What are the Key Facts of Chile?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Chile |
|
Continent |
South America |
|
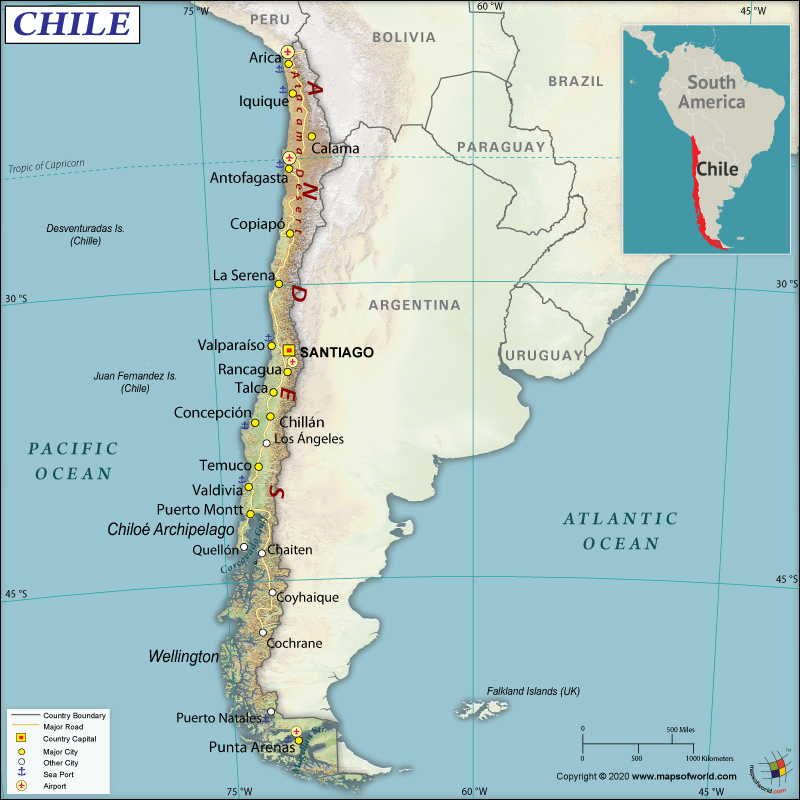
Capital |
Santiago |
|
Largest City |
Santiago |
|
Coordinates |
-30.000000, -71.000000 |
|
Area |
291,930.4 sq. mi ( 756,096.3 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
4,847 mi ( 7,801 km) |
|
Coastline |
3,999 mi (6,435 km) |
|
Currency |
Peso (CLP) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Peru, Bolivia, Argentina |
|
Population |
17,574,003 (2017 Census) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
18 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Himno Nacional de Chile” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Sebastián Piñera |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 25,283.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 15,923.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.843 (2017), Rank: 44 |
|
Literacy Rate |
96.40 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
35 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
13 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
56 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−3 and −5 (CLT and EAST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.cl |
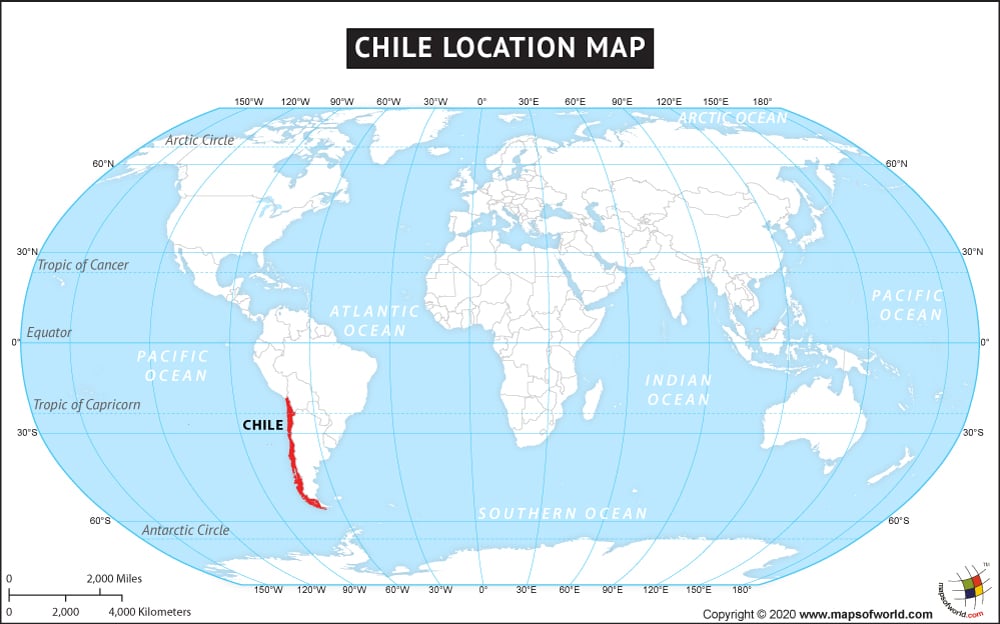
Where is Chile?
Chile is located in the southern parts of South America, bordering the South Pacific Ocean. It shares its borders with Argentina, Bolivia, and Peru.
