About Ecuador
Explore this Ecuador map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Ecuador location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Ecuador history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name | Republica del Ecuador, (Republic of Ecuador) |
| Capital | Quito |
| Population | 12.9 million (2001) |
| Area | 283,561 sq km or 109,483 sq mi |
| Currency | US dollar, Sucre ($1 = 1 sucre) |
| Religion | Christianity |
| Literacy | 90% |
| Languages | Spanish (official), Quenchuan, other Tribal dialects |
| Major Cities | Guayaquil, Cuenca, Machala, Portoviejo, Ambato |
| Climate | Equatorial and Tropical |
Ecuador is located on the equator and was perhaps therefore named so. Ecuador is the Spanish word for “equator”. Ecuador’s history dates back to 15,000 and 20,000 BC, traces of which can be found in archaeological sites located all across Ecuador. Once part of the Inca Empire, Ecuador came under Spanish rule in 1533. It became independent in 1830.
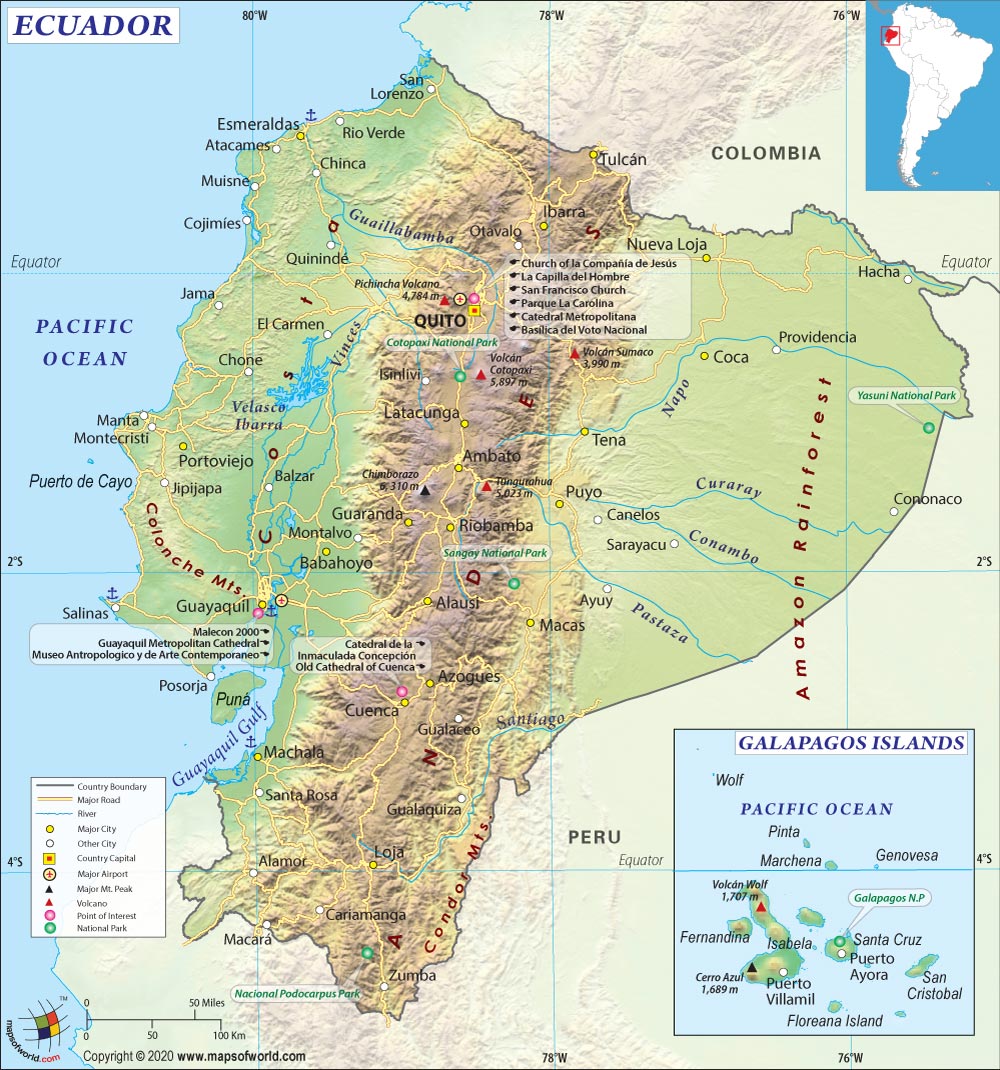
Location of Ecuador
Ecuador, a republic in northwestern South America, is bounded by Colombia on the north, by Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean on the west. The country also includes the Galapagos Islands (Colon Archipelago) in the Pacific, about 965 km (about 600 mi) west of the mainland.
