
Map of Croatia
| Official Name | Republic of Croatia |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Zagreb |
| Largest City | Zagreb |
| Coordinates | 45.166667, 15.500000 |
| Area | 16,577 sq mi ( 42,933 sq km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,390 mi ( 2,237 km) |
| Coastline | 3,625.8 mi ( 5,835.1 km) |
| Currency | Kuna (HRK) |
| Neighboring Countries | Slovenia, Hungary, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro |
| Maritime Neighbors | Italy |
| Population | 4,154,200 (2017 est.) |
| Official Language | Croatian |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 25 June, Independence from Yugoslavia |
| National Anthem | “Lijepa nasa domovino” |
| Form of Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
| President | Zoran Milanovic |
| Prime Minister | Andrej Plenković |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $26,295.5 (World Bank, 2017) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $13,386.5 (World Bank, 2017) |
| HDI | 0.831 (2017), Rank: 46 |
| Literacy Rate | NA |
| Space Agency | Cooperation Agreement with European Space Agency |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 74 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 44 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | Right |
| Calling Code | +385 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Internet TLD | .hr |
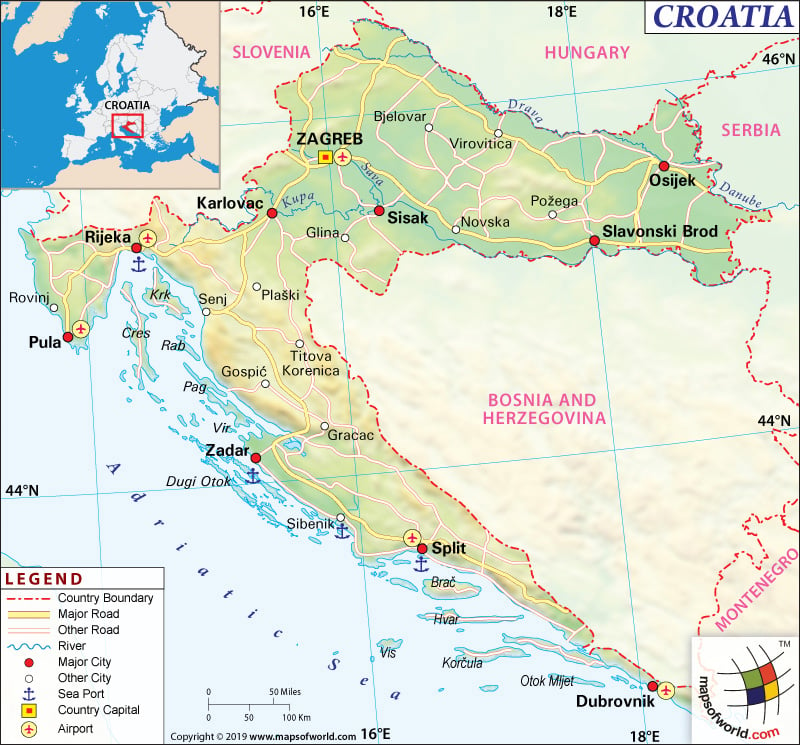
Croatia is located on the European continent, at the crossroads of Central Europe and South-East Europe. Check out this Map of Croatia and Other 12 Related Croatian Maps for more info about Croatia.
Croatia is a part of the Balkans and Mitteleuropa. It is spread over 56,594 square kilometres (or 21,851 square miles). The country shares its borders with Serbia (to the East), Hungary (to the North East), Slovenia (to the North West), Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina (to the South West), Italy (maritime border), and the Adriatic Sea (in the South).
The country’s territorial waters encompass 18,981 square kilometres (or 7,329 square miles) in a zone spread across 12 nautical miles (22 km or 14 miles). Croatia’s major geomorphological parts include the Dinaric Alps, the Pannonian Basin, and the Adriatic Basin.
Most of Croatia is made up of lowlands, located in the northern regions. 53.42% of the country has less than 200 meters (660 feet) above sea level elevation. Horst and Graben’s structures are predominant in the plains. In the Dinaric Alps, the Lika and Gorski Kotar areas have the highest concentration of ground at relatively high elevations.
Croatia has a warm temperate Mediterranean climate. It is characterized by dry and warm summers with the temperature of the warmest month remaining above 22°C on average. The winters are predominantly wet. The northern and northeastern areas of the country are warm temperate humid climates with the warmest month having a temperature lower than 22°C on average. In four or more months, the temperature is above 10°C on average. The Dinaric Alps mountains in the central part of Croatia are covered with large forests and the region experiences an alpine climate.
