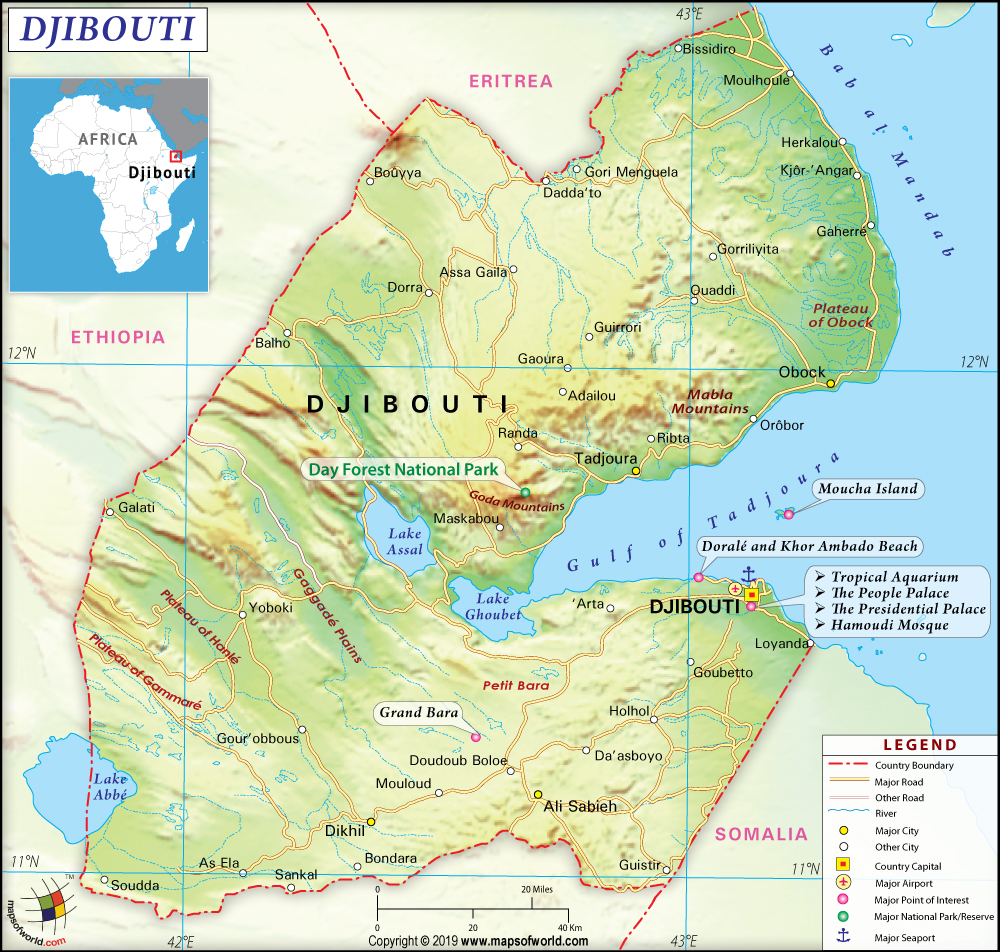
About Djibouti
Explore this Djibouti map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Djibouti location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Djibouti history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name | The Republic of Djibouti (Jumhouriyya Djibouti) |
| Capital | Djibouti |
| Population | 906,000 |
| Area | 8,958 square miles |
| Currency | France (DJF) |
| Religion | Islam |
| Literacy | 70.3 |
| Languages | French, Arabic, Affar, Issa |
| Climate | Hot and dry through out the year |
Known initially as French Somaliland and then as French Territory of Afars and Issas, Dijibouti gained independence on June 27, 1977. Geography of Djibouti
The Republic of Djibouti is a country located in the north-east Africa on the Gulf of Aden at the southern entrance to the Red Sea. It is surrounded by Eritrea to the north; Ethiopia to the north, west, and south; and Somalia to the southeast.
Djibouti is made up of plateaus and mountains towards the north and south of the gulf. The highest mountain Moussa Ali stands 6768 ft tall along the northern border where the Ethiopian and Eritrean boundaries meet.
Towards the west, lies the desert lowland with depressions containing several salt lakes, the largest being Lake Abbé situated along the Ethiopian border. Very little of the country’s land is arable, and there are no regularly flowing rivers or streams. Djibouti relies on an underground aquifer for fresh water. Djibouti is hot and dry all year round, especially during summers. The average temperature varies from 23° to 29°C in January and from 31° to 41°C in July. Annual rainfall ranges from 127 mm in the capital to 380 mm in the mountains.
In the first stages of its existence the people of Djibouti used to trade in skins and hides, in exchange of spices and perfumes, with people from ancient Egypt, India and China. The Afars and Somalis were the first ethnic groups who started practicing Islam following close contact with the Arabian Peninsula. They ruled from 1862 to 1894 till the French established their supremacy in 1896. This reign lasted till 1977 when Djibouti gained its independence.
