What are the Key Facts of Bahrain?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Bahrain |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Manama |
|
Largest City |
Manama |
|
Coordinates |
26.000000, 50.550000 |
|
Area |
300.5 sq. mi ( 778.3 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi (0 km) |
|
Coastline |
100 mi ( 161 km) |
|
Currency |
Bahraini dinar (BHD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Saudi Arabia, Qatar |
|
Population |
1,569,446 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
16 December (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Bahrainona” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary Islamic constitutional monarchy |
|
King |
Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 47,219.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 24,050.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.846 (2017), Rank: 43 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
97.46 % (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
Bahraini National Space Science Agency (NSSA) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
66 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
3 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+973 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.bh |
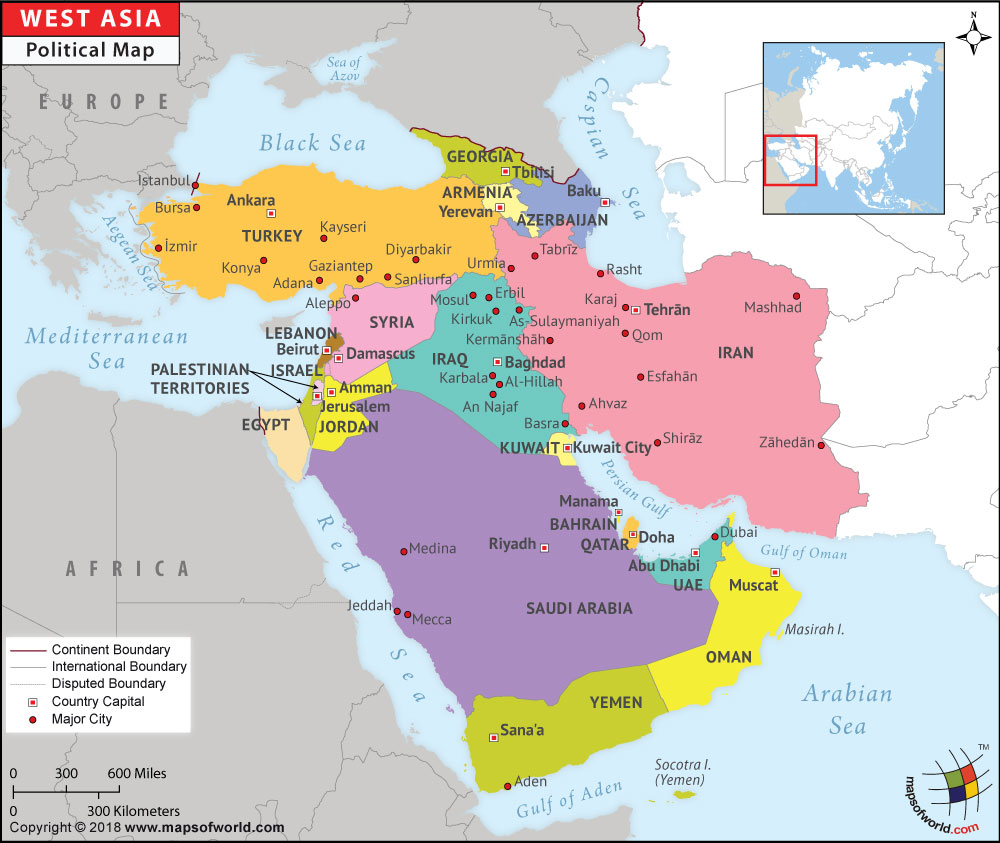
Where is Bahrain?
Bahrain is a west Asian country that is located in the Persian Gulf. This small archipelago centered around Bahrain Island is situated between Saudi Arabia’s northeastern coast and the Qatar peninsula.
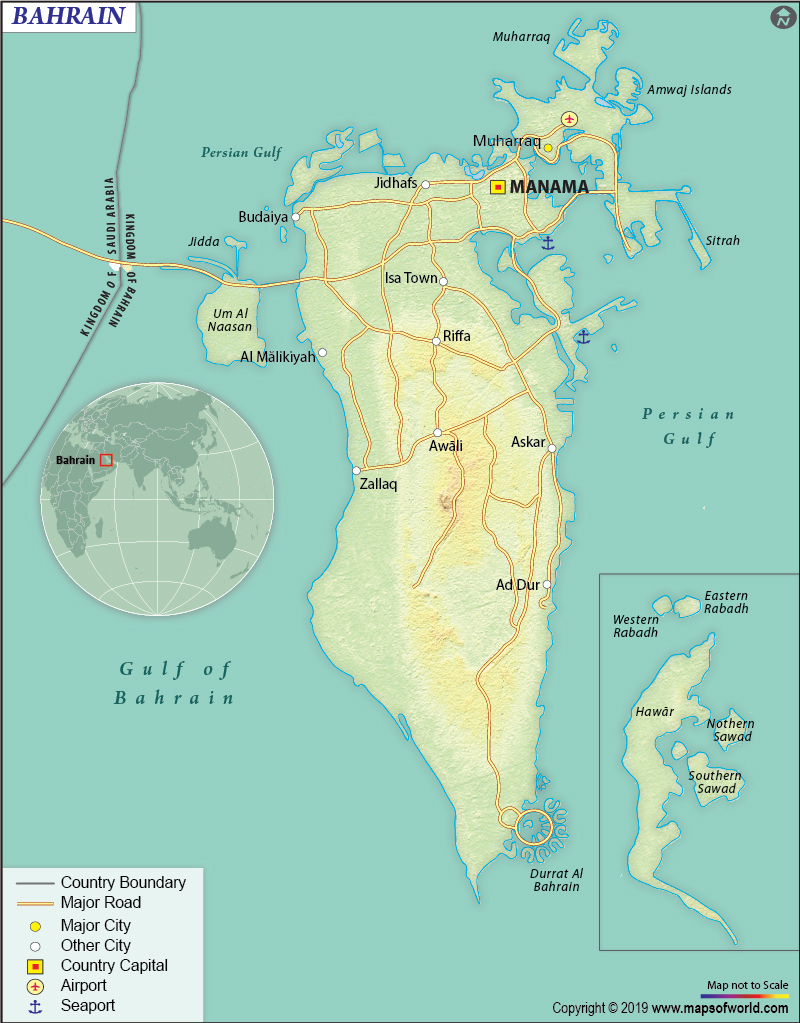
What is the Geography of Bahrain?
