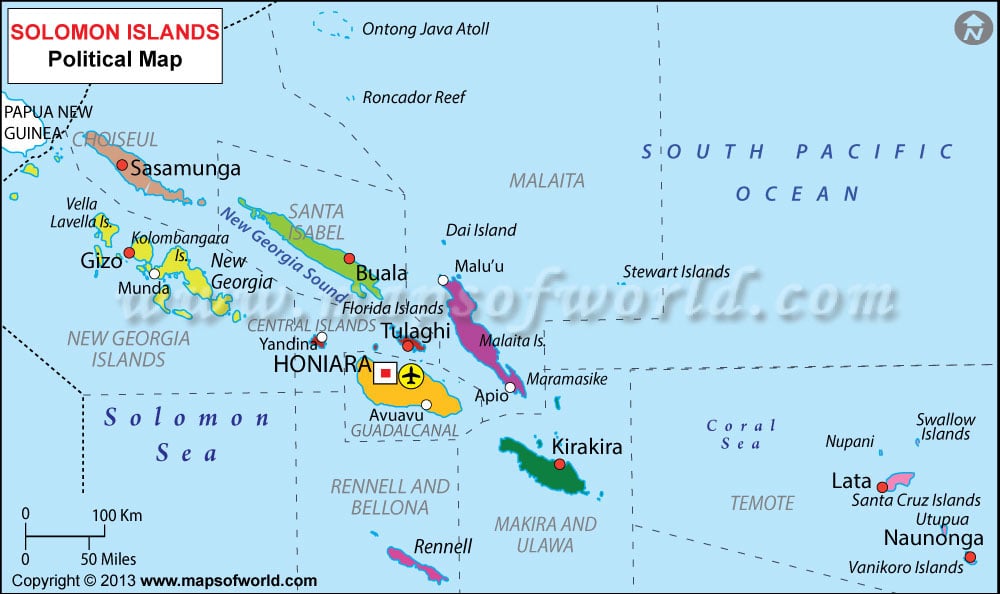
About Solomon Islands
Explore this Solomon Islands map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Solomon Islands location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Solomon Islands history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Conventional name | Solomon Islands |
| Capital City | Honiara |
| Language | English, Melanesian pidgin, Pijin and 74 other indigenous languages |
| Currency | Solomon Islands Dollar |
| Religion | Christian |
| National Anthem | “God Save Our Solomon Islands” |
| Newspaper | Solomon Islands Broadcasting Commission and Solomon Islands Star |
| Places to Visit | Auki, Honiara, Lake Te’Nggano, Mataniko Falls and National Museum & Cultural Centre |
| Transport | Airways: the Solomon Islands have an international airport in Henderson. There are three flights departing from Brisbane in Australia per week; Waterways: a good option if you have time. Cruise ships to Honiara are available; but are rare. Otherwise you can hitch a lift on a yacht from US’s West Coast or Australia’s north east coast |
| Shopping | mother-of-pearl items; decorative walking sticks; woodcarving; inlaid wood; copper murals; conch shells; rare varieties of cowries; carved fish, turtle and bird patterns on shells, wood and stone; ebony carvings, shell-inlays; jewellery making; canoe prows; shell arm bands; shields; and basket weaving and plaiting |
Comprising of a collection of Volcanic and coral islands, the Solomon Islands played a crucial role during the World War-II. It was also a part of the British colony from whose dominion it attained liberation in the year 1978. Even despite all this, there continued to be a perpetual unrest in the islands that arose from ethnic conflict between the Guadalcanal natives and the Malaita island natives.
The tension accelerated, resulting in armed conflict in the year 1998, and ended in 2003 after Australian intervention. Now, however, the islands are an ideal tropical place that attracts multitudes of tourists. It is also the best destination for water-sport enthusiasts. The islands were christened by a Spaniard, Alvaro de Mendana, who was the first European to sink anchor at the islands.
Physical Map of Solomon Islands
The Solomon Islands fall in the group of islands that are better known as Oceania. The islands together measure some 900 miles in total length. There are some 900 islands in the archipelago, of which the Cristobal, Santa Cruz, Guadalcanal, New Georgia, Malaita, Choiseul and Santa Isabel are the most important of the lot.
The islands in the archipelago are of two types: they are either of volcanic origin or are coral atolls. The six main islands in the group are volcanic, and so are mostly mountainous and blanketed with dense rain forests. Some of the volcanoes on in the island are also active.
The lowest point on the islands is the coral atolls, while the highest region is the Makarakomburu Mountain.
Location of Solomon Islands
The archipelago of Solomon Islands is located in the southern region of the Pacific Ocean. Papua New Guinea is the nearest big land mass northwest of it. The Solomon Islands are a part of the group of islands better known as Oceania. The continent of Australia lies a little further off, south west of it. The water bodies, aside of the South Pacific Ocean that surrounds the Solomon Islands are the Solomon Sea, the coral Sea and the Arafura Sea.
Climate of Solomon Islands
The Solomon Islands have a typically tropical climate. So monsoons are a recurring feature on the islands. The monsoon season, however, spans between November and March. Being tropical, the islands sport warm and humid conditions. The heat during the summer months often scales temperatures in the 80ºs. However, between the months of April and November, the climate is ‘pleasant’; with the best spell falling between July and September, as during this time precipitation is at is minimal and so humidity is also less.
Flora and Fauna of Solomon Islands
The flora of the Solomon Islands comprise mainly of rainforests. There are also mangroves and swamps to be found, particularly near the coast. The coasts are also lined with coconut palms. Aside of these, there are considerable number of flowering plants like orchids and bougainvillea. As a direct result of this, there are plenty of butterflies also to be found on the island. Fauna in the islands comprise of an enormous number of bat and rat species; many of whom are unique to the island. Some of the species available are Bougainville monkey-faced flying fox, Cusp-toothed fruit bat, Montane monkey-faced bat, Emperor rat, Poncelet’s giant rat, black-bellied fruit bat, Florida naked-tailed rat, flower-faced bat, Isabel naked-tailed rat, king rat, large-eared sheath-tailed bat, flying fox, Malaita tube-nosed bat, old world leaf-nosed bat, Ontong Java flying fox, orange fruit bat, Santa Cruz flying fox, Temotu flying fox and Vanikoro flying fox. The other mammals in and around the islands are Dugongs and Humpback Whales.
People of Solomon Islands
The population of the Solomon Islands comprises mostly of a Melanesian concentrate. They alone make up almost 95% of the population in the Solomon Islands. The other ethnic races who reside on the islands are minorities. They are Polynesians, Micronesians, Chinese, Europeans and mixed races. As a whole the people of the islands are called ‘Solomon Islanders’. However, they are very clan and tribe conscious. This has led to the break-out of rivalry. The people on the islands live a simple and traditional lifestyle. However, do not mistake the islanders for being unfriendly; because they are the friendliest people you will ever encounter any where on the planet.
Arts, Culture and Music of Solomon Islands
- Art:Traditional forms of art on the island comprise mainly of the use of natural materials. The chief of the artifacts are made of different types of wood – especially ebony, shell and leaves. Inlay works are a specialty of the Solomon Islands. Among them the most famous are the wood inlays and pearl shell inlay. Weaving and plaiting of baskets are also of considerable artistic and utilitarian significance. Making traditional war accessories like shields and canoes are also considered a form of art. The making of battle canoes having “Nuzu nuzu” prows is an important skill.
- Culture: The Solomon Islanders are a very traditional lot who still adhere to the ethnic way of life to a great extent. There is also a strong national and clan consciousness in them. However, they live a simple life full of the old world charm that is sadly missing from the modern life in most countries.
- Music:The traditional musical genres in the Solomon Islands are predominantly Melanesian. However, external influences have also contributed to form a composite musical tradition that is distinct and unique. Most music in the Solomon Islands is of the folk variety. ‘Panpipe orchestras’ and ‘bamboo music’ are two widespread types. The chief musical instruments that accompany the singing and dancing in the islands are slit-drums, panpipes, ukuleles and bamboo tubes.
Flag of Solomon Islands
The Solomon Islands flag is a simple rectangular flag that is dominated by the colors blue and green; with white and yellow also being there to a minor extent. The flag is divided into two right-angled triangles by a thin yellow stripe running from bottom left to top right. The upper triangle is blue in color while the lower one is green. The blue half of the flag has five white five-pointed stars. As a whole the five white stars on the blue backdrop represents the five important groups surrounded by the ocean. The color yellow stands for sunshine that the islands receive in abundance. Green is symbolic of the green forests that blanket the islands.
Economy of Solomon Islands
The land mass of the Solomon Islands, though tiny, is rich in naturally available resources. In fact, natural resources are the single largest sustaining source in the islands. The minerals available on the islands are gold, lead, phosphates, zinc, bauxite and nickel. The agricultural produce of the land includes important crops like palm kernels, potatoes, coconuts, fruits, cocoa beans, vegetables and rice which have high export value. The other naturally available commodities of commercial significance are fish and timber. As far as industry goes, mining and tourism are the chief ones seconded by oil-extraction form palms and copra making.