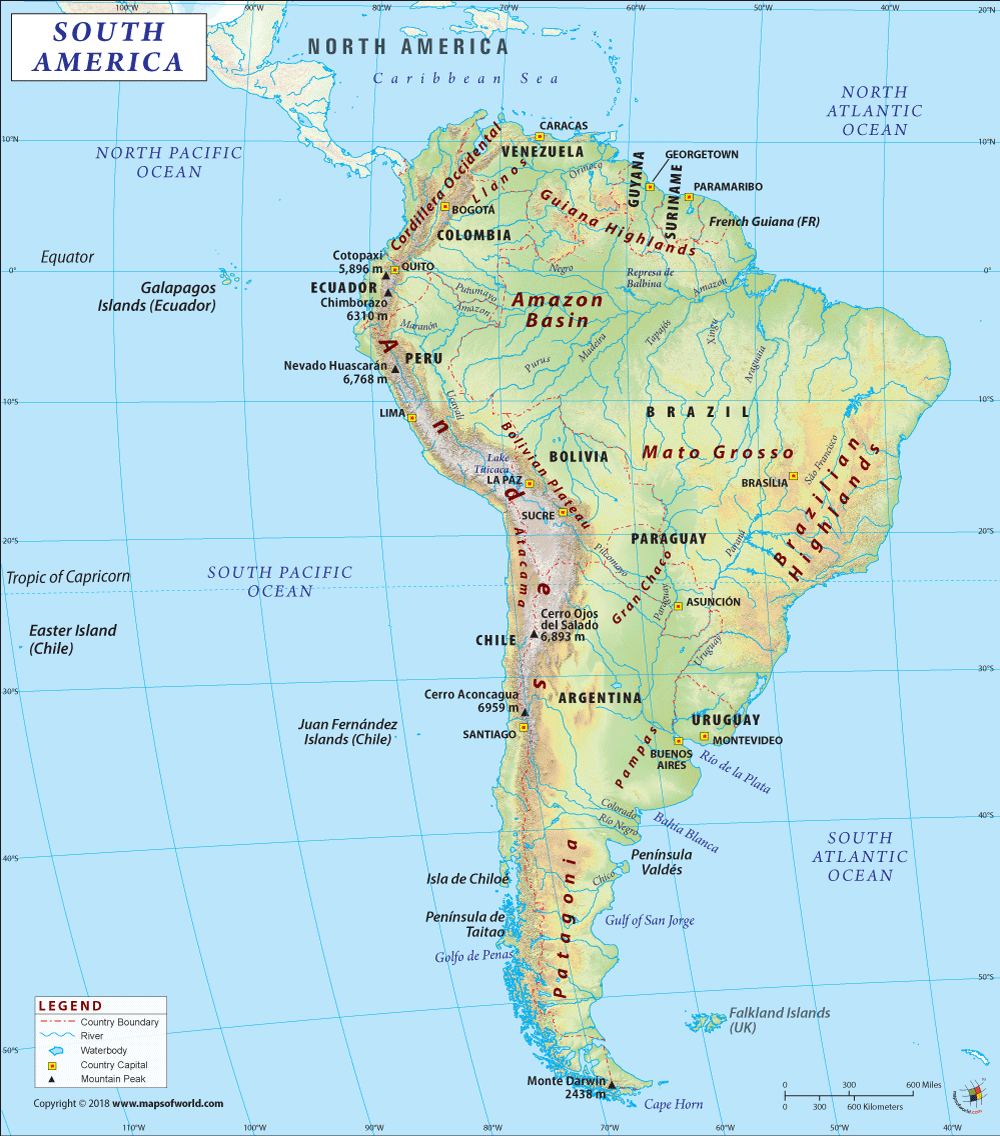
Where is Ecuador?
Ecuador is a country located in the northwestern part of South America. It is bordered on the east and south by Peru (1,529 km or 950 mi), on the north by Colombia (708 km or 440 mi), and on the west by the Pacific Ocean.
What is the Geography of Ecuador?
Ecuador is spread across a total area of 283,561 sq. km (109,484 sq. mi) including the Galapagos Islands. While the land area is spread across 276,841 sq. km (106,889 sq. mi), water area is spread across 6,720 sq km (2,595 sq. mi). Ecuador shares its 2,237 km (1,390 mi) long boundary with its two neighboring countries (Peru and Colombia). It has a huge coastline of 2,237 km (1,390 mi) along the Pacific Ocean.
