
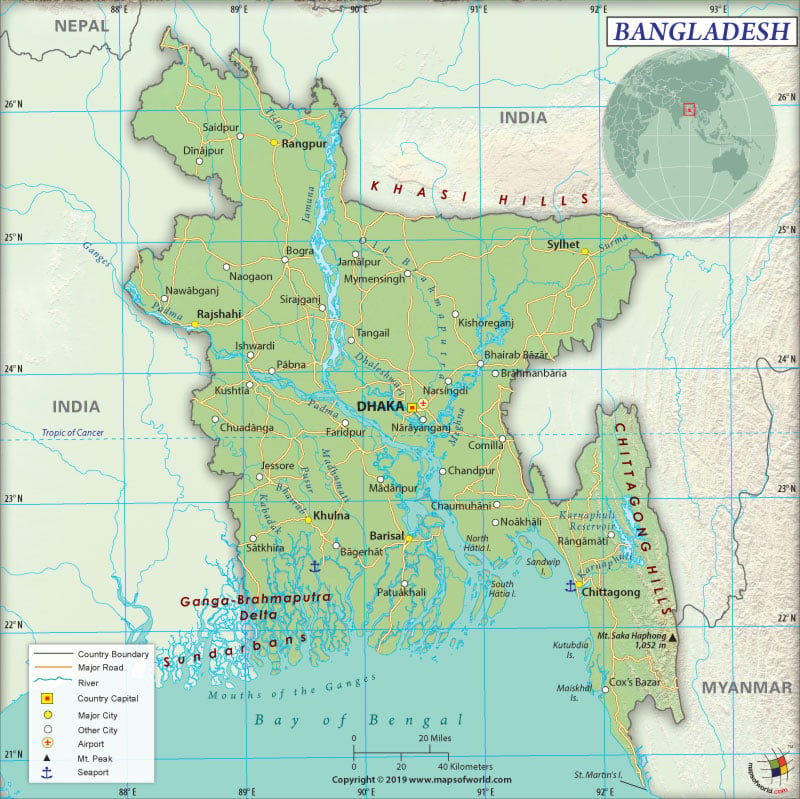
Map of Bangladesh which lies in the continent of Asia
| Official Name | People’s Republic of Bangladesh |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Dhaka |
| Largest City | Dhaka |
| Coordinates | 24.000000, 90.000000 |
| Area | 56,980 sq. mi ( 147,570 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 2,742 mi ( 4,413 km) |
| Coastline | 360 mi ( 580 km) |
| Currency | Bangladeshi taka (BDT) |
| Neighboring Countries | India, Myanmar |
| Population | 161,376,708 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | Bengali |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | December 16 (Victory Day), March 26 (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Amar Shonar Bangla” |
| Form of Government | A unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
| President | Abdul Hamid |
| Prime Minister | Sheikh Hasina |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 4,364.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 1,698.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.608 (2017), Rank: 136 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | 73.91 % (UNESCO, 2018) |
| Space Agency | Space Research and Remote Sensing Organization (SPARRSO) |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 44 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 0 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | left |
| Calling Code | +880 |
| Time Zone | UTC+6 (BST) |
| Internet TLD | .bd |
Bangladesh is a South Asian country that borders the Bay of Bengal and is located between India and Myanmar. The People’s Republic of Bangladesh shares its land boundary with India to the east, north, and west and Myanmar to the Southeast. The Bay of Bengal is located in the south of Bangladesh.
Bangladesh is spread across a total area of 147,570 sq. km (56,980 sq. mi), out of which 130,170 sq. km (50,259 sq. mi) is land area and 18,290 sq. km (7,062 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 4,413 km (2,742 mi) long land boundary that is shared with India (4142 km or 2,574 mi) and Myanmar (271 km or 168 mi). Its coastline is 580 km (360 mi) long.
The terrain mostly consists of flat alluvial plain with hills in the southeast portion. The mean elevation of the country is 85 m (279 mi). While Keokradong is the highest elevation point of Bangladesh at 1,230 m (4,035 mi), the lowest elevation point is the Indian Ocean at 0 m (0 ft).
