
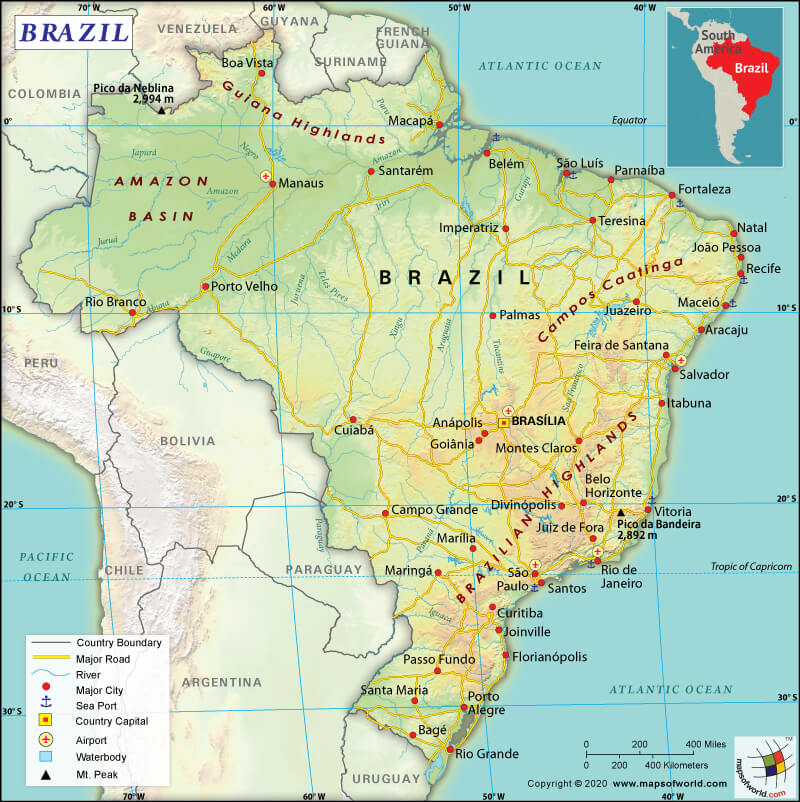
Map of Brazil which lies in the Continent of South America
| Official Name | Federative Republic of Brazil |
| Continent | South America |
| Capital | Brasília |
| Largest City | São Paulo |
| Coordinates | -10.000000, -55.000000 |
| Area | 3,287,956 sq. mi ( 8,515,767 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 10,032 mi ( 16,145 km) |
| Coastline | 4,655 mi ( 7,491 km) |
| Currency | Real (R$) (BRL) |
| Neighboring Countries | Uruguay, Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia, Peru, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana |
| Population | 211,049,530 (World Bank, 2019) |
| Official Languages | Portuguese |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 7 September (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Hino Nacional Brasileiro” |
| Form of Government | Federal presidential constitutional republic |
| President | Jair Bolsonaro |
| Vice President | Hamilton Mourão |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 15,258.9 (World Bank, 2019) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 8,717.2 (World Bank, 2019) |
| HDI | 0.761 (2019), Rank: 79 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 93.23 (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | Brazilian Space Agency (AEB) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 11 (SIPRI, 2019) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 129 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | 55 |
| Time Zone | UTC−2 to −5 (BRT) |
| Internet TLD | .br |
Brazil is an Eastern South American country bordering the Atlantic Ocean.
Brazil is spread across a total area of 8,515,767 sq. km (3,287,956 sq. mi), out of which 8,358,140 sq. km (3,227,096 sq. mi) is land area and 157,630 sq. km (60,861 sq. mi) is water area. This estimate of the total area includes Arquipelago de Fernando de Noronha, Penedos de Sao Pedro e Sao Paulo, Ilhas Martin Vaz, Ilha da Trindade, and Atol das Rocas. Brazil’s coastline is 7,491 km (4,655 mi) long.
Here is Brazil Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
Brazil has a 16,145 km (10,032 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with ten countries. The country shares border with Bolivia (3,403 km or 2,115 mi), Peru (2,659 km or 1,652 mi), Venezuela (2,137 km or 1,328 mi), Colombia (1,790 km or 1,112 mi), Paraguay (1,371 km or 852 mi), Guyana (1,308 km or 813 mi), Argentina (1,263 km or 785 mi), Uruguay (1,050 km or 652 mi), French Guiana (649 km or 403 mi), and Suriname (515 km or 320 mi).
