
Map of Costa Rica which lies in the Continent of North America
| Official Name | Republic of Costa Rica |
| Continent | North America |
| Capital | San José |
| Largest City | San José |
| Coordinates | 10.000000, -84.000000 |
| Area | 19,700 sq. mi (51,100 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 411 mi ( 661 km) |
| Coastline | 802 mi ( 1,290 km) |
| Currency | Costa Rican colón (CRC) |
| Neighboring Countries | Nicaragua, Panama |
| Population | 4,857,274 (2016 est.) |
| Official Languages | Spanish |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 15 September (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Himno Nacional de Costa Rica” |
| Form of Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
| President | Carlos Alvarado |
| Vice President | Epsy Campbell Barr, Marvin Rodríguez |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 17,645.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 12,026.5 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.794 (2017), Rank: 63 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 97.86 (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 149 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 4 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +506 |
| Time Zone | UTC−6 (CST) |
| Internet TLD | .cr |
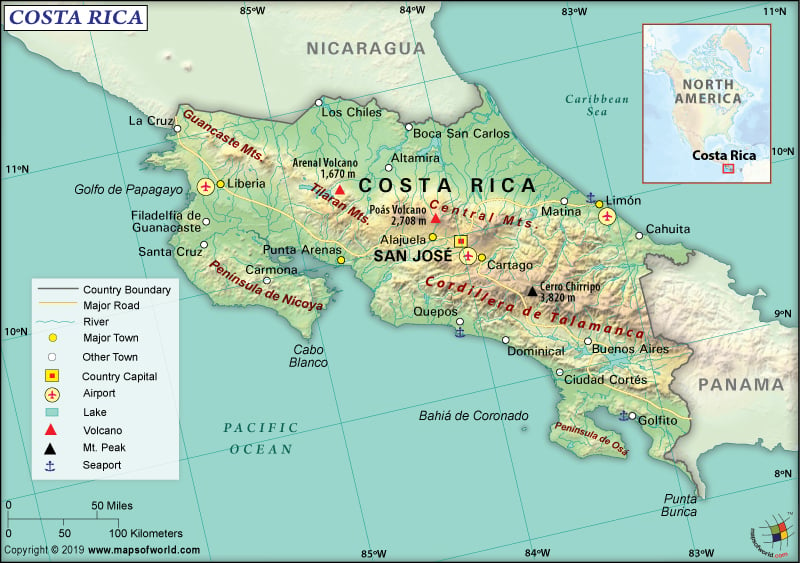
Costa Rica is a Central American country that is located between Panama and Nicaragua and borders both the North Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
Costa Rica is spread across a total area of 51,100 sq. (19,700 sq. mi), out of which 51,060 sq. km (19,714 sq. mi) is land area and the rest (40 sq. km or 15 mi) is water a.rea. It has a 661 km (411 mi) long boundary, which is shared with two neighboring countries: Panama 348 km (216 mi) and Nicaragua 313 km (194 mi).
Costa Rica has a significantly long coastline, which runs for 1,290 km (802 mi). The Pacific Ocean is the lowest elevation point of the country at 0 m (0 ft). There are fourteen major river systems such as San Juan River, Reventazón River, Suerte River, Tamarindo River, Tempisque River, Nosara River, etc.
The terrain consists of vast coastal plains, which can be divided into North, South, and Central Pacific regions. These plains are separated by the rugged mountains that include more than 100 volcanic cones. Many are active volcanoes too. The major mountains of the country are Cerro Chirripó (the highest elevation point of Costa Rica at 3,819 m or 12,530 ft), Cerro Ventisqueros, Cerro Kámuk, etc. The mean elevation point of Costa Rica is 746 m (2,448 ft).
The landform of this Central American nation is dominated by the Sierra Madre mountains. The cone-shaped Arenal in the Tilaran Mountains is the most active volcano, which erupts almost every day. The Central Mountains in the southeastern parts house many more volcanoes such as Irazu, Barva, Poas, etc. Along the Panama borders in the south, the higher elevation Talamanca Mountains are located.
To the south of Lake Nicaragua and eastward along the San Juan River, the heavily-forested northern plains are located. The rainforest is located in the southern regions of the country, especially edging the Central Mountains and along the Caribbean coastline’s sandy beaches.
The Pacific coastline is very narrow and is covered by picturesque beaches. Many small bays indent the coastline. The hook-shaped peninsulas protect both the Gulf of Nicoya and the Gulf of Dulce, which in turn indent the coastline. The coastal hills of the mountains rise abruptly from the beaches in the western parts of Costa Rica.
The Costa Rican climate in the coastal areas and plains remains hot across the year. The plateau in the tierras templadas has a milder climate. As the country is located near the Equator, the variation in temperature is very low. Rainfall takes place throughout the country and that’s why there is a dense cover of rainforest almost throughout Costa Rica.
There are mainly two seasons found in Costa Rica and they are the rainy season and dry season. While the rainy season lasts from May-to-November, the dry season lasts from December-to-April. An equatorial climate can be found in the eastern plains and coasts, mainly because of abundant rainfall across the year.
Costa Rica is an upper-middle-income economy that has not only experienced steady economic growth in the last two and half decades. Its economic growth is mainly propelled by an outward-oriented strategy, which is primarily based on gradual trade liberalization and openness to FDI. The main strengths of the Costa Rican economy are steady growth, social contract, and political stability.
The nominal GDP of the economy grew at a rate of 2.664% to become US$ 60.126 billion in 2018. During 2000-2013, the per capita GDP grew at 4.5%, which is significantly higher than the 3.8% regional average.
The major exports of the country are optical/technical/medical apparatus, fruits, nuts, coffee, tea, spices, vegetables, miscellaneous food preparations, etc. In 2018, US$ 11.3 billion worth of goods were exported. The major imported items are mineral fuels (including petroleum oil), machinery, electronic equipment, vehicles, plastics, etc. In 2018, they imported US$ 16.6 billion worth of goods, giving rise to US$ 5.3 billion trade deficit.
In 2018, the unemployment rate was 8.13% and 21.1% of the Costa Rican population (1,142,069 people) lived in poverty. 360,783 Costa Ricans live in extreme poverty.
Costa Rica has 161 airports, out of which 47 have paved runways and 114 have unpaved runways. The most important airports of the country are Juan Santamaría International Airport, Tobías Bolaños International Airport, Liberia International Airport, etc.
The country has 5,035 km (3,129 mi) long roadway and 278 km (173 mi) of the railway (all of them are narrow gauge). 730 km (454 mi) of the waterway is also available, which is mainly suitable for small craft navigation on a seasonal basis. There are two major seaports in the country. While Caldera port is situated on the Pacific Ocean, the Puerto Limon seaport is located on the Atlantic Ocean (Caribbean). There are 11 merchant marine ships in Costa Rica.
WTO, UN, IMF, ILO, Union Latina, Interpol, UNESCO, BCIE, CACM, CD, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, MIGA, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, SICA, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), NAM (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), OIF (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…