Broadly, there are 4 main geographic locations in Ecuador. They are La Costa (the coastal region), La Sierra (the highlands), La Amazonía (also called “El Oriente” or the east), and La Región Insular (the Galapagos Islands).
Since the coastal region or La Costa includes fertile and productive land areas, it is mostly used for cultivation of rice crop and banana plantations. On the other hand, fisheries are most active in the main coastal cities including Guayaquil. The provinces located in the west of the Andean range include Santa Elena, El Oro, Manabí, Los Ríos, Guayas, and Esmeraldas.
In addition, the highlands or La Sierra include the volcanoes of the country as well as the snow-capped peaks. Traditional crops such as quinoa, maize, and potato are cultivated in this region. Some of the most important provinces in this area include Tungurahua, Pichincha, Loja, Imbabura, Chimborazo, Carchi, Cañar, and Azuay.
Similarly, the La Amazonía region mainly consists of the Amazonian forests including the Amazon national parks and Amerindian untouchable zones. Zamora-Chinchipe, Sucumbíos, Pastaza, Orellana, Napo, and Morona Santiago are the main jungle provinces. The upper Amazonian region has large petroleum reserves. La Región Insular consists of the Galápagos Islands that are located 1,000 km (620 mi) west of the Ecuadorian mainland in the Pacific Ocean.
Further, the mean elevation of Ecuador is 1,117 m (3,665 ft). While Chimborazo is the highest elevation point at 6,267 m (20,561 ft), sea level at Pacific Ocean is the lowest elevation point. It is important to note that Chimborazo is the highest point on earth farthest from its center. Other major mountains of Ecuador are Cotopaxi, Cayambe, Antisana, Altar, etc. Major rivers in the country are Amazon, Marañón, and Putumayo.
Accordingly, the Ecuadorian climate varies from one region to the other. The coastal lowlands generally keep warm, with the average temperature revolving around 25 °C (77 °F). Ocean currents also affect the coastal climate. January-to-April remains hot and rainy.
The Quito city and other cities in the mountainous region have a consistent subtropical highland climate. The annual average temperature remains around 17.8 °C (64 °F). During the day, average temperature revolves around 21 °C (70 °F) and at night the average temperature plunge to around 10 °C (50 °F). While dry (winter) season lasts from June-to-September, wet (summer) season lasts from October-to-May in Ecuador.
What is the Economy of Ecuador?
The World Bank’s report shows that Ecuador’s nominal GDP in 2018 was US$108.398 billion and the economy was growing at 1.4% in the same year. Ecuador is a developing country whose economic prowess is significantly dependent on commodities such as petroleum and agricultural products.
In 2017, the total trade constituted 42% of the Ecuadorian GDP. Petroleum accounted for 32% of the export revenues of the country in the same year. 1/3rd of the public-sector revenue comes from oil. As many Ecuadorian emigrants are employed abroad, remittances also play an important role in the economy (accounting for 2.7% of the economy in 2017). Other than oil, its other major export items are bananas and shrimp. In recent years, the exports of items such as cut flowers and canned fish are also increasing.
Unemployment rate in the country was 3.9% in 2018. Ecuador’s National Institute of Statistics and Census (INEC) has said that the poverty rate increased from 21.5% to 24.5% and extreme poverty from 7.9% to 9% during December 2017-June 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Ecuador?
All kinds of transportation facilities are available in the country. However, roadways is the main form of transport in Ecuador. 43,216 km (26,853 mi) of roadways are there in the country, out of which only 8,161 km (5,071 mi) are paved and most of them (35,055 km or 21,782 mi) are unpaved. Buses, taxis, and car rental facilities can be found in all major cities of the country.
Airways are also significantly developed. There are 432 airports in Ecuador. While 104 have paved runways, 328 have unpaved runways. 2 heliports are also present in the country. Railways have limited reach and are mainly there for tourism purposes. 965 km (600 mi) long railways (all of them narrow gauge) are present in the country. 1,500 km (932 mi) of waterways are also present in Ecuador. Esmeraldas, Puerto Bolivar, and Manta are the major seaports.
What International Organizations is Ecuador part of?
WTO, CAN, IMF, CD, UN, CELAC, UNESCO, FAO, Union Latina, G-11, ILO, G-77, UNCTAD, IADB, IAEA, UNHCR, IBRD, UNIDO, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, MIGA, MINUSTAH, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, OPEC, PCA, UNAMID, UNASUR, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), Mercosur (associate), WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), SICA (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer)