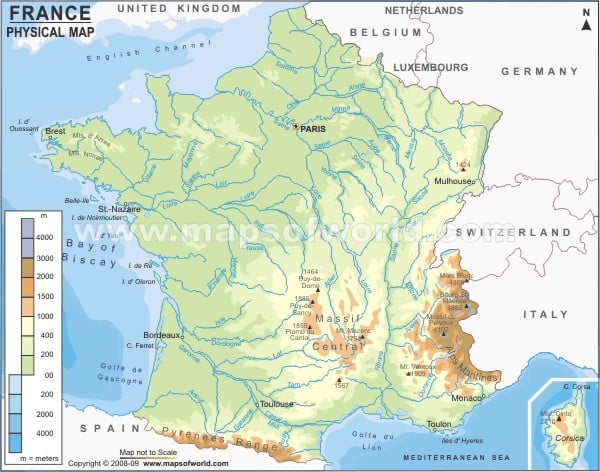
France, known as the French Republic officially, is a transcontinental country. It spans Western Europe and overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
Physical Features of France
France’s metropolitan area extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and North and Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. The overseas territories include Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, French Guiana in South America, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. The country has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. Metropolitan France shares its boundary with Luxembourg, Belgium in the northeast, Germany and Switzerland in the east, Monaco, and Italy in the southeast and Spain and Andorra in the southwest and south.
Paris, the capital of France, is marked on the map. The France Physical Map is beneficial for school presentations. A map legend at the bottom helps all the signs, characters, graphics, and symbols used throughout the map. Metropolitan France has a diverse topography and natural landscapes. Some of the relief features of the country are listed below:
The Massif Central
The vast plateau in the middle of Central France covers an area of about 33,000 square miles (86,000 square km), about one-sixth of the country’s size. The area borders the Rhone-Saone Valley on the east, the Aquitaine Basin on the Southwest, the Languedoc lowlands on the south, and the Paris Basin on the north.
Pyrenees
This mountain range sprawls over the border of France and Spain. It forms a divide between the two countries, with the microstate of Andorra in between. This range extends for nearly 500 km (310 mi), with the highest peak of Aneto at an elevation of 3,404 meters (11,168 ft) above sea level. The French Pyrenees from east to west includes Pyrenees-Orientales, Ariege, Haute-Garonne, Aude, and Pyrenees-Atlantiques, including Pyrenees National Park.
French Alps
The mountains are part of the great mountain range that extends across Europe. At an elevation of 15,771 feet (4,807), Mont Blanc is the highest peak in Europe and lies along the French-Italian border lying in French territory.
The Great low Plains
The tremendous low plains of France include:
-
The Paris Basin
: This region lies between the Vosges, Ardennes, Massif Armorican, and the Massif Central. The Paris basin comprises sedimentary beds, sand, and clay dip.
-
The Flanders Basin:
This region lies extreme north of the French Basin, including a small part of the Anglo-Belgian Basin
-
The Alsace Plain
: This region lies east of the Paris Basin and is bordered by the Jura mountains on the south, the Vosges on the west, Saone basin on the southwest, Germany on the north, and the Rhine River on the east.
Rivers System in France
The significant rivers in the country are the Seine river, Loire river, Garonne River, Rhone River, and Rhine River. The Loire river is the longest river in the France Metropolitan, flowing 634 miles. The Seine River is the main river of the Paris Basin. Minor rivers and lakes include Some River, Durance River in the Alps, Charente, Annecy lake, and Bourget Lake.