The most common landform of Bangladesh includes the alluvial lowlands of the Plain of Bengal. The Mouths of the Ganges in the Bay of Bengal (the largest delta of the world) is created by numerous rivers as well as their associated streams. The Sundarbans, the ragged and swampy coast, is the major landform. Along the southeastern border with India and Myanmar, the most extensive uplands of Bangladesh (Chittagong Hill Tracts) are located. These linear, north-south belts of hills are covered by tropical forest.
Some of the major mountains in Bangladesh are Saka Haphong, Thingdawl Te Tlang, Jogi Haphong, Dumlong, Zow Tlang, etc. The major rivers in the country are Brahmaputra, Ganges, Teesta, Mahananda, Raidak, Atrai, Suma, etc.
A subtropical monsoon climate persists in Bangladesh. Wide seasonal variations are found in terms of temperature, humidity, and rainfall. There are three seasons that are found here and they are monsoon, winter, and summer. The monsoon rainy season persists during June-October, the hot and humid summer persists during March-June, and the cool and dry winter season persists during October-March. During summer, the maximum temperature ranges within 30-40 °C (86-104 °F). While April is the hottest month, January is the coldest month. The average temperature hovers around 10 °C (50 °F) in January.
Most parts of Bangladesh get an average annual rainfall of at least 2,000 mm (79 in). The relatively drier regions in the western parts of the country (Rajshahi) get around 1,600 mm (63 in) of annual rainfall. Sometimes, the extent of rainfall can also reach 4,000 mm (157 in) or above.
The economy is growing at a rate of 6% per annum since 2005. The nominal GDP grew at a rate of 7.9% in 2018 to become US$288,424 billion. The services sector generates more than 50% of the GDP. Around half of the total workforce is still employed in agriculture.
The garments industry is the backbone of Bangladesh’s industrial sector, accounting for over 80% of the total exports. The foreign exchange reserve of the country swelled mainly because of the remittances sent by the Bangladeshis from abroad.
In 2017, Bangladesh had a negative balance of trade of US$4.73 billion, resulting from the total value of exports and imports of US$39.2 billion and US$44 billion respectively. The major export items are non-knit men’s suits and shirts, non-knit women’s suits, knit sweaters, etc. The major imports are wheat, raw cotton, raw sugar, heavy pure woven cotton, and refined petroleum.
The unemployment rate was 4.31% in 2018. Since 2013, it is hovering at around 4.4%. During 2010-16, around 8 million Bangladeshi (mostly from the rural areas) were pulled out of poverty. The rate of poverty in Bangladesh dropped from 31.5% in 2010 to 24.3% in 2016.
There is 8,370 km (5,201 mi) long waterway in the country, which includes up to a maximum of 3,060 km (1,901 mi) of main cargo routes. During the dry season, the network gets reduced to 5,200 km (3,231 mi).
The major seaport of the country is Chittagong, which is also an important container port. Mongla Port on Sela River is an important river port. Bangladesh has 329 merchant marine vessels, which includes 77 general cargo, 33 bulk carriers, 122 oil tankers, 4 container ships, and 93 others.
Bangladesh has an extensive roadway transport system, which is 369,105 km (229,351 mi) long. While 110,311 km (68,544 mi) is paved, 258,794 km (160,807 mi) is unpaved. Over 2,460 km (1,529 mi) long railway network is also available, out of which 1,801 km (1,119 mi) is narrow-gauge and 659 km (409 mi) is broad-gauge.
There are 18 airports in Bangladesh, out of which 16 have paved runways and 2 have unpaved runways. Some of the major airports of the country are Hazrat Shahjalal International Airport, Osmani International Airport, Osmani International Airport, etc.
UN, IMF, WTO, ILO, WHO, ADB, UNESCO, NAM, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CP, D-8, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, OIC, OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, CICA (observer), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…