
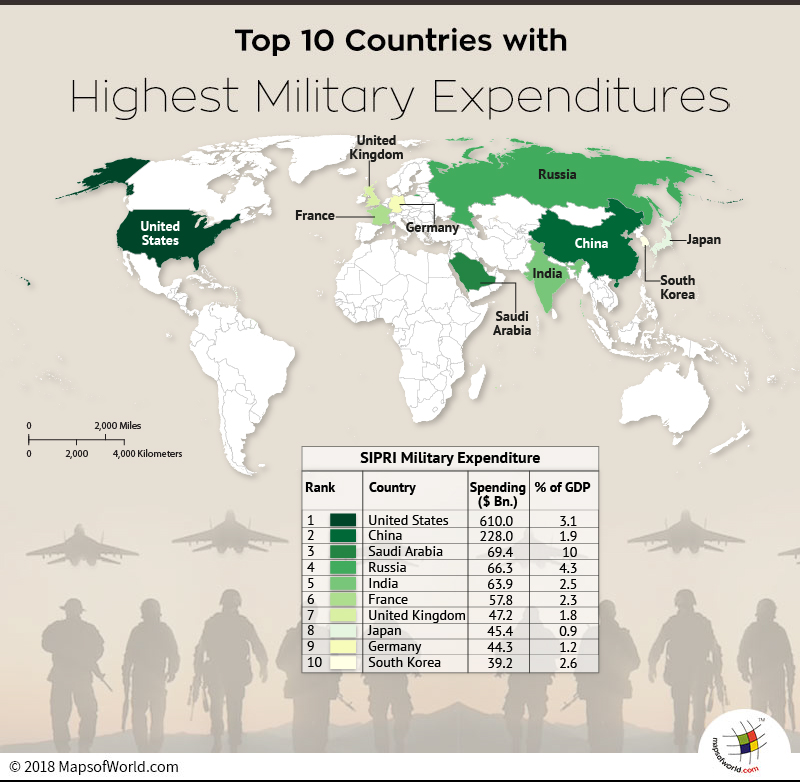
United States, alone accounts for 38% of the global military expenditure. it makes the largest defence spendings.
The father of economics ‘Adam Smith,’ was the first economist to consider the implications of defense expenditure for a society’s well-being. He proposed that a viable military force, is a prerequisite for a government to perform its utmost duty of protecting the society from invasion and violence from independent states. The government acts on behalf of the public to ensure that the military is well resourced to defend the nation.
The SIPRI research states that, the five biggest military spenders in 2017 were the United States, China, Saudi Arabia, Russia and India. They collectively account for 60% of the world’s military expenditure.
A nations requirement for military security (internal and external) are affected by various factors. These factors could be largely determined by geography, like location and the relations with neighboring countries. Another issue attributing to the level of expenditure is the military capacity of the nation. The difference between the military capability and military expenditure is that the latter is the input measure, which may differ than the output of military activities, such as military strength. Additional factors include economic, political and strategic issues. The military burden is the economic burden as a share of GDP used for military activities.
A country has to its disposal two options with the limited amount of fixed resources. The public expenditure can be invested in the social or the economic sector. This dilemma is explained by the ‘guns and butter curve,’ which reflects the two options that the government has as production possibilities. The guns represent the military expenditure whereas the butter represent the food or social sector. This condition of opportunity cost, where in order to produce more of guns the government needs to reduce its production of butter, represents the social cost of public spending.
Government expenditure has a long run impact on economic growth. In addition to the social impacts of the allocation of military spending, the economic benefits have indirect and direct results. The employment generation by the active troops as well as a considerable infrastructure build up around them requires contractors, traders, consultants to support the military, positively affecting the economic growth. Contradictorily, the diversion of skill and talent towards supporting military research and development, negatively affects the economic potential. Also, reduction in defense spending could make a nation vulnerable, as an external threat would negatively affect the political functioning and further hinder the productivity levels. Hence a question of reducing military spending leads to a debate of ‘peace dividend’ or ‘peace penalty.’
The global military spending rose to its highest since the cold war with the US, China and Saudi Arabia topping the list. The United States alone accounts for 35% of the global military expenditure, more than the combined expenditure of the next seven highest countries. These surging figures are supported by military leaders and elected officials, by arguing that the country plays a unique role in contributing to the international order and faces challenge in securing its citizens.
China, has doubled by 13% since 2008, is the second country with the highest military spending. Boosting by 8.1% in 2018, it aims at advancing a modernization drive for its armed forces.
Saudi Arabia’s national priorities saw a shift since the new power structure, revolutionizing the national security structure and leadership. In the face of the real threats the kingdom faces, it aims at spending 10% of its GDP on defense and security.
Below lying table depicts the top 10 countries with the highest military spendings-
| Rank | Country | Spending ($ Bn.) | % of GDP |
| 1 | United States | 610.0 | 3.1 |
| 2 | China | 228.0 | 1.9 |
| 3 | Saudi Arabia | 69.4 | 10 |
| 4 | Russia | 66.3 | 4.3 |
| 5 | India | 63.9 | 2.5 |
| 6 | France | 57.8 | 2.3 |
| 7 | United Kingdom | 47.2 | 1.8 |
| 8 | Japan | 45.4 | 0.9 |
| 9 | Germany | 44.3 | 1.2 |
| 10 | South Korea | 39.2 | 2.6 |
Know more:
Related maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…