Most of Croatia’s territory (accounting for 62% of the territory) consists of a branching river network belonging to the Black Sea catchment basin. The major rivers of the country are the Danube River, Sava River, and Drava River. Both Sava and Drava rivers are the tributaries of the Danube River. The Danube is the second-longest river in Europe that flows through ten countries. Length of the Danube, Sava, and Drava rivers are 1,777 miles, 615 miles, and 439 miles respectively.
Major mountains in Croatia are Dinara, Kamešnica, Biokovo, Velebit, Plješevica, and many more. The highest mountain in the country is Dinara (1,831 meters or 6,007 feet), which is located in the Dinaric Alps (or Dinarides range). Other major peaks of Croatia are Kurljaj, Sveti Jure, Vaganski vrh, Ozeblin, Bjelolasica (Kula), Sveta Gera, Kalnik, and many more.
The Adriatic Sea mainland of the country is 1,777.3 kilometres (or 1,104.4 miles) long. There are 1,246 islands and islets in Croatia, encompassing a coastline of 4,058 kilometres or 2,522 miles. This is the Mediterranean’s most indented coastline.
Croatia became a sovereign nation in 1991 when Yugoslavia was broken along ethnic and religious lines. During 2000-2007, the Croatian economy grew by 4-6%, thanks to the flourishing tourism industry and credit-driven consumer spending. However, it entered a recessionary phase in 2008.
The country joined the European Union in July 2013 while it was passing through a 6-year long recessionary phase (2008-2014). The EU grants along with the advantages of joining a single market helped Croatia recover, which started around 2015. The export increased from 40% of GDP in mid-2013 to more than 50% of GDP in 2018. Estimates of 2018 show that the country’s nominal GDP was US$ 60.69 billion and per capital GDP was US$14,815.
Croatia is a developed high-income economy that is predominantly based on services. Tertiary sector contributes over 70% to the GDP. The six years of recession led to a cumulative decline of the GDP by 12.5%. However, the economy is recovering steadily now and the economic growth rate of Croatia is revolving around 2.5%- 3.5% during 2016-2019.
The unemployment rate is declining, thanks to the strong performance of the tourism sector (accounting for 19.6% of Croatia’s GDP) and the supporting investments towards expanding tourism capacity. Over 70% of the workforce is engaged in the services sector, followed by manufacturing (26.2%) and agriculture (3.7%). The unemployment rate has come down from 15% in 2016 to 8.6% in April 2019. Human Development Index of Croatia is very high (0.831), giving the country 46th rank in the list of countries having high HDI.
Tourism is the main source of income for people in Croatia. More than 14 million tourists flock to this country every year, mostly in the months of summer and during winter for snow sports such as skiing. The country ranks among the top 20 most popular destinations of the world. The revenue generated by tourism in Croatia is over €8 billion.
Croatia’s economic output is heavily dependent upon trade. Experts believe low trade-weighted average tariff (which is just 1.2%) bolsters trade in the country. 2017 figures show that Croatia’s export is valued at $16.45 billion and import at $22.34 billion. Shipbuilding is the main export item of the industrial sector, accounting for 10% of the total goods exported.
Transportation System of Croatia is mainly dependent upon road, railways, water and airways. The roadways mainly include motorway network, which was mainly built to connect the capital Zagreb to other regions of the country as well as other major European routes as well as four Pan-European corridors. Till now, the country has successfully completed motorways of over 1,100 kilometers (680 miles). Croatia has an extensive highway network coupled with the state, county and local road routes. For inter-city transport, buses are more common than railways.
Croatia has a developed and extensive railway network across the country. 2,722 kilometers(1,691 miles) of railway tracks are there. Croatian Railways operates 985 kilometers(612 miles) of electrified railways and 254 kilometers (158 miles) of double track railways in Croatia.
Air transport is also significantly developed in Croatia. There are 68 airports across the country out of which 9 airports are international airports (including Zagreb, Split, Zadar, Osijek, Rijeka, Dubrovnik, and Pula). The most notable airlines of the country are Croatia Airlines and Trade Air.
Water transport is available on the sea and rivers. Rijeka, Zadar, Split, and Ploče are the main sea ports of Croatia. While Port of Rijeka is the busiest cargo seaport in the country, Split and Zadar are the busiest passenger ports. River transport is mainly based on Sava and Danube. Drava River also has some extent of water connectivity. Vukovar is the largest river port, which is located on Danube River. The coastal cities and islands are well connected with highly developed water transport system including ferry lines.
Croatia is part of the following international organizations:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…