
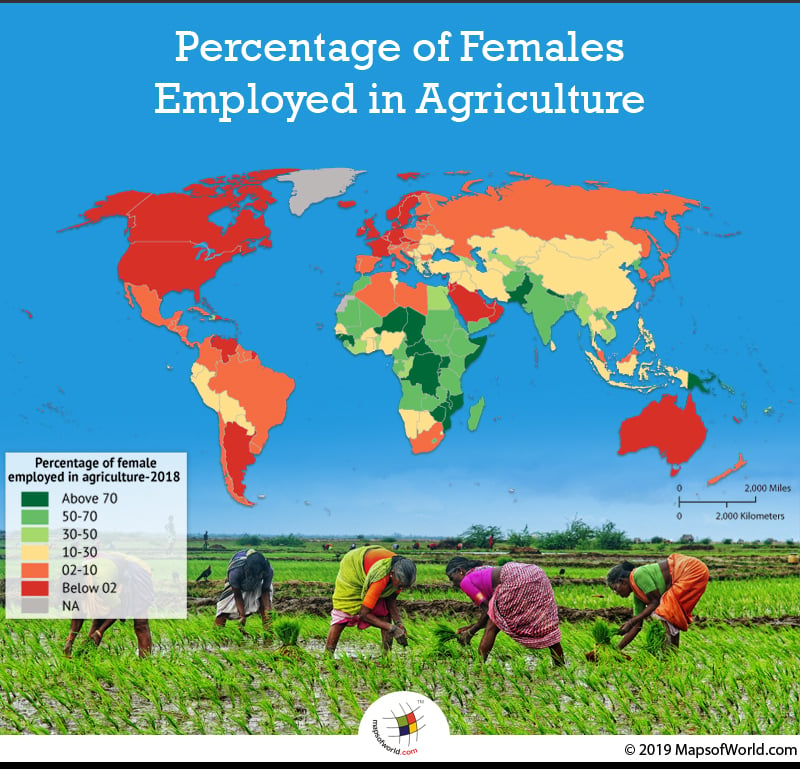
Map of World depicting percentage of females employed in agriculture
The activity of agriculture is globally recognised as the driving engine of the economies. With nations featuring high number of poor population, the agricultural sector is seen as the main tool to attain growth and elevate poverty. This is due to the large proportion of the people dependent on it as a source to earn livelihood. Yet, it is most under performing sector in most developing countries. Women representing a crucial resource in agriculture and the rural economy, face many constraints as against their male counterparts, in terms of access to productive resource.
Varying roles involving women, like farming, labor work and entrepreneurship, make essential contributions to the agricultural economies, and range considerably within and between regions. With agricultural and social forces changing around the world, transformations in the agricultural sector are also evident. Rural women employed in agricultural activities, often manage complex households and multiple livelihood pursuits. These largely revolve around producing agricultural crops for subsistence and commercial uses, tending animals, preparing food, working for additional wages in agricultural enterprises, collecting fuel and water, engaging in trade and marketing, taking care of family members and maintaining their homes. While these activities demand time and energy, they are usually referred to as ‘non-economic activities‘, and does not fall within the purview of ‘economically active employment‘.
This also brings forth another significant constraint hindering women development and growth. While records state the women population make tremendous contributions to the agricultural and rural economies, the exact contribution in terms of magnitude and nature of the work is hard to assess. The global average is witnessed to be dominated by Asia, with sub-regional averages ranging from 35% to 50%. In case of sub-Saharan Africa, women employed in agricultural activities account for almost 50%. The developing countries of the Americas, reveal much lower average female labor force employed in agriculture. Whereas the South American countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru, contribute to the rising figures and dominate the average. Universally, agriculture is a significant sector to women than men, in terms of employment. The figures show that both the level of development and the distribution of employment varies across regions, with significant gaps between male and female level of employment in agriculture.
A precise breakdown of time use by farming activity, also reveal that women are typically involved in all the activities including land preparation, fertiliser application, weeding, harvesting and storage, but did not provide a majority of labor. Yet, compared to men, women and girls are much more affected by the social ills of poverty and disease. Even though, the migration trends show movement of men to urban areas, in search of secondary and tertiary work opportunities, the women in the labor market receive starvation wages.
Women empowerment, rendering equal rights and access to land are hence the only means to reach higher economic growth, food security and enhanced conditions for future generations. Women form the backbone of the development of national and rural economies, comprising 43% of the world’s agricultural labor force, rising to 70% in some countries. These countries have women engaged in field work, but do not have access and control over agricultural land and productive resources. With agriculture becoming the prime alternative to rural women, there is a need to frame and direct better policy measures to deal with cultural resistance and adaptations. The call of the hour requires investments and better support wages. Additionally, measures that facilitate a transition to a type of agriculture that respects environment and conservation of natural resources, in sync with benefitting women, seem necessary.
