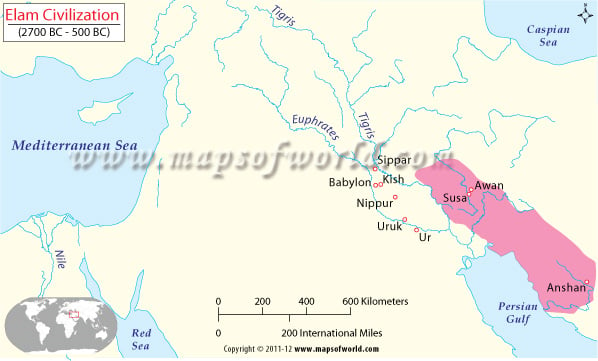
While Sumerian culture thrived in southern Mesopotamia, the Elam civilization took root to the east of the Mesopotamian valley, in what is now southwest Iran and southern Iraq. The Elam society grew, distinct from the Semitic Akkadians and the indigenous Sumerians, from around 2700 BC through 500 BC. The Elam Empire was one of the longest-surviving in the world.
The name Elam itself is the Sumerian and later Hebrew (Bible) reference to the culture that was known to the Akkadians as Elamu. The Elamites referred to their land as Haltamti. The growth of the civilization in and around the capital city, Susa, prompted historians and geographers to call the country Susiana.
The history of Elam is roughly divided into three periods: the Old Elamite Period, the Middle Elamite Period, and the Neo-Elamite Period.
The Three Elamite Periods
In the Old Elamite Period, three separate dynasties of kings ruled the city-states of Elam. Susa, Awan, and Ashan were the major centers and were closely linked by trade, culture, and alliances. Conflict with and dominance over the various Sumerian cities was frequent but short-lived.
The Igehalkid and Shutrukid kings of the Middle Elamite Period seem to have brought much stability. The later kings seem to have been ambitious and invaded Babylon. This was a mistake that cost Elam its independence for over four centuries. Babylonian kings invaded many parts of Elam, and the cultural influences of the Babylonians and the Assyrians caused a steady decline in Elamite culture.
The wealth and prosperity of the land compensated for the political instability of the later Elamite Period. The Elamites held dominion over parts of Persia and over Khuzestan in the Zagros Mountains. The Persians grew in numbers and clout around 500 BC, but held on to the Elamite culture for a while. The end of the Elam came with Alexander the Great’s conquest of Mesopotamia.
Lost Kingdom of Arrata
Sumerian texts speak of an ancient civilization, highly advanced and culturally rich. Archaeologist Yousef Majidzadeh discovered artifacts and remains from the Jiroft Civilization near Kerman in Iran. The civilization, historians believe, is the same as the Arrata and predates 3000 BC. Among the discoveries, a ziggurat, a tower, domestic settlements, and cemeteries fascinated the archeologist and provided rare insight into the culture of the times. The Elamite inscriptions found provided evidence of the language and writing of ancient Elam.
Matrilineal Ascendancy
Elam is one of the oldest matriarchal civilizations in the world, as matrilineal ascendancy was the norm. The kings were referred to as the “son of a sister.’ The Elamite pantheon was replete with goddesses and symbolism pertaining to femininity. The snake or the serpent, the fish, and the moon, considered feminine symbols, are often depicted on ritual pottery and on temple sculptures.
Elam Culture
The Elamite culture had a significant influence on Persian culture, and later Persian courts even adopted the Elamite language as the official language. The Ilam province of Iran derives its name from the Elam.