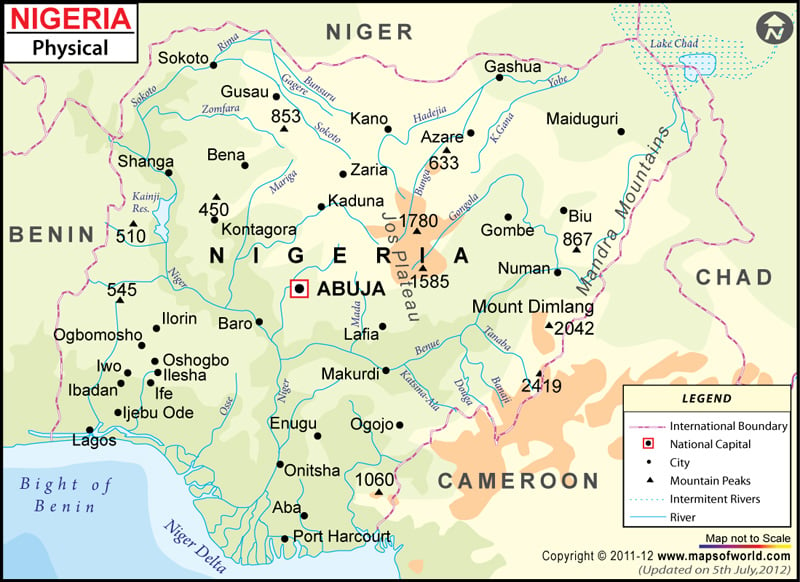
Nigeria, known as the Republic of Nigeria officially, is West Africa. It shares its boundary Chad in the northeast, Niger in the north, Benin in the West and Cameroon in the east. Nigeria’s geography lies between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea to the south in the Atlantic Ocean. The capital city of Nigeria, Abuja, is marked on the map.
Nigeria Physical Features
The country covers a total area of 923,769 square kilometres (356,669 sq mi). One can point out the latitudes and longitudes of Nigeria on the map along with international boundaries. The country lies between latitudes 4. N and 14. N and longitudes 2. E and 15.E. A map legend at the bottom helps all the signs, characters, graphics, and symbols used throughout the map. The Nigeria Physical Map can be used for school work, presentation and other purposes. Based on relief,Nigeria can be divided into the following topographic features:
Plains and Niger and Benue Valley
The most significant geographical region of Nigeria is the valleys of Niger and Benue River. They merge into each other, forming a “y” shaped at the confluence at Lokoja.
The plains lie in the north of valleys in Nigeria. The Borno Plains lie in the northeastern corner of the country, while Sokoto plains are in the country’s northwestern corner. The tables in the regions are gently undulating and become waterlogged during the rainy season. Coastal plains are found in the southeast and southwest of the country.
Niger Delta
Niger Delta is one of the world’s largest fan-shaped river Deltas in the world. The Delta is located in the southern part of Nigeria. The riverine area of the Delta is a belt of swamps bordering the Atlantic. The coastal wetlands are formed by a reticulate pattern of interconnected meandering creeks and tributaries of the Niger River. The region is very densely populated and is a petroleum-rich region. The Delta region was once a significant producer of Palm oil.
Plateau and Hills
The plateaus in the region are high plains with shallow and broad valleys dotted with isolated mountains called inselbergs or numerous hills. The Jos Plateau consists of lava surface rises in the country’s centre. Another plateau UDI-Nsukka Plateau rise above the plain at the height of about 1,000 feet(300 metres). The mountains area of the country lies along the southeastern border of the country with Cameroon. The country’s highest point is the Chappal Waddi peak, at an elevation of 7,936 feet is, in the Gotel Mountains.
Principal Rivers of Nigeria
The most significant rivers of Nigeria are the NigerRiver and its tributary Benue river, which converge and empty into Niger Delta. The other rivers include the Kaduna, Sokoto and Gangola lie north of the Niger-Benue trough and drain into Lake Chad. Short Rivers drain coastal areas and flow into the Gulf of Guinea.