Complimenting such measures, are the efforts that should be directed in the creation of favourable conditions in agricultural areas, including road network reinforcement for transportation, commercialisation and processing of the end products. The social policies of health, education, welfare also require amendments, with focus on the strengthening of rural women dependent on agricultural as a mode of income. The new emerging techniques in respect to the modern agriculture, tailored to meet local conditions and using resources in sustainable manner, should be imparted to rural women to be more productive. Hence, participation in policies that benefit rural women can help attain and sustain higher levels of productivity, generate incomes and eradicate poverty.
| S.No. | Country Name | 2018 |
| 1 | Afghanistan | 55.73 |
| 2 | Angola | 55.53 |
| 3 | Albania | 42.29 |
| 4 | United Arab Emirates | 0.13 |
| 5 | Argentina | 0.01 |
| 6 | Armenia | 36.59 |
| 7 | Australia | 1.63 |
| 8 | Austria | 3.63 |
| 9 | Azerbaijan | 41.94 |
| 10 | Burundi | 96.29 |
| 11 | Belgium | 0.69 |
| 12 | Benin | 33.78 |
| 13 | Burkina Faso | 20.18 |
| 14 | Bangladesh | 59.43 |
| 15 | Bulgaria | 4.47 |
| 16 | Bahrain | 0.05 |
| 17 | Bahamas, The | 0.44 |
| 18 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | 16.73 |
| 19 | Belarus | 7.21 |
| 20 | Belize | 5.23 |
| 21 | Bolivia | 28.25 |
| 22 | Brazil | 4.23 |
| 23 | Barbados | 1.79 |
| 24 | Brunei Darussalam | 0.43 |
| 25 | Bhutan | 64.81 |
| 26 | Botswana | 17.86 |
| 27 | Central African Republic | 74.99 |
| 28 | Canada | 0.95 |
| 29 | Switzerland | 2.55 |
| 30 | Channel Islands | 3.22 |
| 31 | Chile | 5.25 |
| 32 | China | 24.24 |
| 33 | Cote d’Ivoire | 40.14 |
| 34 | Cameroon | 51.86 |
| 35 | Congo, Dem. Rep. | 76.79 |
| 36 | Congo, Rep. | 36.49 |
| 37 | Colombia | 7.62 |
| 38 | Comoros | 63.01 |
| 39 | Cabo Verde | 8.16 |
| 40 | Costa Rica | 4.47 |
| 41 | Cuba | 7.62 |
| 42 | Cyprus | 1.06 |
| 43 | Czech Republic | 1.76 |
| 44 | Germany | 0.87 |
| 45 | Djibouti | 52.52 |
| 46 | Denmark | 0.99 |
| 47 | Dominican Republic | 1.29 |
| 48 | Algeria | 3.13 |
| 49 | Ecuador | 24.57 |
| 50 | Egypt, Arab Rep. | 36.66 |
| 51 | Eritrea | 66.42 |
| 52 | Spain | 2.22 |
| 53 | Estonia | 1.89 |
| 54 | Ethiopia | 59.52 |
| 55 | European Union | 3.04 |
| 56 | Finland | 2.11 |
| 57 | Fiji | 38.67 |
| 58 | France | 1.56 |
| 59 | Gabon | 56.78 |
| 60 | United Kingdom | 0.63 |
| 61 | Georgia | 45.45 |
| 62 | Ghana | 26.42 |
| 63 | Guinea | 70.38 |
| 64 | Gambia, The | 36.69 |
| 65 | Guinea-Bissau | 70.13 |
| 66 | Equatorial Guinea | 41.51 |
| 67 | Greece | 11.33 |
| 68 | Guatemala | 9.26 |
| 69 | Guam | 0.05 |
| 70 | Guyana | 6.23 |
| 71 | Hong Kong SAR, China | 0.14 |
| 72 | Honduras | 9.38 |
| 73 | Croatia | 5.05 |
| 74 | Haiti | 34.14 |
| 75 | Hungary | 2.79 |
| 76 | Indonesia | 28.53 |
| 77 | India | 57.06 |
| 78 | Ireland | 1.52 |
| 79 | Iran, Islamic Rep. | 21.07 |
| 80 | Iraq | 23.56 |
| 81 | Iceland | 1.93 |
| 82 | Israel | 0.50 |