What is the Geography of Chile?
Chile is spread across a total area of 756,096.3 sq. km (291,930.4 sq. mi), out of which 743,812 sq. km (287,187 sq. mi) is land area and rest 12,290 sq. km (4,745 sq. mi) is water area. This South American country has a total land boundary of 7,801 km (4,847 mi), which is shared with three countries: Argentina 6691 km (4,158 mi), Bolivia 942 km (585 mi), and Peru 168 km (104 mi). Chile has a 6,435 km (3,999 mi) long coastline.
The long, pencil-thin Chile is located between the world’s most extended mountain range, Andes, and the Pacific Ocean. From one tip of the country to the other, there are incredibly diverse landforms. The terrain is characterized by the rugged Andes (with snow-capped peaks) in the east, volcanoes, fjords, glaciers, driest desert of the world, fertile central valley, low coastal mountains, and numerous archipelagos. Varied archipelagos (mainly mountainous islands) are located in the far south near the coastline.
Northern and Southern Patagonian ice fields enrich the diverse landscape of Chile. Besides Antarctica and Greenland, the world’s most enormous continental mass of ice is found in this South American country. Many glaciers start branching off from these ice fields and continue till sea level. The water melting from these glaciers gathers to form lakes. The second-largest South American lake, General Carrera, is formed from the meltwater of such glaciers.
Dozens of rivers rise in the Andes mountain range’s upper reaches. These rivers either flow to the eastern direction entering the neighboring country Argentina or flow to the Pacific Ocean. The longest rivers of the country are Loa, Bío-Bío, Maipo, Maule, Baker, etc.
The plateau in the valley has an elevation within 2,000 ft (610 m) and 4,000 ft (1,219 m). The mean elevation of the country is 6,138 ft (1,871 m). While the highest elevation point is Nevado Ojos del Salado at 6,880 m (22,572 ft), the lowest elevation is sea level at the Pacific Ocean. The significant mountains of Chile are Ojos del Salado, Llullaillaco, Marmolejo, Pomerape, Acotango, and many more.
Chile has a diverse climate as it extends 2,500 mi (4,025 km) from north to south. While you get a milder climate near the coast, a far colder climate can be found in the mountainous areas. Overall, the climate can be characterized as temperate. While summer lasts from December-to-February, winter lasts from June-to-August.
Arid temperate climate can be found in the northern parts of Chile. The temperature in this arid desert climate varies from a maximum of 32 ˚C (90 ˚F) to a minimum of -2 ˚C (28 ˚F). In the central region, the Mediterranean climate can be found. The wet season in the central fertile region lasts from May to August. In the southern parts, the climate is cold and damp. A humid subtropical climate can be found in the Easter Island. Very high annual rainfall takes place in most of the southern parts, especially from Region VII and down.
What is the Economy of Chile?
Chile has a market-oriented economy that is driven mainly by a high level of foreign trade as well as strong financial institutions. Exports account for 1/3rd of the total GDP. The main export item is copper, which also contributes to 20% of the government revenue.
In 2018, the nominal GDP of Chile was US$298 billion, and it grew at 4%. The growth rate of the country was, on an average, 5% from 2003 to 2013. It came down to 1.4% in 2017 because of the global financial crisis. However, it rebounded to 4% in 2018. The Chilean economy is the fastest growing in entire Latin America in recent decades. The country has been successful in bringing down the poverty level (population living under a per day income of US$ 5.5) from 26% in 2000 to 7.9% in 2015. It further dropped to 6.4% in 2017.
What is the Transportation System of Chile?
The main form of transport in Chile is the road. The country has 77,801 km (48,383 mi) of roadways, out of which more than half are paved, and the rest are unpaved. The main highways of Chile are five namely 7, 9, 68, and 181. The country has 2,653 km (1,648 mi) long freeways, and one of the most important ones is Autopista del Sol. Though buses are the primary road transport system in Chile, on-call taxis and collectives are also a prevalent mode of transport.
Over 7,282 km (4,525 mi) of railways are also there in Chile, out of which 3,853.5 km (2,394 mi) are narrow gauge, and 3,428 km (2,130 mi) is the broad gauge. Electricity driven trains run 1,691 km (1,051 mi) across the country. Almost all the trains are operated by Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado (a state-owned company). Airways are also significantly developed. There are 481 airports in Chile, out of which 90 have paved runways, and 391 have unpaved runways. One heliport is also there in the country.
There are 222 merchant marine ships in Chile. The major seaports are Coronel, Valparaiso, San Vicente, San Antonio, Puerto Ventanas, Lirquen, and Huasco.
What International Organizations is Chile part of?
Union Latina, WTO, APEC, WHO, UN, BIS, UNWTO, CD, UNESCO, CELAC, UNASUR, FAO, G-15, G-77, Pacific Alliance, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, NAM, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, UNCTAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, MIGA, MINUSTAH, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMOGIP, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, CAN (associate), ICC (national committees), Mercosur (associate), ITUC (NGOs), OECD (enhanced engagement), SICA (observer), WFTU (NGOs)