Flora and Fauna of Djibouti
As the country is mainly rocky in nature, the vegetation is mainly made up of scattered drought-tolerant grasses and shrubs. There are also a number of species of woody and herbaceous plants, including boxwood and olive trees. Wildlife includes jackals, hyenas, ostriches, and gazelles.
Thousands of birds migrate in this country from Europe and Asia during the winter season. Many tourists especially bird watchers visit Djibouti to have a glimpse of the rare species of birds here. The birds which are found here include ostrich, grebes, tropic birds, pelicans, frigate birds, flamingoes, ducks and many others. Red River Hog is one of the rare animals found in the rain forests of Djibouti. African wild dog is considered now as an endangered species.
The wilderness of Djibouti is also home to a number of reptiles including the Nile crocodile, sand snake, puff adder snake and chameleons. There are around eleven different types of scorpions found here in Djibouti.
The dense forests of acacia, olive and juniper are the habitats of different types of mammals. The terrestrial mammals commonly found in Djibouti include hedgehog, big-eared free-tailed bat, wild dog, African ass or African wild donkey, desert wart-hog, gazelles of waller, lesser kudu, oryx, beira, vervet monkey and hyrax.
Economy
Livestock herding forms the backbone of Djibouti’s economy. Agriculture is an important part of the Ethiopians. Most of the land is barren and major portion of the food items produced is imported.
Services are the basis of Djibouti’s economy and the strategic location of the country has also contributed to the situation. It is one of the free trade zones in northeastern Africa. Almost 66.67% of the Djiboutians live at the capital. Djibouti serves as a refueling center and a transit port, which is used by international ships. The natural resources of Djibouti are limited as is the industrial sector. Hence it is highly dependent on international assistance for its payments and development projects.
Transport, communications, and warehousing, also contribute significantly to the economy.
Demographics
Over sixty per cent of the population comprises ethnic Somali origin, who form the majority in the south. Afars make up thirty percent of the population and are concentrated in the north. The remaining ten per cent is made up of Arab, French, and other small groups. French and Arabic are the official languages while Somali and Afar are also spoken widely in the south and north, respectively. Islam is the main religion but Christianity is also practiced.
Banks in Djibouti
There are privatized as well as the Government undertaken Djibouti banks that help extensively in the economy of Djibouti. TheDjibouti banks have adopted the latest technology to provide smart services to the customers. The banks in Djibouti have set up their call centers, where the customers can call and meet their queries at any point of the day. The customer care executives of these Djibouti banks are always careful to provide the best services to the customers. The local citizens of Djibouti can conveniently open their accounts in the Djibouti banks after proving their national identity. Travelers and foreigners on jobs or for business in Djibouti can also safely deposit their money in the Djibouti banks after producing their job certificates or business establishment certificates to the concerned bank authorities.
The banks in Djibouti offer interest on the deposited money of the customers. These Djibouti banks also pay loans to the customers on flexible conditions. Customers have opportunities and facilities to return the loans to the banks in easy installments. The currency and foreign exchange position of Djibouti is taken care of by The Central Bank of Djibouti.
Few of the popular banks in Djibouti include:
- The Central Bank of Djibouti
Address: PO Box 2118,
Ave Saint Laurent du Var, Djibouti - Banque pour le Commerce et l’Industrie
Address: PO Box 2122,
Place Lagarde, Djibouti - Banque Indosuez Mer Rouge
Address: PO Box 88,
10 Place Lagarde, Djibouti - Commercial Bank of Ethiopia
Address: PO Box 187,
Rue de Marseille, Djibouti - Banque de Developpement de Djibouti
Address: PO Box 520,
Angle Ave Georges Clémenceau et rue Pierre Curie, Djibouti
Industries in Djibouti
The extensive growth of industries in Djibouti since the late 20th century has contributed to the economy of Djibouti. The private companies from Europe and USA have invested more than 200 million dollars in Djibouti since that period. The industries in Djiboutihave exploited the natural resources of Djibouti to strengthen the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Djibouti. According to the 2012 estimates, the Djibouti GDP was recorded to be 2.379 billion dollars. The natural resources that have contributed extensively in drawing the private sectors to invest in Djibouti include:
- Energy resources – solar and geothermal
- Minerals – perlite, salt, limestone, gypsum,granite, marble, sand and gravel
The mining industries have always been the pride of Djibouti. The mining industries of Djibouti mostly concentrated on the mining of gold.
Agricultural activities form one of the important bases of the economy of Djibouti. The agro-industries have developed fairly in Djibouti and mainly deal with fruit and vegetable items.
The banking and insurance sectors form one of the other major industry types of Djibouti. The public works and construction industries have grown in a large scale since the year 2000. The cement industries have also grown in big numbers in Djibouti.
The industries of Djibouti export their items m