
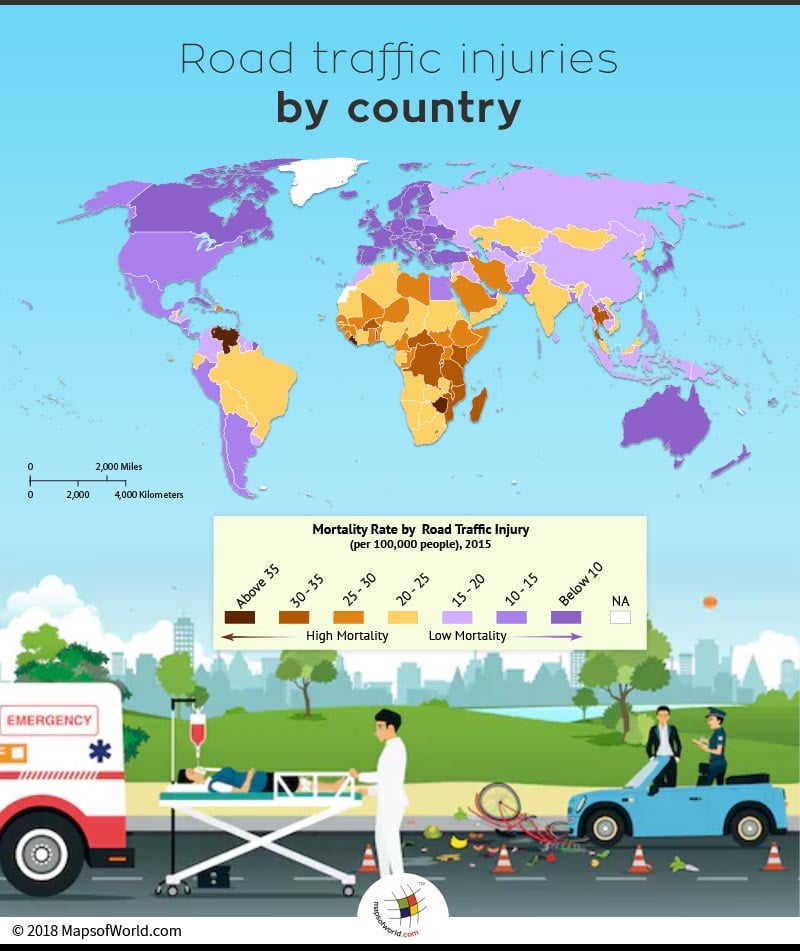
Zimbabwe, accounts for the highest number of road accidents and injuries due to road traffic.
A road traffic accident is any vehicular accident occurring on the roadway i.e. originating, terminating or involving a vehicle partially on the roadway.
The first step towards creating a safe transport system is recognizing the obstacles and the errors of the system and considering people’s vulnerability to serious injuries. Few of the main causes of the high rate of death due to road accidents are:
Speeding: The increase in the average speed is directly proportional to both the crash occurring and the severity of the consequences.
Under the Influence: In the case of drink-driving, the risk of a road traffic starts at low levels of blood-alcohol concentration and increases with the increase in BAC. Whereas in case of drug-influence, the risk of incurring a road accident relies on the degree of the effect of the psychoactive drug consumed.
No Precautions: Simply following the basic traffic rules of wearing a seat belt, helmet and child restraints reduce the risk of the severity of the accident. It avoids fatality and death among infants by 70%.
Distracted Driving: The most highlighted reason for impaired driving is the increased use of mobile phones while driving. Using a phone while driving reduces the reaction time to exert brakes or respond to the traffic signals, resulting in crashes and accidents.
Road Infrastructure: Creating adequate facilities for all types of commuters including pedestrians, cyclists, motorcyclists, car-drivers and heavy-vehicle drives should be ideally kept in mind while laying the plans for road networks. Measures such as safe crossing points, footpaths, cycling lanes, zebra crossings should be installed to substantially reduce the risk of accidents.
Safe-Vehicles: The implementation of the ‘UN Regulations on Vehicle Safety,’ applied to countries’ manufacturing and production standards, can potentially save lives. These would require them to meet front and side impact regulations, include electronic safety, install airbags and seat belts in vehicles, to averse the occurrence of vehicular crash.