| 83 | Italy | 2.31 |
| 84 | Jamaica | 9.05 |
| 85 | Jordan | 1.13 |
| 86 | Japan | 2.96 |
| 87 | Kazakhstan | 14.21 |
| 88 | Kenya | 63.85 |
| 89 | Kyrgyz Republic | 27.59 |
| 90 | Cambodia | 30.38 |
| 91 | Korea, Rep. | 4.41 |
| 92 | Kuwait | 0.05 |
| 93 | Lao PDR | 69.75 |
| 94 | Lebanon | 15.65 |
| 95 | Liberia | 46.14 |
| 96 | Libya | 9.21 |
| 97 | St. Lucia | 4.10 |
| 98 | Sri Lanka | 29.23 |
| 99 | Lesotho | 58.22 |
| 100 | Lithuania | 5.30 |
| 101 | Luxembourg | 0.68 |
| 102 | Latvia | 4.13 |
| 103 | Macao SAR, China | 1.15 |
| 104 | Morocco | 59.22 |
| 105 | Moldova | 27.78 |
| 106 | Madagascar | 64.96 |
| 107 | Maldives | 2.20 |
| 108 | Mexico | 3.69 |
| 109 | North Macedonia | 15.72 |
| 110 | Mali | 63.47 |
| 111 | Malta | 0.22 |
| 112 | Myanmar | 44.91 |
| 113 | Montenegro | 6.84 |
| 114 | Mongolia | 25.97 |
| 115 | Mozambique | 81.76 |
| 116 | Mauritania | 54.48 |
| 117 | Mauritius | 5.90 |
| 118 | Malawi | 76.69 |
| 119 | Malaysia | 6.62 |
| 120 | Namibia | 17.56 |
| 121 | New Caledonia | 1.35 |
| 122 | Niger | 71.48 |
| 123 | Nigeria | 26.39 |
| 124 | Nicaragua | 9.18 |
| 125 | Netherlands | 1.44 |
| 126 | Norway | 0.92 |
| 127 | Nepal | 80.06 |
| 128 | New Zealand | 4.21 |
| 129 | Oman | 0.39 |
| 130 | Pakistan | 72.72 |
| 131 | Panama | 8.57 |
| 132 | Peru | 25.80 |
| 133 | Philippines | 15.15 |
| 134 | Papua New Guinea | 70.19 |
| 135 | Poland | 8.76 |
| 136 | Puerto Rico | 0.48 |
| 137 | Korea, Dem. People’s Rep. | 64.88 |
| 138 | Portugal | 4.12 |
| 139 | Paraguay | 14.81 |
| 140 | French Polynesia | 5.02 |
| 141 | Qatar | 0.03 |
| 142 | Romania | 22.09 |
| 143 | Russian Federation | 3.99 |
| 144 | Rwanda | 76.69 |
| 145 | South Asia | 59.51 |
| 146 | Saudi Arabia | 0.12 |
| 147 | Sudan | 58.84 |
| 148 | Senegal | 27.27 |
| 149 | Singapore | 0.23 |
| 150 | Solomon Islands | 62.46 |
| 151 | Sierra Leone | 57.05 |
| 152 | El Salvador | 3.90 |
| 153 | Somalia | 76.39 |
| 154 | Serbia | 14.74 |
| 155 | South Sudan | 61.98 |
| 156 | Sao Tome and Principe | 12.37 |
| 157 | Suriname | 3.91 |
| 158 | Slovak Republic | 1.35 |
| 159 | Slovenia | 4.75 |
| 160 | Sweden | 1.00 |
| 161 | Eswatini | 10.85 |
| 162 | Syrian Arab Republic | 13.45 |
| 163 | Chad | 83.86 |
| 164 | Togo | 29.00 |
| 165 | Thailand | 27.90 |
| 166 | Tajikistan | 68.97 |
| 167 | Turkmenistan | 21.96 |
| 168 | Timor-Leste | 49.57 |
| 169 | Tonga | 3.44 |
| 170 | Trinidad and Tobago | 1.56 |
| 171 | Tunisia | 11.41 |
| 172 | Turkey | 27.89 |
| 173 | Tanzania | 69.40 |
| 174 | Uganda | 76.04 |
| 175 | Ukraine | 12.97 |
| 176 | Uruguay | 3.80 |
| 177 | United States | 0.75 |
| 178 | Uzbekistan | 37.38 |
| 179 | St. Vincent and the Grenadines | 6.70 |
| 180 | Venezuela, RB | 1.31 |
| 181 | Vietnam | 41.11 |
| 182 | Vanuatu | 62.53 |
| 183 | World | 27.56 |
| 184 | Samoa | 3.25 |
| 185 | Yemen, Rep. | 58.74 |
| 186 | South Africa | 3.66 |
| 187 | Zambia | 62.12 |
| 188 | Zimbabwe | 71.47 |
Related Links:
Related Map:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…