
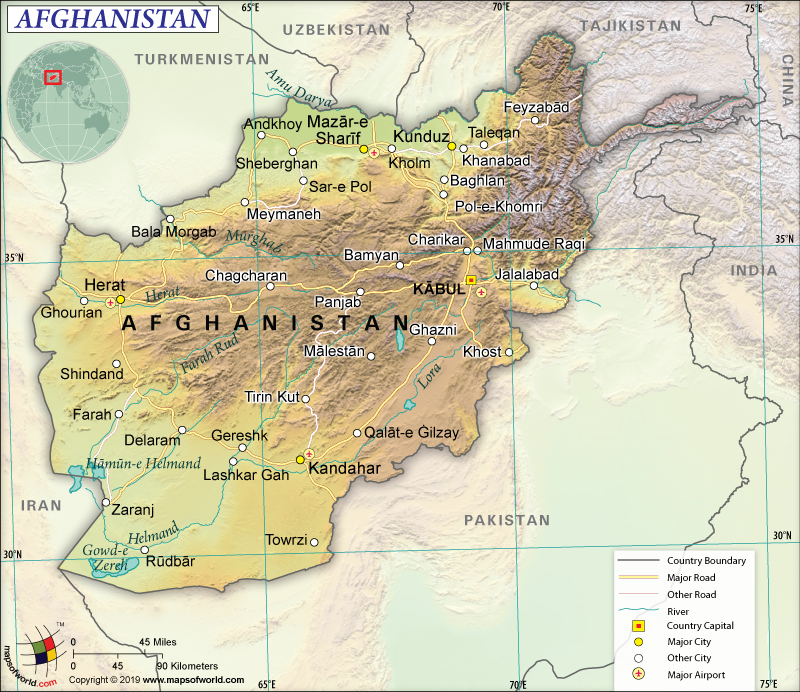
Map of Afghanistan which lies in the Continent of Asia
| Official Name | Islamic Republic of Afghanistan |
| Continent | Asia |
| Capital | Kabul |
| Largest City | Kabul |
| Coordinates | 33.000000, 65.000000 |
| Area | 251,830 sq. mi ( 652,230 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 3,720 mi ( 5,987 km) |
| Coastline | 0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
| Currency | Afghani (Afs) (AFN) |
| Neighboring Countries | India, Pakistan, Iran, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, China |
| Population | 32,225,560 (2019 est.) |
| Official Languages | Pashto, Dari |
| Major Religion | Islam |
| National Day | 19 August (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “Milli Surood” |
| Form of Government | Unitary presidential Islamic republic |
| President | Ashraf Ghani |
| First Vice President | Abdul Rashid Dostum |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 1,951.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 520.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.498 (2017), Rank: 168 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 112 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 2 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +93 |
| Time Zone | UTC+4:30 (AFT) |
| Internet TLD | .af |
Afghanistan is a landlocked country in South-Central Asia. It shares its 5,987 km (3,720 mi) long land boundaries with Pakistan (2,670 km or 1,659 mi) in the east and south, India (117 km or 72 mi) in the north, Tajikistan (1,357 km or 843 mi) in the north, Iran (921 km or 572 mi) in the west, Turkmenistan (804 km or 500 mi) in the north, Uzbekistan (144 km or 89 mi) in the north, and China (91 km or 57 mi) in the far northeast.
Afghanistan is spread over a total area of 652,230 sq. km (251,830 sq. mi), which consists entirely of land area. As the country is completely landlocked, there is no coastline.
In the first place, the terrain in Afghanistan is mainly dotted with rugged mountains. Plains are there in the north and southwest parts of the country. More than half of the landscape is located above the elevation of 2,000 m (6,500 ft). The mean elevation of the country is 1,884 m (6,181 ft). The Himalayas, Karakorum Mountains, and the Pamir Mountains culminate in the high peaks of the Hindu Kush.