Bahrain (consisting one large island along with 32 smaller islands surrounding it) is spread across a total area of 778.3 sq. km (300.5 sq. mi), out of which 760 sq. km (293 sq. mi) is land area and 0 sq. km (0 sq. mi) is water area. It has no land boundary but a 161 km (100 mi) long coastline.
The terrain of Bahrain is dominated by low desert plains that rise gently to the low central escarpment. While an escarpment called Jabal ad Dukhan is the highest elevation point of the country at 135 m (443 ft), the lowest elevation point is the Persian Gulf at 0 m (0 ft).
Around 92% of Bahrain’s landscape is covered by desert, where you will find plains that are both low-lying rocky and sandy. The central and southern parts of the country have coastal salt marshes. The northern part of Bahrain is covered by extensive coral reefs. There are no major rivers/lakes in the country. Some of the major islands are Jidda Island, Nabih Saleh, Umm as Sabaan, etc.
The Nabih Saleh’s landscape is dotted by freshwater springs as well as date palm groves. Most of the uninhabited islands in the archipelago have become important nesting places for migratory birds.
A desert climate prevails in Bahrain, which is characterized by very hot summers and mild winters. Two main seasons are there. While the hot season prevails during April-October (within which May-to-mid-October remains very hot), the cooler season persists during December-February. There are two transitional months: March and November. During these months, the weather remains warm but there are no excesses.
There is a low temperature between day and night because of the influence of the sea. Humidity remains high. However, winds blowing from Arabia’s interior lessen the humidity level. The temperature remains pleasant during December-February, the months of winter in Bahrain. Rainfall is scarce as well as sporadic. Warm days can prevail when the wind starts blowing from the southern parts of the country. Warm days can also be there and the peak temperature can go up to around 30 °C (86 °F). However, this rarely occurs.
Cool and windy days can sometimes prevail during January-February when the temperature at nighttime can come down to around 10 °C (50 °F) and at midday can hover around 15 °C (59 °F).
It can be very hot and sunny during the summers. In the month of May and October, the highs can reach 34-36 °C (93-97 °F) and during June-September it can reach around 38-40 °C (100-104 °F).
The heat becomes tough to bear during summer because of the humidity from the Persian Gulf. August and September are the months when Bahrain gets the highest temperature-humidity combo.
A hot and dry wind called Qaws blow round the year. The moist wind known as Shamal blows more frequently during summer. The extent of rainfall is very low, which is just 70 mm (2.8 in) annually.
The best time to visit Bahrain is between mid-November and mid-March (more preferably during December-February) because of the pleasant and mild weather.
What is the Economy of Bahrain?
The economy of Bahrain is dependent on oil and natural gas, contributing around 85% to the budget revenues. Other major export items are aluminum, finance, and construction.
In 2016, the sovereign debt rating had been downgraded to “junk” by the 3 major credit rating agencies after the lower world energy prices prevailing since the last few years. In 2017, the budget deficit of the Bahrain government was 10%.
The nominal GDP of Bahrain grew at a rate of 1.778% in 2018 in comparison to 3.804% in 2017. The nominal GDP was US$ 37.746 billion in 2018. The country had a negative balance of trade of US$1.55 billion in 2017 as the values of export and import were US$5.58 billion and US$7.13 billion respectively.
The rate of unemployment was 0.96% in 2018. Extreme poverty (people living below US$1 per day) is virtually absent in Bahrain. However, the inequality of income distribution is high. The richest 20% of the population owns around 41.6% of the total income. The poverty level (people living below US$5 per day) is around 12.2%.
What is the Transportation System of Bahrain?
Bahrain has a total roadway of 4,122 km (2,561 mi), out of which 3,392 km (2,108 mi) is paved and 730 km (254 mi) is unpaved. There are 4 airports in the country and all of them have paved runways. 1 heliport is also there. Bahrain International Airport is the main airport of the country. Sitrah and Mina’ Salman are the major seaports of Bahrain. 259 merchant marine ships are there, out of which 12 are general cargo, 1 bulk carrier and container ship each, 4 oil tankers, and 241 other vessels.
What International Organizations is Bahrain part of?
UN, WTO, UNESCO, IMF, NAM, WHO, ILO, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, CICA, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, OAPEC, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), IOM (observer), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link: