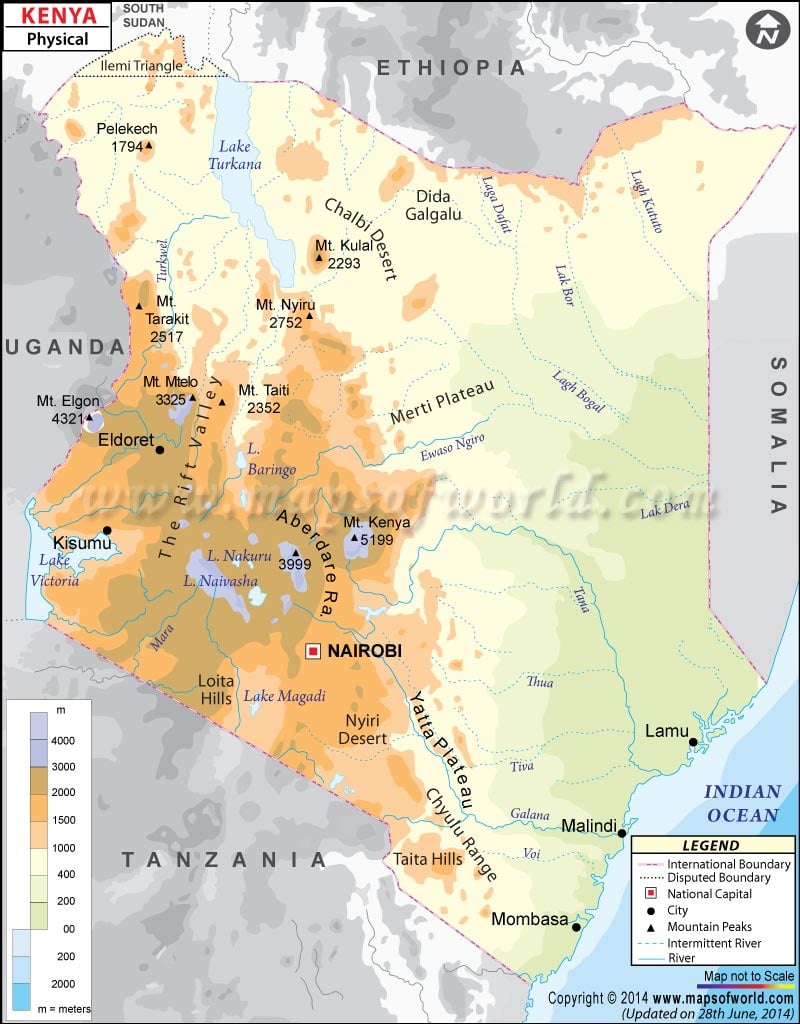
Kenya is a country in Eastern Africa known as the Republic of Kenya officially. Kenya shares its boundary with Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, South Sudan to the northwest, the Indian Ocean to the southeast, and Tanzania to the south. Latitudes and Longitudes can also be noted. The latitudinal extent of the country is between 5. N and 5. S and the longitudinal extent of the country are between 34. E and 42. E. The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is also marked on the map.
Physical Features of Kenya
Kenya covers a total area of 580,367 km2 (224,081 sq miles). The country is bisected by the Equator horizontally. The country is geographically varied ranging from cold snow-capped mountains, vast forests, and agricultural regions to the western Rift Valley region, to desert areas like the Chalbi Desert and Nyiri Desert. Kenya Can be divided into the following geographic regions:
Lake Victoria Basin
The region is a plateau area rising eastward to Rift Highlands from the Lakeshore. The basin lies between 3,000 and 4,000 feet above sea level. The grassland of this plateau is divided in half by the Kano plain. The region consists of a series of Lakes and is bordered by cliffs on the east and west. Winam Gulf (Kavirondo Gulf) is formed at the northeastern corner of Lake Victoria. It is a shallow inlet and connected to lake Victoria by a 3 miles wide channel. At the extreme north of the basin Mount Elgon, an extinct volcano is located rising up to 14,178 feet (4,321 meters).
Rift Valley and Kenyan Highlands
The Great Rift Valley runs through Kenya from north to south direction and is part of an intra-continental ridge system. The Valley floor is broken by a chain of volcanoes and of which some are still active. The Rift Valley splits the highland region into two areas Aberdare Range to the east and Mau Escarpment to the west. In the western part, the highlands extend from Mount Tenderest-Mau Escarpment towards Uasin Gishu Plateau in the north. On the eastern part, they extend from Nyeri Saddle to Mount Kenya, which has its highest peak at 17,058 feet (5,199 meters).
Arid and semi-arid Areas in Kenya
The arid and semiarid areas in the northeast and north are part of a vast area extending from the Ugandan border through Lake Rudolf to the plateau area between Kenyan and Ethiopian highlands. This region includes the Chalbi Desert east of Lake Rudolf.
Coastal Plains of Kenya
The area is a narrow strip of land along the Indian Ocean about 10 miles wide in the south, it widens to about 100 miles in the north around the Tana River lowland. The area runs for about 250 miles (400 km). Towards the Far northeast, it merges into the lowlands of Somalia and includes the natural harbors of Mombasa.
Important Lakes in Kenya
Kenya has 64 (9.50%) of the total lakes that are found in Africa. Major lakes within the Kenyan Rift Valley include Lake Turkana, Lake Baringo, Lake Nakuru, Lake Logipi, Lake Magadi, Lake Elmenteita, and Lake Naivasha. Lake Turkana (Lake Rudolf) is located at the northern end of the Great Rift Valley.
Physical Map of Neighbouring Countries