In addition, Mt. Nowshak is the highest elevation point of Afghanistan at 7,485 m (24,446 ft). The lowest elevation point of Afghanistan is Amu Darya (258 m or 846 ft), which is a fertile plain in front of the Amu Darya River. Other major rivers of the country are Helmand, Hari, and Panj. In the southern region of the country, the land is covered by the scattered salt flats and rolling desert below the mountains.
Major mountains of Afghanistan are Noshaq, Lunkho, Kōh-e Bandakā, Baba Tungi, etc. Band-e Amir, a part of the Hindu Kush Mountains, is the first national park of the country that includes 6 blue lakes including Band-e Zulfiqar, Band-e Pudina, Band-e Panir, Band-e Haibat, Band-e Qambar, and Band-e Gholaman.
Moreover, Afghanistan has arid continental climate characterized by hot/sunny summers and cold/relatively rainy winters. However, climatic conditions vary substantially as per altitude and area. Deserts are found in the southern parts of the country. High altitudes are rather cold. Even in summertime, the far-east region of Afghanistan is relatively rainy because of the Indian monsoon that affects the climate.
Further, there are 4 distinct seasons in Afghanistan: summer, winter, autumn, and spring. The temperature reaches 50 ⁰C during summer in the lowlands, especially in eastern and southern parts of Afghanistan. In winter, the temperature reaches around 20 ⁰C.
Furthermore, winter temperature may reach as low as -25 ⁰C in the mountainous regions. It can further go down in the higher mountain areas. Snowfall varies according to altitude. However, it generally takes place from October-to-April.
During autumn, the rainfall takes place in the lowlands. At the beginning of a year, rainfall takes place. The agriculture in northern Afghanistan (known as Lalmi) is mainly dependent upon this autumn rain. While the semi-desert or desert areas get as low as 500 mm (20 in) of rain every year, the far eastern parts along the Pakistan border get as much as 1,000 mm (40 in) rain every year.
The wettest month of the year is March. During June-to-September, rain doesn’t take place. The rainfall amount increases in the easternmost region during July-August.
Afghanistan is a war ravaged and extremely poor country whose economy is mainly dependent upon international assistance as well as remittances sent by its expatriates. In 2018, the nominal GDP of the country was US$19.363 billion and it increased by 1% only.
At the same time, the economy witnessed strong progress in the export sector, which reached US$875 million in 2018. This has been possible because of the opening of the air corridors since June 2017. National Air Corridor Program has helped the country export its items to UAE, India, Kazakhstan, EU, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey.
However, the Afghan economy has a US$4.19 billion negative trade balance (2017 data). The main export items are grapes, tropical fruits, insect resins, coal briquettes, and other kinds of nuts. The major imports of Afghanistan are wheat flour, armored vehicles, refined petroleum, delivery trucks, and raw sugar.
Accordingly, the economic recovery of Afghanistan is slow and the continued insecurity concerning terrorism has curtailed both consumer demand and private investment. Though the fiscal condition has improved, poverty has increased. While the unemployment rate is still around 25% of the labor force, the poverty rate is around 55%.
Afghanistan has 34,903 km (21,688 mi) of roadways, out of which 17,903 km (11,124 mi) is paved and 17,000 km (10,563 mi) is unpaved. 1,200 km (746 mi) of waterways are present in the country, especially on Amu Darya River. There are two river ports in Afghanistan and they are Kheyrabad and Shir Khan. The total number of airports in Afghanistan is 43, out of which 25 have paved runways and 18 have unpaved runways. The country also has 9 heliports.
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, WHO, Interpol, ADB, UNCTAD, CICA, UNAMA, CP, UNESCO, ECO, UNHCR, FAO, SAARC, G-77, IAEA, UNIDO, IBRD, ICAO, UNWTO, ICCt, WMO, ICRM, WIPO, IDA, SACEP, IDB, NAM, IFAD, ITU, IFC, IFRCS, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, MIGA, OIC, OPCW, UPU, WCO, EITI (candidate country), ICC (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), ISO (correspondent), OSCE (partner), SCO (dialogue member)
Related Links:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…