Preventive Measures:
Rapid-Motorizations, coupled with poor road conditions and population growth, has unleashed the likeliness of road accidents. Promoting efficient patterns of land-use and creating shorter, safer routes for users can reduce their vulnerability. Improving public transportation and stringer law enforcement can bring expected reduction in fatalities. Enforcement of the traffic laws, will lead to compliance and changed behavioral patterns of the people.
A lack of vehicular visibility has also resulted in major road accidents. In poorly-lit areas the larger vehicles tend to crash into the smaller motorists or two-wheelers, resulting in extreme crashes and fatalities.
Global Response:
Declaring 2011-2020 as the ‘Decade of Action’ for road safety the various governments have collectively stepped forward to address this public issue. This indicates the growing awareness within the countries with the rising number of fatalities from road injuries and accidents.
The World Injury Conference, in 2016, produced ‘The Tampere Declaration’ to call for strong and coordinated global commitment to reduce the impact of injuries and violence.
The WHO works in collaboration with national and international stakeholders to support member states in the policy planning and road safety implementation. It provides technical support to member states, for example WHO in collaboration with the Bloomberg Initiative for Global Road Safety (BIGRS) 2015-2019, works towards reducing the fatalities in low and middle-income countries.
Save LIVES: A road safety technical package by the WHO focuses on speed management, leadership, infrastructure design and improvement, vehicle safety standards, enforcement of traffic laws and post-crash survival.
The adoption of ‘UN 2030 Sustainable Development Goals’ also aim to work towards halving the global number of deaths and injuries from road traffic crashes by 2020.
Below lying table depicts the countries with the highest number of injuries from road accidents:
| Country | Traffic injury (per 100,000 people) | Country | Traffic injury (per 100,000 people) | |
| Zimbabwe | 45.4 | Armenia | 15.7 | |
| Venezuela | 41.7 | Indonesia | 15.5 | |
| Liberia | 35.1 | Samoa | 15.5 | |
| Malawi | 34.2 | Guyana | 15.3 | |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 33.5 | Haiti | 15.3 | |
| Tanzania | 33.4 | Afghanistan | 15.2 | |
| Mozambique | 33.1 | Vanuatu | 15.2 | |
| Sao Tome and Principe | 33.1 | Bhutan | 15.0 | |
| Rwanda | 32.9 | Laos | 15.0 | |
| Burundi | 32.7 | Costa Rica | 14.9 | |
| Togo | 31.9 | Nicaragua | 14.9 | |
| Central African Republic | 31.8 | St. Vincent and the Grenadines | 14.7 | |
| Thailand | 31.7 | Pakistan | 14.3 | |
| Madagascar | 31.4 | Argentina | 14.1 | |
| Burkina Faso | 30.7 | Albania | 13.6 | |
| Kenya | 30.5 | Trinidad and Tobago | 13.5 | |
| Gambia | 30.4 | Egypt | 13.3 | |
| South Sudan | 29.3 | Peru | 13.3 | |
| Comoros | 28.6 | Lithuania | 13.0 | |
| Sierra Leone | 28.5 | Mauritius | 12.9 | |
| Niger | 28.4 | Bangladesh | 12.8 | |
| Cameroon | 28.1 | Qatar | 12.8 | |
