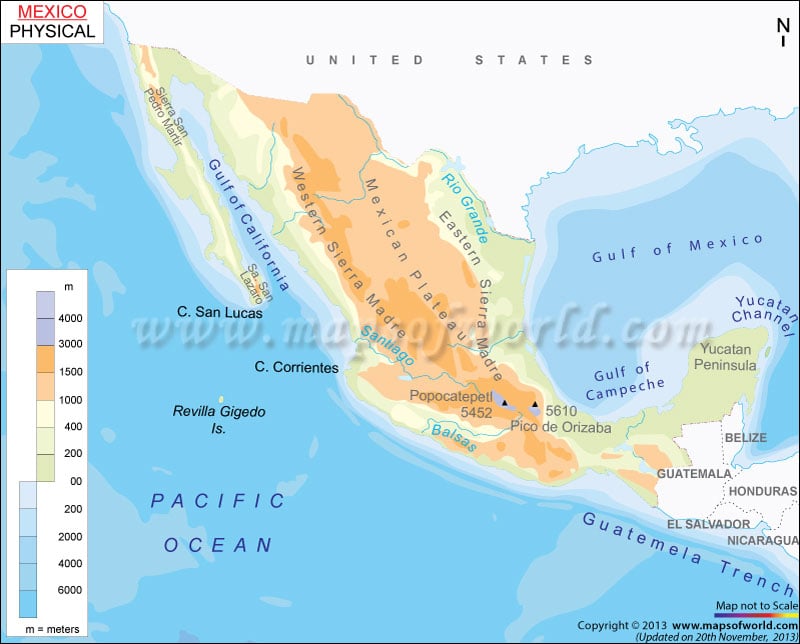
Mexico, known as the United Mexican States, is located in the southern part of North America. It shares its boundary with to the north with the United States, to the west and south with the Pacific Ocean, to the southeast with Belize, Guatemala, and the Caribbean Sea, and to the east with the Gulf of Mexico.
Mexico Physical Features
The country covers 1,972,550 square kilometres (761,610 sq mi) and has a 9,330-kilometre coastline. Mexico lies between latitudes 23. N and longitude 102. W. There is substantial variation in the topography of Mexico. The country can be divided into the following physiographic regions:
Baja California Peninsula
The region lies in northwestern Mexico. It is an isolated strip of arid land extending between the Gulf of California and the Pacific Ocean. The plateau is unevenly divided between Baja California and Baja California Sur. The region extends into the Sonoran Desert.
Pacific Coastal lowlands
The lowlands begin near the Colorado River Delta and Mexicali in the north. They terminate 900 miles (1,450 km) to the south near Tepic, facing the Gulf of California. The lowlands share its boundary on the east by the steep-sided Sierra Madre Occidental while crossing the states of Sinaloa, Nayarit, and Sonora.
Mexican Plateau
The region is the largest and most densely populated, flanked by the Sierra Madre Occidental and the Sierra Madre Oriental. The area consists of the heavily populated Mesa Central region and vast Mesa del Norte (Northern Plateau).
The Mesa Central region covers large parts of Guanajuato, Michoacan, Queretaro and the Federal District (Mexico City). The Mesa del Norte consists of the stretches of Coahulia, Chihuahua, Durango and Jalisco.
Eastern Sierra Madre Occidental and Western Sierra Madre Oriental
- The Sierra Madre Oriental range is situated on the eastern side of the Mexican plateau. They are folded mountains and are often considered an extension of the Rocky Mountains. They run north to south before merging into Cordillera Neovolcanica.
- The Sierra Madre Occidental is mainly volcanic, forming the western border of the Mexican plateau. Copper Canyon (Barranca del Cobre) is the most spectacular range feature in southwestern Chihuahua state.
Cordillera Neovolcanica
The region is a geologically active mountain range that links the Sierra Madre Oriental with the Sierra Madre Occidental at the southern edge of Mesa Central. The volcanic field, also called Neo-Volcanic Axis, has spectacular peaks, such as Citlaltpetl (Orizaba Peak).
Gulf Coastal Plain and Yucatan Peninsula
The vast area extends around 900 miles (1,450 km) along the Gulf of Mexico. It runs from Tamaulipas state through Tabasco and Veracruz states to the Yucatan Peninsula. In its southeast, Tabasco plain is located. The Gulf coastal plain is narrow and irregular in the south and broader at the northern end of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. The Yucatan Peninsula forms a divide between the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. It lies to the northeast of the Tabasco Plain.
Significant Rivers and Lakes in Mexico
The country has few significant rivers and natural lakes because of its climatic conditions and arrangement of landforms. The largest rivers are found in the central part of Mexico. Some of the significant rivers of the country are the Lerma River, Santiago River, and Panuco River. Important lakes in the country are Lake Chapala, Lake Cuitzeo, and Lake Patzcuaro.