Climate of Ecuador
Due to geographic differences in altitude, longitude and latitude, and the climatic effects of the Pacific Ocean, the Amazon, and the Andes, the various regions and sub regions of Ecuador have very different climates and microclimates. The Pacific coast has a rainy season between December and May and a dry one from June to November. The Highlands, on the other hand, have a rainy and cold climate from November to April and a dry one from May to October. In the Amazon, the climate is rainy and humid between January and September, with temperatures between 23 and 36 degrees centigrade, and it is dry between October and December. The Galapagos has a temperate climate with temperatures ranging between 22 and 32 degrees centigrade.
Physical Map of Ecuador
Ecuador is geographically divided into four regions – the Amazon, the Highlands, the Coast, and the Galapagos Islands. Ecuador’s coastal region consists of fertile plains, rolling hills, and sedimentary basins traversed by many rivers that run downwards from the Andes Mountains to the Pacific Ocean. The Andes crosses the country from north to south. The Occidental and the Oriental Ranges are born out of this mountain system as it divides in the province of Loja, forming plains and valleys along the Andean Corridor. Between the two ranges is a plateau that is three thousand meters high. The Amazon Region and its five provinces can be geographically divided into two sub regions: the High Amazon and the Amazon Lowlands. The Highlands is comprised of the Andean foothills, which slowly descend towards the Amazon River Basin. The Lowlands, found further to east, are home to some of the nation’s most beautiful and important rivers: the Putumayo, the Napo, and the Pastaza. The Archipelago of Colon (commonly known as the Galapagos Islands) is made up of 13 main islands, 17 islets, and dozens of ancient rock formations. The volcanically formed islands, encompassing an area of 8,000 kilometers in all, lies roughly 1,000 kilometers off the coast of the Ecuadorian mainland. Apart from its beautiful beaches and unique and varied ecosystems, the Galapagos Islands are home to towering active volcanoes that reach altitudes up to 1,600 meters.
Flora And Fauna of Ecuador
Ecuador is one the most biologically diverse nations. The nation’s drastic geographic and climatic variations have led to the evolution of thousands of species of flora and fauna, most of which thrive in habitats protected by the State and by private organizations. Despite its tiny size, Ecuador is home to rain forests, jungles, mountains, islands, deserts, valleys, and snowcapped peaks. One of its main attractions is the Galapagos Archipelago and its marine reserve, which contain endemic species unique to the area.
Ecuador is home to ten percent of the world’s plant species, the majority of which grow in the northeastern Amazon, where an estimated 10,000 species thrive. The diversity of the climate here has given rise to more than 25,000 species of trees. Moreover, the Andes is home to an estimated 8,200 plant and vegetable species. In the orchid family alone, 2,725 species have been identified in the area. In the Galapagos, there are about 600 native species and 250 more, which were introduced by man. Three of the twelve key biodiversity zones identified by the naturalist Norman Myers can be found on the Ecuadorian mainland.
Ecuador is home to 8 percent of the world’s animal species and 18 percent of the planet’s birds. Around 3,800 species of vertebrates have been identified in Ecuador as well as 1,550 species of mammals, 350 reptile species, and 375 species of amphibians, 800 fresh water fish species, and 450 salt-water fish species. Ecuador is also home to 15 percent of the world’s endemic bird species. Moreover, there are more than a million species of insects and 4,500 species of butterflies that live in Ecuador.
Ecuador has a diverse population composed of people of European, Native American, and African descent. The majority are mestizos, individuals of mixed European and Native American ancestry. Most of the Native Americans live in poverty in the highlands region, where a small elite of European descent controls most of the land and wealth.
Flag of Ecuador
The flag of Ecuador has three horizontal bands of yellow (top, double width), blue, and red with the coat of arms superimposed at the center of the flag; similar to the flag of Colombia, which is shorter and does not bear a coat of arms.
Economy of Ecuador
Ecuador has substantial oil resources and rich agricultural areas. Because the country exports primary products such as oil, bananas, and shrimp, fluctuations in world market prices can have a substantial domestic impact. Ecuador joined the World Trade Organization in 1996. The Ecuador Government is presently working on strategies to increase productivity in the oil, communication and electric sectors.
Arts, Culture and Music of Ecuador
Ecuador is a multiethnic and multicultural nation. Several different indigenous nationalities continue to live their traditional lifestyles in rural villages and towns throughout the nation. In the cities, you find mainly mestizos, African Ecuadorians, and whites.

 Wall Maps
Wall Maps