What European Countries are Not Members of the EU?
Ukraine Russia Standoff – Latest Update
- Russian Attack on Yavoriv Military Base
- Renowned US journalist Brent Renaud was killed when Russian troops opened fire on a car
- Ukraine Accuses Russia of using Banned Phosphorus Munitions
- Jake Sullivan Warns China to Avoid Helping Russia
Here are some important maps related to Ukraine-Russia War Crisis:
- Ukraine-Russia War Crisis – Updated Information
- Ukraine Map
- Russia Map
- Russia Ukraine Map
- Kyiv (Kiev) Map
- Where is Kyiv (Kiev)
- NATO Members Map
- Where is Russia on Map
- Where is Ukraine on Map
- Where is Crimea on Map
- Where is Chernobyl
EU or European Union was created in 1993 by the European Economic Community (EEC) and is a unique political and economic union. EEC was formed with the Treaty of Rome in 1957 and came into effect in 1958. The founding members of EEC were Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany, and the Community aimed at economic integration and a common market. With the Maastricht Treaty in 1993, EEC became the EU showing that it would cover a much wider area than just economic integration.
Over the years, the EU has grown as well as shrank to include the following 27 member countries from Europe:
| Austria | Italy |
| Belgium | Latvia |
| Bulgaria | Lithuania |
| Croatia | Luxembourg |
| Cyprus | Malta |
| Czechia | The Netherlands |
| Denmark | Poland |
| Estonia | Portugal |
| Finland | Romania |
| France | Spain |
| Germany | Slovakia |
| Greece | Slovenia |
| Hungary | Sweden |
| Ireland |
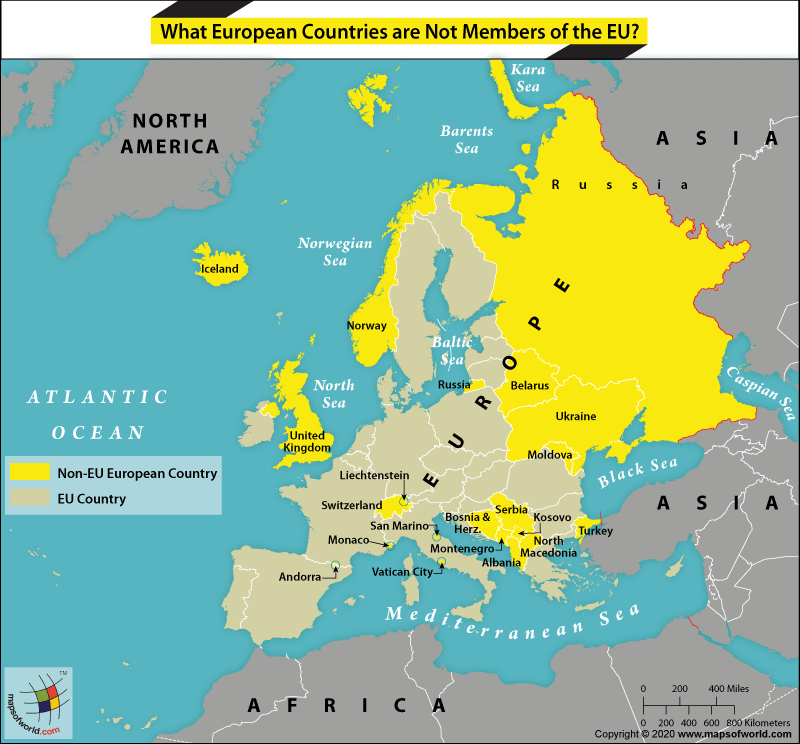
There are still some countries in Europe that are not a part of the EU. These are:
- The United Kingdom
- Iceland
- Norway
- Russia
- Liechtenstein
- Switzerland
- Andorra
- Monaco
- San Marino
- Vatican City
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Serbia
- Montenegro
- Kosovo
- Albania
- North Macedonia
- Turkey
- Belarus
- Ukraine
- Moldova
A major blow to the EU came on June 23, 2016, when citizens of the UK, in a referendum, voted for its exit from the Union by 52% to 48% of votes. On March 29, 2017, the UK formally notified the European Council of its intention to leave the EU by provoking Article 50 of the Lisbon Treaty, which would result in the amendment of the two treaties that form the basis of the EU. Under it, the British Prime Minister Theresa May started the two-year process for ‘Brexit’ (Britain’s exit). In the following years, the withdrawal process was delayed further. Eventually, after a series of political turmoils in the UK, the withdrawal process was finally resolved. And on January 30, 2020, at 11 p.m. (GMT), the UK left the EU.
The reason for the creation of the EU in the post-World War II scenario was the belief that economic cooperation and interdependence among countries would lessen the chance of a conflict. Thus, when the EEC was established between 6 countries; Belgium, Germany, France, Italy, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands, a huge single market was created, which until now, had continued to grow and develop. This economic union evolved with time to include policy areas as well, and in 1993, the EEC became the EU. EU is based on the Rule of Law and governed by the Principle of Representative Democracy.
Obtaining a membership to the EU is a complicated procedure. A country that wishes to become a member must fulfill certain conditions, known as the Copenhagen Criteria. These include a free-market economy, a stable democracy and the rule of law, and the acceptance of all EU legislation, including the euro. A country that wishes to become an EU member has to submit an application to the Council. The Council asks the Commission to see if the country meets the conditions specified in the Copenhagen Criteria. If the opinion of the Commission is positive, then a mandate is negotiated by the Council, which takes a lot of time to reach.
These are some of the candidate countries that fulfill the Copenhagen Criteria and are in the process of integrating EU legislation into national law:
- Albania
- Montenegro
- Serbia
- North Macedonia
- Turkey
There are also some potential candidate countries that do not yet fulfill all the requirements of EU membership. These include:
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Kosovo
The euro (€) is the official currency of 19 out of 27 EU member countries. Together, these countries are known as the Eurozone.
The greatest achievement of the EU as an entity is said to be the Schengen Area. It implies an area without any internal borders between countries where citizens, non-EU nationals, businesses, and tourists can move freely without being subjected to passport checks and other kinds of border control to the movement of people, goods, services, and capital.
There are currently 26 Schengen Area member countries.
| Austria | Liechtenstein |
| Belgium | Lithuania |
| Czech Republic | Luxembourg |
| Denmark | Malta |
| Estonia | Netherlands |
| Finland | Norway |
| France | Poland |
| Germany | Portugal |
| Greece | Slovakia |
| Hungary | Slovenia |
| Iceland | Spain |
| Italy | Sweden |
| Latvia | Switzerland |
It must be noted that of these countries, three – Iceland, Norway, and Switzerland, are not members of the EU but are associate members of the Schengen Area.
Related Links:

