What are the Key Facts of Bhutan?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Bhutan |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Thimphu |
|
Largest City |
Thimphu |
|
Coordinates |
27.500000, 90.500000 |
|
Area |
14,824 sq. mi ( 38,394 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
706 mi ( 1,136 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Ngultrum (BTN) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
India, China |
|
Population |
727,145 (2017 Census) |
|
Official Languages |
Dzongkha |
|
Major Religion |
Buddhism |
|
National Day |
17 December (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Druk tsendhen” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
King |
Jigme Khesar Namgyel Wangchuck |
|
Prime Minister |
Lotay Tshering |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 10,516.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 3,360.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.612 (2017), Rank: 134 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
66.56 % (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+975 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+6 (BTT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.bt |
Where is Bhutan?
Bhutan is a South Asian country that is located between India and China. It is situated in the eastern Himalayan region. Bhutan shares its land border with China’s Tibet Autonomous Region in the north, Tibet’s Chumbi Valley in the west, and with India in the west (Sikkim state), east (Arunachal Pradesh state), and south (Assam and West Bengal state).
Bhutan Flag
One of the national symbols of the Kingdom of Bhutan, the Bhutanese national flag was officially adopted in 1969. The flag of Bhutan is diagonally separated into two halves: the upper left half is orange/ yellow and the lower right half is orange. In the middle of the flag is an emblem of a white dragon facing to the right. The dragon is seen holding jewels in its claws and these signify the nation’s wealth.
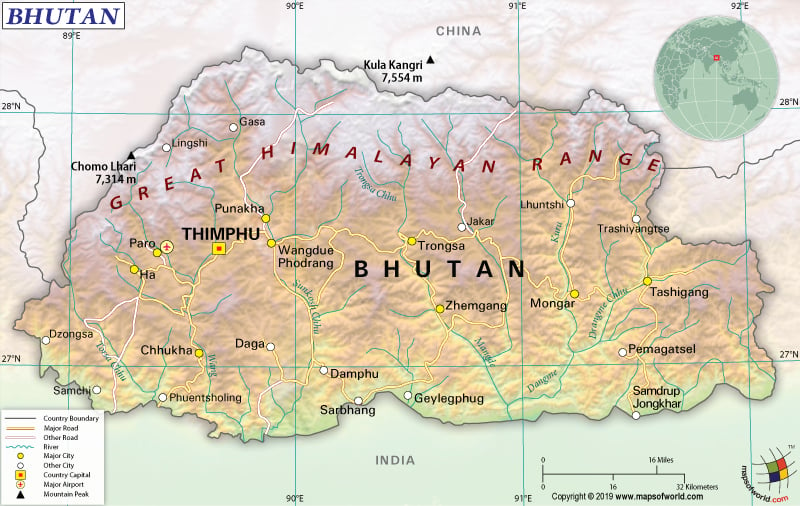
What is the Geography of Bhutan?
Bhutan is spread across a total area of 38,394 sq. km (14,824 sq. mi), out of which 38,394 sq. km (14,824 sq. mi) island area and no water area. It has a 1,136 km (706 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with India (659 km or 409 mi) and China (477 km or 296 mi). As it is landlocked, there is no coastline.
The terrain is mostly mountainous. However, some fertile valleys, as well as savanna, are also there. The mean elevation of Bhutan is 2,220 m (7,283 ft). While Gangkar Puensum is the highest elevation of the country at 7,570 m (24,836 ft), the lowest elevation point is Drangeme Chhu at 97 m (318 ft).
Other major mountains in Bhutan are Liangkang Kangri, Chomolhari Kang,
Tongshanjiabu, Kangphu Kang I, Chomolhari, Liangkang Kangri, etc. The major rivers in the country are Drangme Chhu, Wang Chhu, Mo Chhu, and Torsa Chhu.
The landscape of Bhutan mainly consists of steep mountains as well as deep valleys having rugged land. The southern border with India is dominated by the lowlands. The central region of the country consists of the lower Himalayas. The massive peaks of the Himalayas are mainly located along the northern border with China.
The climatic condition in Bhutan varies in accordance with the altitude. The climatic condition in the highest mountainous regions in the northern parts of Bhutan is very similar to the arctic climate. The weather in the southern parts gets cool winters (December-February) and hot/humid summers (June-August).
Bhutan usually gets heavy monsoon. The best time to visit the lower parts of the country is during winter. The highest regions get freezing cold during winter. Spring persists during March-May and autumn from late September to November. Both spring and winter are the best times to visit Bhutan. During these seasons, the weather remains sunny, warm, and dry.
The climatic condition ranges from semi-tropical to alpine, depending on the altitude. With every increase of 1,000 m (3,281 ft) height, there is a drop in temperature by 7 ˚C (44.6 ˚F). A tropical climate prevails during the monsoon season in Southern Bhutan. The temperature revolves around 15 ˚C (59 ˚F) during winter and around 30 ˚C (86 ˚F) during summer. The eastern regions are warmer than the western regions of Bhutan.
The sub-tropical climate is found in the central parts of Bhutan. The winters remain cool. Harsh climate is found in the northern regions, which involves 2-3 times rainfall during winters. In high mountainous regions, the average temperature revolves from 0 °C (32 °F) during winter to 10 C (50 °F) during summer and the average rainfall is around 350 mm (14 in).
What is the Economy of Bhutan?
The economy of Bhutan is small and is mainly dependent upon hydropower, forestry, and agriculture. Industrial production is mainly cottage industries. Hydropower is the largest export of the country, which accounts for 40% of total exports and 25% of the total revenue of the Bhutanese government.
The nominal GDP of Bhutan has decreased from 8.022% in 2016, 4.629% in 2017 to 2.291% in 2018. The nominal GDP was US$2.535 billion in 2018. The economy imports more valued products than its exports. In 2017, it exported US$194 million value of items and imported US$482 million value of products. It resulted in a negative balance of trade amounting to US$288 million.
The major export items of Bhutan are ferroalloys, dolomite, carbides, raw plastic sheeting, gypsum, etc. The major import items of the country are cars, forging machines, iron reductions, large construction vehicles, refined petroleum, etc. While India, France, Germany, Italy, and Nepal are the major export destinations of Bhutan, the major import partners of the country are India, the USA, Singapore, Japan, and South Korea.
The unemployment rate has dropped from 3.96% in 2009 to 2.2% in 2019. The rate of poverty has dropped from 12% in 2012 to 8.2% in 2017. The poverty rate reduced as much as 19.7% during 2004-2012. Reports say that emphasis on increasing economic prosperity by improving the living standard of people of the country has helped the Bhutanese government decrease the poverty rate significantly. Some of the pioneering poverty reduction programs implemented since 1961 include Rural Economy Advancement Program, National Rehabilitation Program, Common Minimum Program, etc.
What is the Transportation System of Bhutan?
The transport system in Bhutan is limited because it is difficult to build roadways as well as other infrastructure. It has a 12,205 km (7,584 mi) long roadway, out of which 437 km (272 mi) is an urban roadway. There are three airports in the country, out of which 2 are paved and one is unpaved. These airports are Paro International Airport, Bathpalathang Airport, and Yonphula Airport.
What International Organizations is Bhutan part of?
UN, WHO, IMF, UNESCO, SAARC, NAM, ADB, BIMSTEC, CP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IFAD, IFC, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, OPCW, SACEP, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), IOM (observer), ISO (correspondent)
Related Links: