Countries on the Equator
The equatorial belt is home to the most expansive rainforests in the world. The South American Amazon rainforest is not only the largest in the world but is also exceptionally rich in flora and fauna. In this article, we will learn about the countries on the equator, what is the equator and more.
What is the Equator?
The equator is like a big imaginary line around the middle of the Earth. It splits the Earth into two halves, the top part called the Northern Hemisphere, and the bottom part called the Southern Hemisphere. It’s right in the middle between the North and South Poles. Because it’s in the middle, places on the equator get the strongest sunlight, making them usually warm. As the Earth rotates, locations along the Equator experience relatively consistent day lengths and temperatures throughout the year, giving rise to a tropical climate in many regions.
Because of Earth’s tilt, the equator experiences nearly equal day and night hours throughout the year. It’s also the widest part of Earth, with the circumference slightly larger than around the poles. People use the equator to find their way around the Earth and study the weather and geography.
Where is the Equator?
The Equator isn’t a location in itself, since it’s an imaginary line that circles the entire Earth. The Equator is like a giant circle line that goes around the Earth, but you can’t go to a specific spot and call that “the Equator.” It’s all over, but we call it 0 degrees latitude which extends horizontally around the Earth. This imaginary line passes through several countries in Africa, South America, and Asia. Additionally, it crosses the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Indian Ocean.
So, the Equator is the imaginary line, equidistant from the geographic poles, and lies in a plane perpendicular to the Earth’s axis.
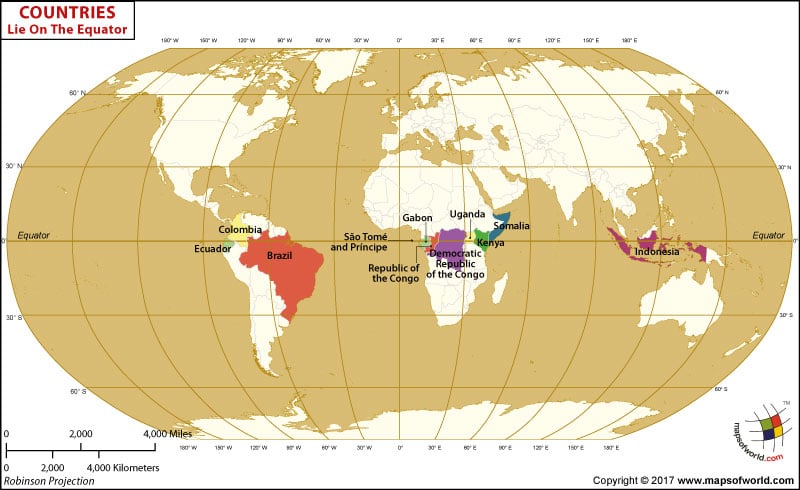
13 Countries on the Equator
-
Ecuador
The Equator runs directly through Ecuador, after which the country is named. A monument called the “Mitad del Mundo” (Middle of the World), is marking the spot.
-
Brazil
The Equator passes through the northern region of Brazil, particularly the state of Amazonas.
-
Colombia
The Equator crosses the southern part of Colombia, near the border with Ecuador.
-
Indonesia
The Equator intersects several islands of Indonesia, including Sumatra, Kalimantan (part of Borneo), Sulawesi, and Halmahera.
-
Gabon
The Equator runs through the western part of Gabon in Central Africa.
-
Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Equator crosses the DRC, particularly in the central and western regions.
-
Uganda
The Equator passes through southern Uganda.
-
Kenya
The Equator crosses central Kenya.
-
Republic of the Congo
The Equator passes through the northern part of the country.
-
São Tomé and Príncipe
This island nation in the Gulf of Guinea, is crossed by the Equator.
-
Maldives
The Equator passes through the territorial seas of Maldives, south of Gaafu Dhaalu Atoll.
-
Somalia
The Equator passes through the northern region of Somalia particularly, in the vicinity of the town of Galdogob.
-
Kiribati
The Equator runs through the northern part of the Line Islands group of Kiribati, specifically intersecting Teraina (Washington Island) and Tabuaeran (Fanning Island).
Interesting Facts about the Equator
- The word “equator” comes from the Latin word “aequator” which means “equalizer”. This is fitting because the equator is the only place on Earth where you experience roughly equal lengths of day and night throughout the year.
- Earth isn’t a perfect sphere, it bulges slightly at the equator due to the centrifugal force caused by its rotation. This bulge means the equator is the widest part of Earth, measuring about 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles) in circumference.
- Places on the equator experience some of the fastest sunrises and sunsets because the sun’s path to the horizon is nearly perpendicular.
- Because of the Earth’s bulge and the extra speed gained from rotation, locations near the equator are ideal for launching rockets and spacecraft. It gives them a bit of a boost into space.
- The Equator is crucial in astronomical calculations, particularly celestial navigation and mapping. It serves as a reference point for measuring declination, the celestial equivalent of latitude.
Related Links
