
Map of Comoros
| Official Name | Union of the Comoros |
| Continent | Africa |
| Capital | Moroni |
| Largest City | Moroni |
| Coordinates | -11.735901, 43.327406 |
| Area | 863 sq mi ( 2,235 sq km) |
| Land Boundaries | 0 mi ( 0 km) |
| Coastline | 211 mi ( 340 km) |
| Currency | Comorian franc (KMF) |
| Neighboring Countries | Maritime neighbors: Mozambique, Madagascar, Mayotte (FR) |
| Population | 850,688 (2018 est. ) |
| Official Languages | Arabic, Comorian, French |
| Major Religion | Sunni Islam |
| National Day | 6 July (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Udzima wa ya Masiwa” |
| Form of Government | Federal presidential republic |
| President | Azali Assoumani |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 2,827.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 1,445.5 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.503 (2017), Rank: 165 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 0 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +269 |
| Time Zone | UTC+3 (EAT) |
| Internet TLD | .kW |
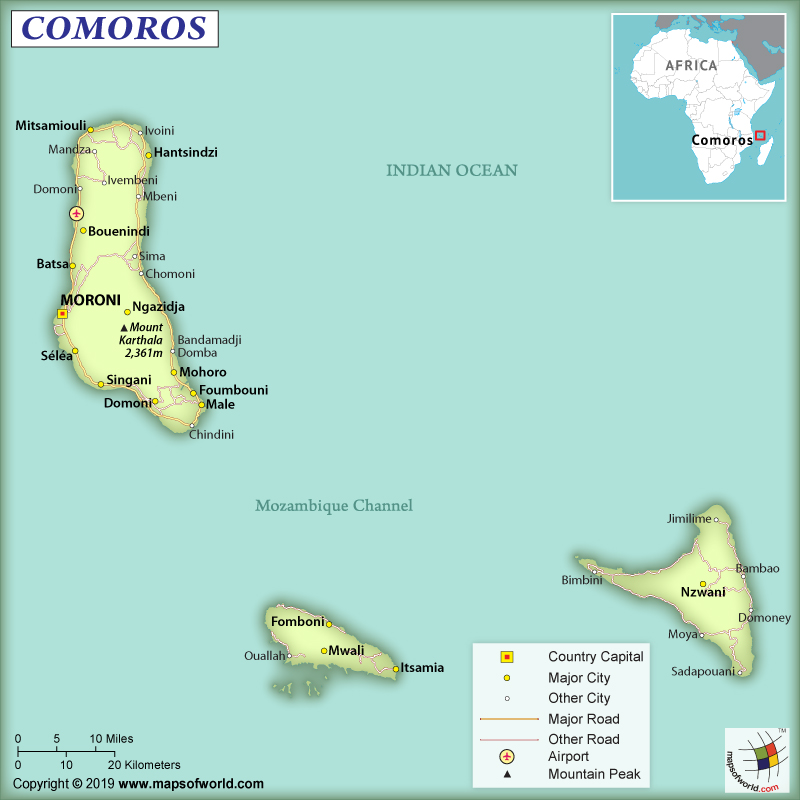
Comoros is an archipelago that is aligned along a northwest-southeast axis at the Mozambique Channel’s northern end between the island of Madagascar and Mozambique. From the eastern coast of Africa, they are located 290 km (180 mi) away.
Comoros consists of 4 main islands – Grande Comore (Njazidja), Mayotte (Mahoré), Anjouan (Nzwani), and Mohéli (Mwali). Though the places are popularly known by their French names, they are officially known by their Swahili names (within the parentheses above). Njazidja is located 231 km (144 mi) away from Mahoré, 79 km (49 mi) away from Mwali, and 129 km (80 mi) away from Nzwani.
Njazidja and Nzwani mostly have mountainous landscapes and that’s why the landscapes are not capable of retaining water properly. The terrains inside the islands include both steep mountains and low hills. Naturally occurring running water is non-existent in these islands. However, Mahoré and Mwali have lots of naturally occurring water sources and streams.