| Guinea | 28.1 | Caribbean small states | 12.6 | |
| Iran | 28.0 | Belarus | 12.6 | |
| Senegal | 28.0 | South Korea | 12.0 | |
| Dominican Republic | 27.8 | Mexico | 11.8 | |
| Benin | 27.7 | Chile | 11.6 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 27.5 | Georgia | 11.6 | |
| Ethiopia | 27.3 | Antigua and Barbuda | 11.5 | |
| Uganda | 27.3 | Bahamas | 11.0 | |
| Somalia | 26.9 | United States of America | 10.8 | |
| Guinea-Bissau | 26.8 | Moldova | 10.7 | |
| Republic of the Congo | 26.7 | Panama | 10.7 | |
| Ghana | 26.1 | Philippines | 10.7 | |
| Lesotho | 26.1 | Montenegro | 10.3 | |
| Libya | 25.3 | North America | 10.3 | |
| Mali | 25.3 | Uzbekistan | 10.2 | |
| Oman | 25.0 | Azerbaijan | 10.0 | |
| Djibouti | 24.9 | Jamaica | 10.0 | |
| Eritrea | 24.9 | Latvia | 9.9 | |
| Swaziland | 24.9 | United Arab Emirates | 9.8 | |
| Zambia | 24.7 | Ukraine | 9.7 | |
| Sudan | 24.6 | Poland | 9.4 | |
| Angola | 24.4 | Croatia | 9.2 | |
| Chad | 24.3 | Romania | 8.9 | |
| Mauritania | 24.2 | Turkey | 8.8 | |
| Cote d’Ivoire | 24.0 | Central Europe and the Baltics | 8.6 | |
| Vietnam | 24.0 | Puerto Rico | 8.2 | |
| Algeria | 23.7 | Slovakia | 8.2 | |
| Jordan | 23.6 | Greece | 8.1 | |
| Namibia | 23.6 | Macedonia | 8.1 | |
| Paraguay | 23.4 | Brunei Darussalam | 8.0 | |
| Bolivia | 23.3 | Seychelles | 7.9 | |
| Kazakhstan | 23.2 | Luxembourg | 7.7 | |
| Tunisia | 23.0 | Portugal | 7.7 | |
| Yemen | 22.8 | Bulgaria | 7.6 | |
| Gabon | 22.7 | Cuba | 7.6 | |
| Brazil | 22.6 | Hungary | 7.5 | |
| Malaysia | 22.3 | Serbia | 7.4 | |
| Belize | 21.3 | Belgium | 7.1 | |
| Cabo Verde | 21.3 | Bahrain | 7.1 | |
| South Africa | 21.3 | Grenada | 6.6 | |
| India | 21.2 | Cyprus | 6.5 | |
| Botswana | 21.0 | Czech Republic | 6.5 | |
| Equatorial Guinea | 20.8 | Slovenia | 6.5 | |
| Mongolia | 20.8 | Estonia | 6.3 | |
| Ecuador | 20.7 | New Zealand | 6.1 | |
| North Korea | 20.7 | Tonga | 6.0 | |
| Nigeria | 20.6 | Canada | 5.8 | |
| Kyrgyzstan | 20.1 | Fiji | 5.8 | |
| Guatemala | 19.9 | Austria | 5.7 | |
| Syria | 19.7 | Italy | 5.6 | |
| Myanmar | 19.5 | Barbados | 5.5 | |
| South Asia | 19.4 | Malta | 5.5 | |
| China | 19.4 | Australia | 5.4 | |
| Lebanon | 19.3 | Palestinian | 5.4 | |
| Cambodia | 19.0 | European Union | 5.4 | |
| El Salvador | 19.0 | France | 5.1 | |
| Colombia | 18.9 | Japan | 4.7 | |
| St. Lucia | 18.8 | Finland | 4.4 | |
| Suriname | 18.7 | Germany | 4.2 | |
| Morocco | 18.6 | Ireland | 4.0 | |
| Solomon Islands | 18.3 | Singapore | 3.7 | |
| Iraq | 17.8 | Switzerland | 3.6 | |
| Kuwait | 17.7 | Spain | 3.6 | |
| Tajikistan | 17.6 | Iceland | 3.6 | |
| Timor-Leste | 17.6 | Netherlands | 3.6 | |
| Russia | 17.4 | Denmark | 3.4 | |
| Turkmenistan | 17.4 | Maldives | 3.3 | |
| Uruguay | 17.4 | Norway | 3.3 | |
| Nepal | 17.3 | Israel | 3.2 | |
| Sri Lanka | 17.2 | United Kingdom | 2.9 | |
| Papua New Guinea | 16.9 | Sweden | 2.9 | |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 16.6 | Kiribati | 2.4 | |
| Honduras | 16.5 | Federated States of Micronesia | 2.0 |
Know more:
Related maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…