Low mountain ranges, as well as forested river valleys, cover the Brazilian Highlands. A natural barrier is created between the interior of Brazil and the Atlantic Ocean by a series of higher mountain ranges, extending from Rio de Janeiro to Fortaleza. The largest freshwater wetland known as Pantanal is located in Brazil. Tributaries of many rivers feed this wetland. Pantanal is around ten times larger than that of the Florida Everglades.
Around 60% of the largest tropical rain forest, Amazon, is situated in Brazil itself. The huge Amazon River along with over 200 tributaries drains this tropical rain forest. The longest river that is situated completely within the confines of Brazilian borders is called the Sao Francisco. Almost the entire stretch of northern South America is covered by a rain forest covered mountainous area, which is relatively flat-topped. It is called the Guiana Highlands. The most spectacular waterfalls are located within Brazil.
The major mountains of the country are Pico da Bandeira (or Flag Peak), Pedra da Mina, Mount Roraima, Pico do Monte Negro, Sugarloaf Mountain, etc. Besides the Amazon and San Fransisco Rivers, there are other major rivers too in the country and they are Parana, Araguaia, Tocantins, Paraguay, and others.
As the country is spread across a large area with a wide array of landforms, the climatic conditions vary from one place to another. There are 6 major climatic subtypes present in Brazil (as per Köppen system) and they are tropical, subtropical, equatorial, oceanic, desert, and subtropical.
While equatorial rainforests are located in the north, semiarid deserts are there in the northeast part of Brazil. The central part of the country has tropical savannas and the south has temperate coniferous forests. Varied microclimates can be found in many regions. Northern Brazil has an equatorial climate, which has no dry season. However, the extent of rainfall varies over the year. The average temperature over the year hovers around 25 °C (77 °F). A savanna climate is found in the central Brazilian region, where the rainfall is seasonal. Even more extreme seasonal rainfall takes place in the interior northeast region of Brazil.
The semiarid climatic region receives less than 800 mm (31.5 in) of rainfall. In a year, this region receives 3-to-5 months of rainfall. However, sometimes these Brazilian regions receive less than the usual rainfall, which consequently leads to long periods of drought.
Subtropical climate conditions are found in the coastal areas (such as south of Bahia) and other regions in the south (such as most parts of Sao Paulo). This climate is characterized by cool winters. However, the yearly average temperature doesn’t go above 18 °C (64.4 °F). These regions also get snowfall and winter frosts occasionally.
Brazil has one of the largest economies of the world. In 2018, the nominal GDP of the country was US$ 1.869 trillion and it grew at 1.118% annual rate. During 2003-2014, the economy witnessed significant progress. The economy successfully decreased inequality and uplifted 29 million people out of poverty. The poorest 40% of the total population witnessed an average rise in income by 7.1%, which is significantly more than the average increase in income of the entire population.
The Brazilian economy started contracting since 2015. The annual growth rate of GDP decelerated to 3.6% in 2015 and 3.4% in 2016. The economy came to halt in May 2018 due to lack of investment (mainly due to volatile political scenario), weak labor market, and continued general strike of the truckers across the country. Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics’ data shows that extreme poverty in the country in 2017 increased by 11%.
Roadways are the primary form of transport for both passengers and freight. 2 million km (1242742 mi) of roadways are present in Brazil, out of which 246,000 km (152,857 mi) is paved and 1.754 million km (1,089,885 mi) is unpaved.
The country has an extensive railway network that is 29,850 km (18,548 mi) long. Most of the railway tracks are narrow gauge (23,341.6 km or 14,503.8 mi) and broad gauge (5,822.3 km or 3,617.8 mi). The rest of the network is dual gauge (492 km or 305.7 mi) and standard gauge (194 km or 120.5 mi).
Airways are significantly developed in the country. There are 4,093 airports, out of which 698 airports have paved runways and 3,395 have unpaved runways. The main international airports are Rio de Janeiro–Galeão International Airport and São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport. 13 heliports are also there in the country.
50,000 km (31,068.6 mi) of waterways is there, mainly in the remote places. Belem, Tubarao, Sao Sebastiao, Santos, Rio de Janeiro, Rio Grande, and Paranagua are the main seaports of Brazil. There are 791 merchant marine ships in the country.
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, BIS, BRICS, UNASUR, CD, UNESCO, CELAC, Union Latina, CPLP, UNIDO, FAO, UNISFA, FATF, UNMIL, G-15, MINUSTAH, G-20, OPANAL, G-24, G-5, G-77, WMO, IADB, UNCTAD, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, NSG, ICCt, Interpol, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, Mercosur, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, OAS, OPCW, PCA, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIFIL, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, AfDB (nonregional member), CAN (associate), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), LAS (observer), NAM (observer), OECD (enhanced engagement), Paris Club (associate), SICA (observer)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…