This country doesn’t have any land border. The total area of the country is 2,235 sq km (863 sq mi). The most significant aspect of these islands is that they are formed by volcanic activity. Comoros Archipelago’s largest island is Ngazidja. The distinctive characteristic features of the terrain in the island is rocky soil, one active volcano (Karthala), one dormant volcano (La Grille), and lack of good harbors.
The smallest island in this archipelago is Mwali. Nzwani is characterized by the distinctive triangular shape of the island. This unique shape is caused by the chain of 3 mountains (Jimilimé, Nioumakélé, and Sima) that originate from 1,575 m or 5,167 ft tall central peak called Mount N’Tingui.
The highest elevation point of Comoros is an active volcano named Mount Karthala having a height of 2,361 m (7,746 ft). The lowest elevation point of the country is the Indian Ocean at 0 m.
Comoros Archipelago’s climate can be categorized as marine tropical. There are mainly two types of seasons. From November to April, the season remains hot and humid, caused by the northeastern monsoon. During March to October, the season remains cool and dry.
Along the coastal areas, the average monthly temperatures vary from 23 °C to 28 °C (73.4 °F to 82.4 °F). The average annual rainfall in Comoros is 2,000 mm (78.7 in). Cyclones generally take place during hot and wet seasons. They cause extensive damages in the country, especially along the coastal belts.
Comoros is one of the poorest countries in the world whose nominal GDP in 2018 was US$1.203 Billion. Around 80% of the population is engaged in the primary sector (including agriculture, forestry, hunting, and fishing). The unemployment rate is also considerably high, which is around 20%.
Major export items are vanilla, perfume essence called ylang-ylang, copra, and cloves. As Comoros has a huge population in comparison to its size, the country is not self-reliant in food production and that’s why has to import rice, food items, petroleum products, consumer goods, etc.
Combating hunger and malnutrition are the main concerns of the country. If the international poverty line (US$1.9 per capita per day) is considered, 18% of the total population in Comoros lives in poverty. The incidence of poverty is higher in rural areas, especially in Mwali Island.
The rate of maternal mortality is significantly high, which is 335 per 100,000 births. 30% of the children below 5-years of age suffer from chronic malnutrition as well as stunted growth. The infant mortality rate is also significantly high. 2017 figures show 69 deaths per 1,000 births of children below 1-year. The death rate of children below the age of 5-years is 52.2 per 1,000 births.
The economy is growing at a steady 2.8% in 2018, thanks to the growth experienced in the telecom sector and electricity supply. However, the challenges before the economy are political uncertainty, sluggishness in private sector lending (growing at just 5.1% in 2018), increasing non-performing loans, bank liquidity shortage, government-owned Postal Bank’s governance problems, the bloated wage bill of the civil service, erratic fiscal revenues, and increasing external debt.
The Comoros government has started strengthening the public infrastructural projects including improvement of roads as well as of El-Maarouf hospital’s reconstruction. They are also trying to boost the tourism and telecom industries. Remittances from the Diasporas still help in supporting private consumption. All these factors are likely to help average real GDP reach 3.2% in the coming years.
The roadways mainly serve the coastal areas of Comoros. The surface travel becomes difficult in the mountainous terrains. The country has 880 km (547 mi) of road, out of which 673 km (418 mi) are paved ones.
There are 4 airports in Comoros and all of them have paved runways. While one airport has 2,438 m (7,999 ft) long runways, other 3 airports have shorter than 1,523 m (4,997 ft) runways. The country has 3 seaports and they are Moutsamoudou, Moroni, and Fomboni. Comoros doesn’t have any railway network or a merchant marine.
UN, ACP, AfDB, WHO, AMF, IMF, AOSIS, AU, NAM, COMESA, FAO, FZ, ILO, G-77, IBRD, OPCW, ICAO, Interpol, ICCt, ICRM, UNCTAD, IDA, IDB, IFAD, UNESCO, IFC, IFRCS, UNIDO, IMO, IOM, IMSO, InOC, IOC, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, OIC, OIF, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs), WTO (observer), CAEU (candidates)
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…